Abstract
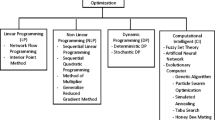
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs) have been widely used to search for optimal strategies for the planning and management of water resources systems, particularly reservoir operation. This study provides a comprehensive diagnostic assessment of state of the art of the non-animal–inspired EA applications to reservoir optimization. This type of EAs does not mimic biologic traits and group strategies of animal (wild) species. A search of pertinent papers was applied to the journal citation reports (JCRs). A bibliometric survey identified 14 pertinent non-animal–inspired EAs, such as the genetic algorithm (GA), simulated annealing (SA), and differential evolution (DE) algorithms, most of which have a number of modified versions. The characteristics of non-animal–inspired EAs and their modified versions were discussed to identify the difference between EAs and how each EA was improved. Additionally, the type of application of non-animal–inspired EAs to different case studies was investigated, and comparisons were made between the performance of the applied EAs in the studied literature. The survey revealed that the GA is the most frequently applied algorithm, followed by the DE algorithm. Non-animal–inspired EAs are superior to the classical methods of reservoir optimization (e.g., the non-linear programming and dynamic programming) due to faster convergence, diverse solution space, and efficient objective function evaluation. Several non-animal–inspired EAs of recent vintage have been shown to outperform the classic GA, which was the first evolutionary algorithm applied to reservoir operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboutalebi, M., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2015). Optimal monthly reservoir operation rules for hydropower generation derived with SVR-NSGA-II. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 141(11), 04015029. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000553.
Adami, C. (1998). Introduction to artificial life. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Affenzeller, M., Winkler, S., Wagner, S., and Beham, A. (2018). Genetic algorithms and genetic programming: Modern concepts and practical applications. Chapman and Hall/CRC.
Afshar, A., Shafii, M., & Bozorg-Haddad, O. (2011). Optimizing multi-reservoir operation rules: an improved HBMO approach. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 13(1), 121–139.
Afshar, A., EmamiSkardi, M. J., & Masoumi, F. (2014). Optimizing water supply and hydropower reservoir operation rule curves: an imperialist competitive algorithm approach. Engineering Optimization, 47(9), 1208–1225.
Ahmadi Najl, A., Haghighi, A., & Vali Samani, H. (2016). Simultaneous optimization of operating rules and rule curves for multi reservoir systems using a self-adaptive simulation-GA model. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 142, 04016041. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000688.
Ahmadi, M., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Mariño, M. A. (2014). Extraction of flexible multi-objective real-time reservoir operation rules. Water Resources Management, 28(1), 131–147.
Arunkumar, R., & Jothiprakash, V. (2013). Chaotic evolutionary algorithms for multi-reservoir optimization. Water Resources Management, 27(15), 5207–5222.
Asgari, H., Bozorg-Haddad, O., Pazoki, M., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2015). Weed optimization algorithm for optimal reservoir operation. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 142(2), 04015055. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000963.
Ashofteh, P. S., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2015). Evaluation of climate-change impacts on multiobjective reservoir operation with multiobjective genetic programming. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 141(11), 04015030. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000540.
Assad, A. M., and Packard, N. H. (1992). Emergent colonization in artificial ecology. Proceedings of the first European Conference on Artificial Life, MIT press, 143–152.
Atashpaz-Gargari, E., and Lucas, C. (2007). Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition, IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Singapore, 25-28 September, 4661–4667.
Bäck, T. (1992). The interaction of mutation rate, selection, and self-adaptation within a genetic algorithm. In R. Männer & B. Manderick (Eds.), Proceedings of Parallel Problem Solvingfrom Nature II (pp. 85–94). Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Back, T., Fogel, D., & Michalewicz, Z. (2000). Handbook of evolutionary computation. Bristol: IOP Publishing Ltd. and Oxford University Press.
Bagis, A., & Karaboga, D. (2007). Evolutionary algorithm-based fuzzy PD control of spillway gates of dams. Journal of Franklin Institute, 344(8), 1039–1055.
Baltar, A., & Fontane, D. (2008). Use of multiobjective particle swarm optimization in water resources management. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 134(3), 257–265.
Bashiri-Atrabi, H., Qaderi, K., Rheinheimer, D. E., & Sharifi, E. (2015). Application of harmony search algorithm to reservoir operation optimization. Water Resources Management, 29(15), 5729–5748.
Blickle, T. (1997). Theory of evolutionary algorithms and applications to system synthesis. Zurich: Swiss Federal school of Technology.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Afshar, A., & Mariño, M. A. (2006). Honey-bees mating optimization (HBMO) algorithm: a new heuristic approach for water resources optimization. Water Resources Management, 20(5), 661–680.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Adams, B. J., & Mariño, M. A. (2008). Optimum rehabilitation strategy of water distribution systems using the HBMO algorithm. Journal of Water Supply: Reaserch and Technology. AQUA, 57(5), 337–350.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Afshar, A., & Mariño, M. A. (2009). Optimization of non-convex water resource problems by honey-bee mating optimization (HBMO) algorithm. Engineering Computations, 26(3), 267–280.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Afshar, A., & Mariño, M. A. (2011a). Multi reservoir optimization in discrete and continuous domains. Water Management, 164(2), 57–72.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Moradi-Jalal, M., & Mariño, M. A. (2011b). Design-operation optimization of run-of-river power plants. Proceedings of ICE-Water Management, 164(9), 463–475.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Jahandideh-Tehrani, M., & Mariño, M. A. (2013). Discussion of investigating the vulnerability of dry-season water supplies to climate change: a case study of the Gwangdong Reservoir Drought Management System, Korea by Donghoon cha; Sangeun lee; and Heekyung Park. Water Resources Management, 27(7), 1893–1896.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Karimirad, I., Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2014a). Development and application of the bat algorithm for optimizing the operation of reservoir systems. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 141(8), 04014097–04014091.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Moravej, M., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2014b). Application of the water cycle algorithm to the optimal operation of reservoir systems. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 141(5), 04014064. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000832.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Hosseini-Moghari, S. M., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2015). Biogeography-based optimization algorithm for optimal operation of reservoir systems. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 142(1), 04015034. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000558.
Bozorg-Haddad, O., Azarnivand, O., Hosseini-Moghari, S. M., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2017). Optimal operation of reservoir systems with the symbiotic organisms search (SOS) algorithm. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 19(4), 507–521. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2017.085.
Cai, X., McKinney, D. C., & Lasdon, L. S. (2001). Solving nonlinear water management models using a combined genetic algorithm and linear programming approach. Advances in Water Resources, 24(6), 667–676.
Chang, F. J., & Chen, L. (1998). Real-coded genetic algorithm for rule-based flood control reservoir management. Water Resources Management, 12(3), 185–198.
Chang, F. J., Chen, L., & Chang, L. C. (2005). Optimizing the reservoir operating rule curves by genetic algorithms. Hydrological Processes, 19(11), 2277–2289.
Chang, L. C., Chang, F. J., Wang, K. W., & Dai, S. Y. (2010). Constrained genetic algorithms for optimizing multi-use reservoir operation. Journal of Hydrology, 390(1–2), 66–74.
Chen, L. (2003). Real coded genetic algorithm optimization of long term reservoir operation. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 39(5), 1157–1165.
Chen, L., & Chang, F. J. (2007). Applying a real-coded multi-population genetic algorithm to multi-reservoir operation. Hydrological Processes, 21(5), 688–698.
Chen, L., McPhee, J., & Yeh, W. W. G. (2007). A diversified multi objective GA for optimizing reservoir rule curves. Advances in Water Resources, 30(5), 1082–1093.
Chen, L., Tan, C. H., Kao, S. J., & Wang, T. S. (2008). Improvement of remote monitoring on water quality in a subtropical reservoir by incorporating grammatical evolution with parallel genetic algorithms into satellite imagery. Water Research, 42(1–2), 296–306.
Chen, D., Chen, Q., Leon, A. S., & Li, R. (2016a). A genetic algorithm parallel strategy for optimizing the operation of reservoir with multiple eco-environmental objectives. Water Resources Management, 30(7), 2127–2142.
Chen, S., Shao, D., Li, X., & lei, C. (2016b). Simulation-optimization modeling of conjunctive operation of reservoirs and ponds for irrigation of multiple crops using an improved artificial bee colony algorithm. Water Resources Management, 30(9), 2887–2905.
Cheng, C. T., Wang, W. C., Xu, D. M., & Chau, K. W. (2008). Optimizing hydropower reservoir operation using hybrid genetic algorithm and chaos. Water Resources Management, 22(7), 895–909.
Cieniawski, S. E., Eheart, J. W., & Ranjithan, S. (1995). Using genetic algorithm to solve a multiobjective groundwater monitoring problem. Water Resources Research, 31(2), 399–409.
Cui, L. J., & Kuczera, G. (2003). Optimizing urban water supply headworks using probabilistic search methods. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 129(5), 380–387.
Dariane, A. B., & Karami, F. (2014). Deriving hedging rules of multi-reservoir system by online evolving neural networks. Water Resources Management, 28(11), 3651–3665.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, A., & Meyarivan, T. (2002). A fast and elitist multi objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 6(2), 182–197.
Dessalegne, T., & Nicklow, J. W. (2012). Artificial life algorithm for management of multi-reservoir river systems. Water Resources Management, 26(5), 1125–1141.
Duan, Q., Sorooshian, S., & Gupta, V. (1992). Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resources Research, 28(4), 1015–1031.
Ehteram, M., Karami, H., Mousavi, S. F., & El-Shafie, A. (2017a). Optimizing dam and reservoirs operation based model utilizing shark algorithm approach. Knoledge-Based Sytems, 122, 26–38.
Ehteram, M., Karami, H., Mousavi, S. F., Farzin, S., & Kisi, O. (2017b). Optimization of energy management and conversion in the multi-reservoir systems based on evolutionary algorithms. Journal of Cleaner Production, 168, 1132–1142.
Emmerich, M., Beume, N., & Naujoks, B. (2005). An EMO algorithm using the hypervolume measure as selection criterion. Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization, Springer, Berlin, 62–76.
Esat, V., and Hall, M. J. (1994). Water resources system optimization using genetic algorithms, Proceeding of 1st International Conference on Hydro informatics, Balkema, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 225–231.
Eskandar, H., Sadollah, A., Bahreininejad, A., & Hamdi, M. (2012). Water cycle algorithm– A novel metaheuristic optimization method for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Computers and Structures, 110-111, 151–166.
Fallah-Mehdipour, E., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Mariño, M. A. (2011). MOPSO algorithm and its application in multipurpose multi reservoir operations. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 13(4), 794–811.
Fallah-Mehdipour, E., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Mariño, M. A. (2013). Extraction of multi crop planning rules in a reservoir system: application of evolutionary algorithms. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 139(6), 490–498.
Fitzpatrick, J. M., & Grefenstette, J. J. (1988). Genetic algorithm in noisy environment. Machine Learning, 3(2), 101–120.
Fogel, D. B. (2000). Evolutionary computation: principles and practice for signal processing. Bellingham: SPIE press.
Forrest, S., Perelson, A. S., Allen, L., and Cherukuri, R. (1994). Self-nonself discrimination in a computer. (PDF). Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Symposium on Research in Security and Privacy. Los Alamitos, CA. pp. 202–212.
Fowe, T., Nouiri, I., Ibrahim, B., Karambiri, H., & Paturel, J. E. (2015). OPTIWAM: An intelligent tool for optimizing irrigation water management in coupled reservoir–groundwater systems. Water Resources Management, 29(10), 3841–3861.
Garousi-Nejad, I., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2016). Application of the firefly algorithm to optimal operation of reservoirs with the purpose of irrigation supply and hydropower production. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 142(10), 04016041–04016041.
Geem, Z. W., Kim, J. H., & Loganathan, G. V. (2001). A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. Simulation, 76(2), 60–68.
Giuliani, M., Herman, J. D., Castelletti, A., & Reed, P. (2014). Many-objective reservoir policy identification and refinement to reduce policy inertia and myopia in water management. Water Resources Research, 50(4), 3355–3377.
Giuliani, M., Castelletti, A., Pianosi, F., Mason, E., & Reed, P. (2015). Curses, tradeoffs, and scalable management: advancing evolutionary multi objective direct policy search to improve water reservoir operations. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 142(2), 04015050. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000570.
Goldberg, D. E. (1985). Optimal initial population size for binary-coded genetic algorithms, TCGA Report No. 85001, University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa.
Guedes, L. S. M., Vieira, D. A. G., Lisboa, A. C., & Saldanha, R. R. (2015). A continuous compact model for cascaded hydro-power generation and preventive maintenance scheduling. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 73, 702–710.
Hadka, D., & Reed, P. (2012). Diagnostic assessment of search controls and failure modes in many-objective evolutionary optimization. Evolutionary Computation, 20(3), 423–452.
Hakimi-Asiabar, M., Ghodsypour, S. H., & Kerachiam, R. (2009). Multi-objective genetic local search algorithm using Kohonen’s neural map. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 56(4), 1566–1576.
Hakimi-Asiabar, M., Ghodsypour, S. H., & Kerachiam, R. (2010). Deriving operating policies for multi-objective reservoir systems: application of self-learning genetic algorithm. Applied Soft Computing, 10(4), 1151–1163.
Han, S. S., & May, G. S. (1997). Using neural network process models to perform PECVD silicon dioxide recipe synthesis via genetic algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 10(2), 279–287.
Hassaballah, K., Jonoski, A., Popescu, I., & Solomatine, D. P. (2012). Model-based optimization of downstream impact during filling of a new reservoir: case study of Mandaya/Roseires reservoirs on the Blue Nile River. Water Resources Management, 26(2), 273–293.
Hayashi, D., Satoh, T., & Okita, T. (1996). Distributed optimization by using artificial life. Transactions of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan, 116(5), 584–590.
Herrera, F., and Lozano, M. (1997). Heterogeneous distributed genetic algorithms based on the crossover operator, 2nd IEE/IEEE International Conference on Genetic Algorithms in Engineering Systems: Innovations and Applications, 203–208.
Holland, J. H. (1975). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
Hossain, M. S., & El-Shafie, A. (2014). Performance analysis of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm in optimizing release policy of Aswan High Dam. Neural Computing and Applications, 24(5), 1199–1206.
Hossain, M. S., El-Shafie, A., Mahzabin, M. S., & Zawawi, M. H. (2018). System performances analysis of reservoir optimization-simulation model in application of artificial bee colony algorithm. Neural Computing and Applications, 30(7), 2101–2112.
Hosseini-Moghari, S. M., Morovati, R., Moghadas, M., & Araghinejad, S. (2015). Optimum operation of reservoir using two evolutionary algorithms: Imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) and cuckoo optimization algorithm (COA). Water Resources Management, 29(10), 3749–3769.
Huang, Y. (2014). Multi-objective calibration of a reservoir water quality model in aggregation and non-dominated sorting approaches. Journal of Hydrology, 510, 280–292.
Hurford, A. P., Huskova, I., and Harou, J. J. (2014). Using many-objective trade-off analysis to help dams promote economic development, protect the poor and enhance ecological health, 38, 72–86.
Jahandideh-Tehrani, M., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Mariño, M. A. (2014). Power generation simulation of a hydropower reservoir system using system dynamics: case study of Karoon reservoir system. Journal of Energy Engineering, 140(4), 04014003. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EY.1943-7897.0000179.
Jahandideh-Tehrani, M., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2015). Hydropower reservoir management under climate change: the Karoon reservoir system. Water Resources Management, 29(3), 749–770.
Jian-Xia, C., Qiang, H., & Yi-min, W. (2005). Genetic algorithms for optimal reservoir dispatching. Water Resources Management, 19(4), 321–331.
Jothiprakash, V., & Arunkumar, R. (2013). Optimization of hydropower reservoir using evolutionary algorithms coupled with chaos. Water Resources Management, 27(7), 1963–1979.
Jothiprakash, V., & Shanthi, G. (2006). Single reservoir operating policies using genetic algorithm. Water Resources Management, 20(6), 917–929.
Kang, M., & Park, S. (2014). Combined simulation-optimization model for assessing irrigation water supply capacities of reservoirs. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 140(5), 04014005. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000726.
Kangrang, A., Compliew, S., & Hormwichian, R. (2010). Optimal reservoir rule curves using simulated annealing. Water Management, 164(1), 27–34.
Khan, N. M., & Tingsanchali, T. (2009). Optimization and simulation of reservoir operation with sediment evacuation: a case study of the Tarbela Dam, Pakistan. Hydrological Processes, 23(5), 730–747.
Kim, T., Heo, J. H., Bao, D. H., & Kim, J. H. (2008). Single-reservoir operating rules for a year using multiobjective genetic algorithm. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 10(2), 163–179.
Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt, J. r., D, C., & Vecchi, M. P. (1983). Optimization by simulated annealing. Science, 220(4598), 671–680.
Kollat, J. B., and Reed, P. M. (2005) The value of online adaptive search: a performance comparison of NSGA-II, Ɛ-NSGAII, and Ɛ-MOEA. In: Coello CC, Aguirre AH, Zitzler E, editors. The Third International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization (EMO 2005). Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Guanajuato, Mexico: Springer Verlag, 3410, 386–98.
Kubota, R., Yamakawa, Y., and Horio, K. (2004). Reproduction strategy based on self-organizing map, for real-coded genetic algorithms, Neural Information Processing-Letters and Reviews 5, November.
Kumar, D. N., & Reddy, M. J. (2007). Multipurpose reservoir operation using particle swarm optimization. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 133(3), 192–201.
Kumphon, B. (2013). Genetic algorithms for multi-objective optimization: application to a multi-reservoir system in the Chi river basin, Thailand. Water Resources Management, 27(12), 4369–4378.
Labadie, J. W. (2004). Optimal operation of multi reservoir systems: state of the art review. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 130(2), 93–111.
Lessmann, S., Stahlbock, R., & Crone, S. F. (2005). Optimizing hyperparameters of support vector machines by genetic algorithms. In IC-AI, 74–82.
Li, Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Qin, H., & Liu, L. (2010). Novel multi objective shuffled frog leaping algorithm with application to reservoir flood control operation. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 136(2), 217–226.
Li, F. F., Wei, J. H., Fu, X. D., & Wan, X. U. (2012). An effective approach to long-term optimal operation of large-scale reservoir systems: case study of the three gorges system. Water Resources Management, 26(14), 4073–4090.
Li, F. F., Shoemaker, C. A., Qiu, J., & Wei, J. H. (2014). Hierarchical multi-reservoir optimization modeling for real-world complexity with application to the Three Gorges system. Environmental Modeling and Software, 69, 319–329.
Lou, J., Chen, C., & Xie, J. (2015). Multi-objective immune algorithm with preference-based selection for reservoir flood control operation. Water Resources Management, 29(5), 1447–1466.
Ma, X., Liu, F., Qi, Y., Li, L., Jiao, L., Deng, X., Wang, X., Dong, B., Hou, Z., Zhang, Y., & Wu, J. (2015). MOEA/D with biased weight adjustment inspired by user preference and its application on multi-objective reservoir flood control problem. Soft Computing, 20, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1789-z.
Mehrabian, A. R., & Lucasc, C. (2006). A novel numerical optimization algorithm inspired from weed colonization. Ecological Informatics, 1(4), 355–366.
Ming, B., Chang, J. X., Huang, Q., Wang, Y. M., & Huang, S. Z. (2015). Optimal operation of multi-reservoir system based-on cuckoo search algorithm. Water Resources Management, 29(15), 5671–5687.
Nain, P. K. S. and Deb, K. (2005). A multi-objective optimization procedure with successive approximate models. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. http://www.iitk.ac.in/kangal/papers/k2005002.pdf. Accessed 21 Sept 2018.
Neboh, A., Adeyemo, J., Enitan, A., & Olugbara, O. (2015). A review on application of evolutionary algorithms to reservoir operation for hydropower production. International Journal of Environmental, Chemical, Ecological, Geological and Geophysical Engineering, 9(9), 1115–1121.
Ngoc, T. A., Hiramatsu, K., & Harada, M. (2014). Optimizing the rule curves of multi-use reservoir operation using a genetic algorithm with a penalty strategy. Paddy and Water Environment, 12(1), 125–137.
Nicklow, J., Reed, S., Savic, D., Dessalegne, T., Harrell, L., Chan-Hilton, A., Karamouz, M., Minsker, B., Ostfeld, A., Singh, A., & Zechman, E. (2010). State of the art for genetic algorithms and beyond in water resources planning and management. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 136(4), 412–432.
Oliveira, R., & Loucks, D. P. (1997). Operating rules for multi reservoir systems. Water Resources Research, 33(4), 839–852.
Parasanchum, H., & Kangrang, A. (2018). Optimal reservoir rule curves under climatic and land use changes for Lampao Dam using genetic algorithm. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 22(1), 351–364.
Pinthong, P., Gupta, A. D., Babel, M. S., & Weesakul, S. (2009). Improved reservoir operation using hybrid genetic algorithm and neuro fuzzy computing. Water Resources Management, 23(4), 697–720.
Qi, Y., Bao, L., Sun, Y., Lou, J., & Miao, Q. (2016). A memetic multi-objective immune algorithm for reservoir flood control operation. Water Resources Management, 30(9), 2957–2977.
Qin, A. K., and Suganthan, P. N. (2005). Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm for numerical optimization, IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 2005) Edinburgh, Scotland, IEEE Press, Septmber, 1785–1791.
Qin, H., Zhou, J., Lu, Y., Li, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2010). Multi-objective cultured differential evolution for generating optimal trade-offs in reservoir flood control operation. Water Resources Management, 24(11), 2611–2632.
Rashid, M. U., Shakir, A. S., Khan, N. M., Latif, A., & Qureshi, M. M. (2015). Optimization of multiple reservoirs operation with consideration to sediment evacuation. Water Resources Management, 29(7), 2429–2450.
Reddy, M. J., & Kumar, D. N. (2007). Multiobjetcive differential evolution with application to reservoir system optimization. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 21(2), 136–146.
Reddy, M. J., & Kumar, D. N. (2008). Evolving strategies for crop planning and operation of irrigation reservoir system using multi-objective differential evolution. Irrigation Science, 26(2), 177–190.
Reed, P. M., Hadka, D., Herman, J. D., Kasprzyk, J. R., & Kollat, J. B. (2013). Evolutionary multi objective optimization in water resources: the past, present, and future. Advances in Water Resources, 51, 438–456.
Reis, L. F. R., Walters, G. A., Savic, D., & Chaudhry, F. H. (2005). Multi-reservoir operation planning using hybrid genetic algorithm and linear programming (GA-LP): An alternative stochastic approach. Water Resources Management, 19(6), 831–848.
Reis, L. F. R., Bessler, F. T., Walters, G. A., & Svaic, D. (2006). Water supply reservoir operation by combined genetic algorithm-linear programming (GA-LP) approach. Water Resources Management, 20(2), 227–255.
Richardson, J. T., Palmer, M. R., Liepins, G., and Hilliard, M. (1989). Some guidelines for genetic algorithms with penalty functions. Proceeding of the third ICGA, Morgan Kaufmann, 191–197.
Salazar, J. Z., Reed, P. M., Herman, J. D., Giuliani, M., & Castelletti, A. (2016). A diagnostic assessment of evolutionary algorithms for multi-objective surface water reservoir control. Advances in Water Resources, 92, 172–185.
Sarker, R., & Ray, T. (2009). An improved evolutionary algorithm for solving multi-objective crop planning models. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 68(2), 191–199.
Schardong, A., Simonovic, S. P., & Vasan, A. (2013). Multi objective evolutionary approach to optimal reservoir operation. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 27(2), 139–147.
Schardong, A., Simonovic, S. P., & Vasan, A. (2015). Coupled self-adaptive multi objective differential evolution and network flow algorithm approach for optimal reservoir operation. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 141(10), 04015015. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000525.
Seng, T. L., & Khalid, M. B. (1999). Tuning of a neuro-fuzzy controller by genetic algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B: Cybernetics, 29(2), 226–236.
Shiau, J. (2009). Optimization of reservoir hedging rules using multi objective genetic algorithm. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 135(5), 355–363.
Shokri, A., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Mariño, M. A. (2013). Algorithm for increasing the speed of evolutionary optimization and its accuracy in multi-objective problems. Water Resources Management, 27(7), 2231–2249.
Simon, D. (2008). Biogeography-based optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 12(6), 702–713.
Smith, R., Kasprzyk, J., & Zagona, E. (2015). Many-objective analysis to optimize pumping and releases in multireservoir water supply network. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 142(2), 04015049. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000576.
Soleimani, S., Bozorg-Haddad, O., Motahareh, S., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2016). Optimal selective withdrawal rules using a coupled data mining model and genetic algorithm. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 142(12), 04016064.
Sreekanth, J., Datta, B., & Mohapatra, P. K. (2012). Optimal short-term reservoir operation with integrated long-term goals. Water Resources Management, 26(10), 2833–2850.
Srinivas, N., & Deb, K. (1995). Multi-objective function optimization using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithms. Evolutionary Computation, 2(3), 221–248.
Stagge, J., & Moglen, G. (2014). Evolutionary algorithm optimization of a multireservoir system with long lag times. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 19(9), 05014011. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000972.
Storn, R. and Price, R. (1995). Differential evolution—a simple efficient adaptive scheme for global optimization over continuous spaces, International Computer Science Institute, ed. T.R.N. TR-95-012, Calif: Berkley.
Su, J., Wang, X., Liang, Y., & Chen, B. (2013). A GA-based support vector machine model for the prediction of monthly reservoir storage. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 19(7), 1430–1437.
Taghian, M., Rosbjerg, D., Haghighi, A., & Madsen, H. (2013). Optimization of conventional rule curves coupled with hedging rules for reservoir operation. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 140(5), 693–698.
Teegavarapu, R. S. V., & Simonovic, S. P. (2002). Optimal operation of reservoir systems using simulated annealing. Water Resources Management, 16(5), 401–428.
Tospornsampan, J., Kita, I., Ishii, M., & Kitamura, Y. (2005a). Optimization of a multiple reservoir system using a simulated annealing—a case study in the Mae Klong system, Thailand. Paddy and Water Environment, 3(3), 137–147.
Tospornsampan, J., Kita, I., Ishii, M., & Kitamura, Y. (2005b). Optimization of a multiple reservoir system operation using a combination of genetic algorithm and discrete differential dynamic programming: a case study in Mae Klong system, Thailand. Paddy and Water Environment, 3(1), 29–38.
Tsoukalas, I., Kossieris, P., Efstratiadis, A., & Makropoulos, C. (2016). Surrogate-enhanced evolutionary annealing simplex algorithm for effective and efficient optimization of water resources problems on a budget. Environmental Modeling and Software, 77, 122–142.
Tung, C. P., Hsu, S. Y., Liu, C. M., & Li, J. S. (2003). Application of the genetic algorithm for optimizing operation rules of the Liyutan reservoir in Taiwan. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 39(3), 649–657.
Valeriano, O., Koike, T., Yang, K., & Yang, D. (2010). Optimal dam operation during flood season using a distributed hydrological model and a heuristic algorithm. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 15(7), 580–586.
Vonk, E., Xu, Y. P., Booij, M. J., & Augustijn, D. C. M. (2016). Quantifying the robustness of optimal reservoir operation for the Xinanjiang-Fuchunjiang Reservoir Cascade. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 16(4), 79–86. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2015.116.
Vucetic, D. (2012). Fuzzy differential evolution algorithm, M.Sc. thesis, The University of Western Ontario, Slobodan Simonovic.
Vucetic, D., & Simonovic, S. P. (2013). Evaluation and application of fuzzy differential evolution approach for benchmark optimization and reservoir operation problems. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 15(4), 1456–1473.
Wang, K. W., Chang, L. C., & Chang, F. J. (2011). Multi-tier interactive genetic algorithms for the optimization of long-term reservoir operation. Advances in Water Resources, 34(10), 1343–1351.
Wardlaw, R., & Sharif, M. (1999). Evaluation of genetic algorithms for optimal reservoir system operation. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 125(1), 25–33.
Wright, A. (1991). Genetic algorithm for real parameter optimization. In G. J. E. Rawlins (Ed.), Foundations of Genetic Algorithm (pp. 205–218). San Mateo: Morgan Kaufmann.
Xu, Y., Yu-bo, J., & Xue, T. (2004). Parameters selection of SVM based on genetic algorithm. Fushun Liaoning 113001: School of Information Engineering, Liaoning University of Petroleum & Chemical Technology.
Xue, F., Sanderson, A. C., Graves, R. J. (2003). Pareto-based multi-objective differential evolution, Proceedings of the 2003 Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC’2003), Canberra, Australia, IEEE Press 2, 862–869.
Yang, C., Chang, L., Yeh, C., & Chen, C. (2007). Multiobjective planning of surface water resources by multiobjective genetic algorithm with constrained differential dynamic programming. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 133(6), 499–508.
Yang, T., Gao, X., Sellars, S. L., & Sorooshian, S. (2014). Improving the multi-objective evolutionary optimization algorithm for hydropower reservoir operations in the California Oroville-Thermalito complex. Environmental Modeling and Software, 69, 262–279.
Yang, G., Guo, S., Li, L., Hong, X., & Wang, L. (2015). Multi-objective operating rules for Danjiangkou reservoir under climate change. Water Resources Management, 30(3), 1183–1202.
Yapo, P. O., Gupta, H. V., & Sorooshian, S. (1998). Multi-objective global optimization for hydrologic models. Journal of Hydrology, 204(1–4), 83–97.
Yuan, X., Yuan, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2002). A hybrid chaotic genetic algorithm for short-term hydro system scheduling. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 59(4), 319–327.
Yun, R., Singh, V. P., & Dong, Z. (2010). Long-term stochastic reservoir operation using a noisy genetic algorithm. Water Resources Management, 24(12), 3159–3172.
Zeng, Y., Wu, X., Cheng, C., & Wang, Y. (2014). Chance-constrained optimal hedging rules for cascaded hydropower reservoirs. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 140(7), 04014010. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000427.
Zhang, Q., & Li, H. (2007). MOAE/D: a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computations, 11(6), 712–731.
Zhou, R., Li, Y., Lu, D., Liu, H., & Zhou, H. (2016). An optimization based sampling approach for multiple metrics uncertainty analysis using generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation. Journal of Hydrology, 540, 274–286.
Zou, R., & Lung, W. (2004). Robust water quality model calibration using an alternating fitness genetic algorithm. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 130(6), 471–479.
Zou, R., Lung, W. S., & Wu, J. (2009). Multiple-pattern parameter identification and uncertainty analysis approach for water quality modeling. Ecological Modeling, 220(5), 621–629.
Funding
The study is financially supported by Iran’s National Science Foundation (INSF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahandideh-Tehrani, M., Bozorg-Haddad, O. & Loáiciga, H.A. Application of non-animal–inspired evolutionary algorithms to reservoir operation: an overview. Environ Monit Assess 191, 439 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7581-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7581-2