Abstract
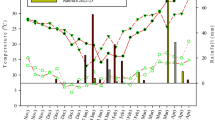
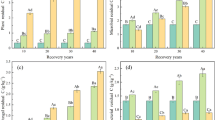
Selection of appropriate residue application method is essential for better use of biomass for soil and environmental health improvement. A laboratory incubation experiment was conducted for 75 days to investigate C and N mineralization of residues of soybean (Glycine max L.), chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.), maize (Zea mays L.), and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) placed on the soil surface and incorporated into the soil. The residue of soybean and chickpea had a greater decomposition rate than that of maize and wheat, despite of their placements. Higher rate of decomposition of the residue of soybean and chickpea was recorded when it was kept on the soil surface while soil incorporation of residue of wheat and maize resulted in faster decomposition. Therefore, these findings could be used as guidelines for management of crop residue application in farmland to improve soil and environmental quality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiven, S., & Recous, S. (2007). Mineralization of crop residues on the soil surface or incorporated in the soil under controlled conditions. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 43, 849–852.
Angers, D. A., & Recous, S. (1997). Decomposition of wheat straw and rye residues as affected by particle size. Plant and Soil, 189, 197–203.
Bremer, E., Van Houtum, W., & Van Kessel, C. (1991). Carbon dioxide evolution from wheat and lentil residues as affected by grinding, added nitrogen, and the absence of soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 11, 221–227.
Coppens, F., Garnier, P., De Gryze, S., Merckx, R., & Recous, S. (2006). Soil moisture, carbon and nitrogen dynamics following incorporation and surface application of labelled crop residues in soil columns. European Journal of Soil Science, 57, 894–905.
Deng, S. P., & Tabatabai, M. A. (1996). Effect of tillage and residue management on enzyme activities in soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 22, 208–213.
Dinesh, R., Chaudhuri, S., Ganeshamurthy, A., & Pramanik, S. (2004). Biochemical properties of soils of undisturbed and disturbed mangrove forests of South Andaman (India). Wetlands Ecology and Management, 12, 309–320.
Dotaniya, M. L., & Datta, S. C. (2014). Impact of bagasse and press mud on availability and fixation capacity of phosphorus in an Inceptisol of north India. Sugar Tech, 16(1), 109–112.
Dotaniya, M. L., & Meena, V. D. (2013). Rhizosphere effect on nutrient availability in soil and its uptake by plants -a review. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India, Section B: Biological Sciences, 85(1), 1–12.
Dotaniya, M. L., Datta, S. C., Biswas, D. R., & Meena, B. P. (2013a). Effect of solution phosphorus concentration on the exudation of oxalate ions by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India, Section B: Biological Sciences, 83(3), 305–309.
Dotaniya, M. L., Prasad, D., Meena, H. M., Jajoria, D. K., Narolia, G. P., Pingoliya, K. K., Meena, O. P., Kumar, K., Meena, B. P., Ram, A., Das, H., Chari, M. S., & Pal, S. (2013b). Influence of phytosiderophore on iron and zinc uptake and rhizospheric microbial activity. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 7(51), 5781–5788.
Dotaniya, M. L., Datta, S. C., Biswas, D. R., & Kumar, K. (2014a). Effect of organic sources on phosphorus fractions and available phosphorus in Typic Haplustept. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 62(1), 80–83.
Dotaniya, M. L., Datta, S. C., Biswas, D. R., Meena, H. M., & Kumar, K. (2014b). Production of oxalic acid as influenced by the application of organic residue and its effect on phosphorus uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in an Inceptisol of north India. National Academy Science Letters, 37(5), 401–405.
Dotaniya, M. L., Datta, S. C., Biswas, D. R., Meena, H. M., Rajendiran, S., & Meena, A. L. (2015). Phosphorus dynamics mediated by bagasse, press mud and rice straw in Inceptisol of North India. Agrochimica, 59(4), 358–369.
Dotaniya, M. L., Datta, S. C., Biswas, D. R., Dotaniya, C. K., Meena, B. L., Rajendiran, S., Regar, K. L., & Lata, M. (2016). Use of sugarcane industrial byproducts for improving sugarcane productivity and soil health-a review. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 185(3), 185–194.
Dotaniya, M. L., Rajendiran, S., Meena, V. D., Saha, J. K., Coumar, M. V., Kundu, S., & Patra, A. K. (2017). Influence of chromium contamination on carbon mineralization and enzymatic activities in Vertisol. Agriculture Research, 6(1), 91–96.
Gadde, B., Bonnet, S., Menke, C., & Garivait, S. (2009). Air pollutant emissions from rice straw open field burning in India, Thailand and the Philippines. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1554–1558.
Giacomini, S. J., Recous, S., Mary, B., & Aita, C. (2007). Simulating the effects of N availability, straw particle size and location in soil on C and N mineralization. Plant and Soil, 301, 289–301.
Gomez, K.A., & Gomez, A. (1983). Statistical procedures for agricultural research, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York.
Guntinas, M. E., Leirós, M. C., Trasar-Cepeda, C., & Gil-Sotres, F. (2001). Effects of moisture and temperature on net soil nitrogen mineralization: a laboratory study. European Journal of Soil Biology, 48, 73–80.
Kushwah, S. K., Dotaniya, M. L., Upadhyay, A. K., Rajendiran, S., Coumar, M. V., Kundu, S., & Rao, A. S. (2014). Assessing carbon and nitrogen partition in kharif crops for their carbon sequestration potential. National Academy Science Letters, 37(3), 213–217.
Li, L. J., Han, X. Z., You, M. Y., Yuan, Y. R., Ding, X. L., & Qiao, Y. F. (2013). Carbon and nitrogen mineralization patterns of two contrasting crop residues in a Mollisol: effects of residue type and placement in soils. European Journal of Soil Biology, 54, 1–6.
Lynch, M. J., Mulvaney, M. J., Hodges, S. C., Thompson, T. L., & Thomason, W. E. (2016). Decomposition, nitrogen and carbon mineralization from food and cover crop residues in the central plateau of Haiti. Springerplus, 5(1), 973–981.
Majumder, B., & Kuzyakov, Y. (2010). Effect of fertilization on decomposition of 14C labelled plant residues and their incorporation into soil aggregates. Soil & Tillage Research, 109, 94–102.
Marmo, L. (2008). EU strategies and policies on soil and waste management to offset greenhouse gas emissions. Waste Management, 28, 685–689.
Mary, B., Recous, S., Drawls, D., & Robin, D. (1996). Interaction between decomposition of plant residue and nitrogen cycling in soil. Plant and Soil, 181, 71–82.
Mengel, K. (1996). Turnover of organic nitrogen in soil and its availability to crops. Plant and Soil, 181, 83–93.
Prajapati, K., Rajendiran, S., Coumar, M. V., Dotaniya, M. L., Ajay, Kundu, S., Saha, J. K., & Patra, A. K. (2016). Carbon occlusion potential of rice phytoliths: implications for global carbon cycle and climate change mitigation. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 14(2), 265–281.
Singh, D., Chhonkar, P.K., & Pandey, R.N. (2005). Soil plant water analysis: a methods manual. New Delhi: Westville.
Vestgarden, L. S. (2001). Carbon and nitrogen turnover in the early stage of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) needle litter decomposition: effect of internal and external nitrogen. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 465–474.
Zibilske, L. M., & Bradford, J. M. (2007). Oxygen effects on carbon, polyphenols, and nitrogen mineralization potential in soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 71, 133–139.
Zibilski, L.M. (1994). Carbon mineralization. In: Bingham JM, Mickelson SH (eds) Method of soil analysis, part 2. Microbiological and biochemical properties. SSSA book series no. 5. ASA, SSSA, Madison.
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful to the Director, HOD and technical staff of the Division of Soil Chemistry & Fertility, ICAR-IISS and equally grateful to the Director, ICAR-IIPR, Kanpur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jat, R.L., Jha, P., Dotaniya, M.L. et al. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in Vertisol as mediated by type and placement method of residue. Environ Monit Assess 190, 439 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6785-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6785-1