Abstract
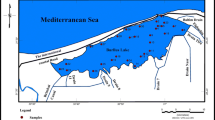
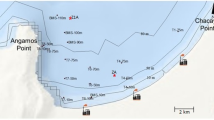
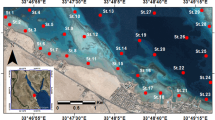
The Red Sea encompasses a wide range of tropical marine habitats that are stressed due to anthropogenic activities. The main anthropogenic activities are hydrocarbon exploration and important trading harbors. This work aims to assess the influence of the Red Sea coastal heavy metal contamination on the marine meiofauna along three sites (Ras Gharib, Safaga, and Quseir). Eight heavy metal (Cu, Cd, Zn, Pb, Cr, Co, Ni, and Mn) contents are considered in four benthic foraminiferal species (Elphidium striatopunctatum, Amphistegina lobifera, Amphisorus hemprichii, and Ammonia beccarii). Quseir Harbor showed the highest level of pollution followed by Safaga and Ras Gharib sites. The analyzed benthic foraminiferal tests displayed noteworthy high concentrations of Cd, Zn, and Pb in Quseir Harbor which could be attributed to the anthropogenic activities in the nearshore areas. Some foraminiferal tests exhibited abnormalities in their apertures, coiling, and shape of chambers. A comparison between normal and deformed foraminiferal tests revealed that the deformed ones are highly contaminated with elevated heavy metal contents such as Fe, Mn, Ni, and Cd. Statistics in addition to geo-accumulation and pollution load indices reveal a whistling alarm for the Quseir harbor. The present data are necessary to improve conservation and management of the Red Sea ecosystem in the near future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale, K. O., Agunbide, F. O., & Olu-Owolabi, B. (2009). Trace metal concentration, site variations and partitioning pattern in water and bottom sediments from coastal area: a case study of Ondo coast, Nigeria. Environmental Research Journal, 3(2), 46–59.
Alve, E. (1991). Benthic foraminifera in sediment cores reflecting heavy metal pollution in Sorfjord, Western Norway. The Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 21(1), 1–19.
Badawi, A., Schmiedl, G., & Hemleben, C. (2005). Impact of late quaternary environmental changes on deep-sea benthic foraminiferal faunas of the Red Sea. Marine Micropaleontology, 58(1), 13–30.
Bates, J. M., & Spencer, R. S. (1979). Modification of foraminiferal trends by the Chesapeake-Elizabeth sewage outfall, Virginia Beach, Virginia. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 9, 125–140.
Bergin, F., Kucuksezgin, F., Uluturhan, E., Barut, I. F., Meric, E., Avsar, N., & Nazik, A. (2006). The response of benthic foraminifera and ostracoda to heavy metal pollution in Gulf of Izmir (Eastern Aegean Sea). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 66(3), 368–386.
Bouchet, V. M. P., Alve, E., Rygg, B., & Telford, R. J. (2012). Benthic foraminifera provide a promising tool for ecological quality assessment of marine waters. Ecological Indicators, 23, 66–75.
Buosi, C., Frontalini, F., Da Pelo, S., Cherchi, A., Coccioni, R., & Bucci, C. (2010). Foraminifera proxies for environmental monitoring in the polluted lagoon of Santa Gilla (Cagliari, Italy). Present Environment and Sustainable Development, 4, 91–103.
Byers, S. C., Mills, L. E., & Stewart, P. L. (1987). A comparison of methods of determination of organic matter in marine sediments, with suggestions for a standard method. Hydrobiologia, 58(1), 43–47.
Closs, D., & Maderia, M. L. (1968). Seasonal variations of brackish foraminifera in the Patos Lagoon, southern Brazil, Escola de Geologia, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul. Escola de Geologia, Publicaco Especial, 15, 1–51.
Coccioni, R. & Marsili, A (2005). Monitoring in polluted transitional marine environments using foraminifera as bioindicators: a case study from the Venice Lagoon (Italy). ICAM Dossier, (3), pp. 250–256.
Debenay, J.-P., & Fernandez, J. M. (2009). Benthic foraminifera records of complex anthropogenic environmental changes combined with geochemical data in a tropical bay of New Caledonia (SW Pacific). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 59(8), 311–322.
Du Châtelet, É. A., Debenay, J. P., & Soulard, R. (2004). Foraminiferal proxies for pollution monitoring in moderately polluted harbours. Environmental Pollution, 127(1), 27–40.
Duchart, P., Calvert, S., & Price, N. (1973). Distribution of trace metals in the pore waters of shallow marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 18, 605–610.
El-Halaby, O. (1999). Taxonomy and ecology of recent foraminiferal species in the Hurghada offshore area. Annals. Geological Survey of Egypt, 22, 193–249.
Elshanawany, R. et al. (2010). Microfossil assemblages as proxies to reconstruct anthropogenic induced eutrophication of two marginal Eastern Mediterranean Basins. PhD thesis, Bremen University, Germany, pp. 1–232.
El-Sorogy, A. S., Abd El-Wahab, M., Nour, H. E., Ziko, A., & Shehata, W. (2006). Faunal assemblages and sedimnet chemistryof some lagoons along rhe Red Sea coast, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Paleontology, 6, 193–224.
El-Taher, A., & Madkour, H. A. (2014). Environmental and radio-ecological studies on shallow marine sediments from harbour areas along the Red Sea coast of Egypt for identification of anthropogenic impacts. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 50(1), 120–133.
Frontalini, F., Buosi, C., Da Pelo, S., Coccioni, R., Cherchi, A., & Bucci, C. (2009). Benthic foraminifera as bio-indicators of trace element pollution in the heavily contaminated Santa Gilla lagoon (Cagliari, Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(6), 858–877.
Gabrié, C., & Montaggioni, L. (1982). Sedimentary facies from the modern coral reefs, Jordan gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Coral Reefs, 1(2), 115–124.
Geslin, E., Debenay, J. P., Duleba, W., & Bonetti, C. (2002). Morphological abnormalities of foraminiferal tests in Brazilian environments: comparison between polluted and non-polluted areas. Marine Micropaleontology, 45(2), 151–168.
Gross, M. G. (1971). Carbon determination. In R. E. Carver (Ed.), Procedures in sedimentary petrology (pp. 573–596). New York: Wiley.
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D. A. T., & Ryan, P. D. (2009). PAST-palaeontological statistics, ver. 1.89 (pp. 1–31). Oslo: University of Oslo.
Haunold, T. G., Baal, C., & Piller, W. E. (1997). Benthic foraminiferal associations in the northern Bay of Safaga, Red Sea, Egypt. Marine Micropaleontology, 29(3), 185–210.
Hegazy, M. N., & Effat, H. A. (2010). Monitoring some environmental impacts of oil industry on coastal zone using different remotely sensed data. Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 13(1), 63–74.
Jayaraju, N., Reddy, B. S. R., & Reddy, K. R. (2008). The response of benthic foraminifera to various pollution sources: a study from Nellore Coast, East Coast of India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 142(1–3), 319–323.
Loeblich, A. R., & Tappan, H. N. (1988). Foraminiferal genera and their classification. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold 970 pp.
Madkour, H. (2004). Geochemical and environmental studies of recent marine sediments and some invertebrates of the Red Sea, Egypt. Doctor’s Thesis South Valley University, Qena, 317 pp.
Madkour, H. A. (2013). Impacts of human activities and natural inputs on heavy metal contents of many coral reef environments along the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6, 1739–1752.
Manosur, A. M., Nawar, A. H., & Mohamed, A. W. (2000). Geochemistry of coastal marine sediments and their contaminants metal, Red Sea, Egypt: a legacy for the future and a tracer to modern sediment dynamics. Sedimentology Egypt, 8, 231–242.
Mohamed, A. W. (2005). Geochemical and sedimentology of core sediments and the influence of human activities: Qusier, Safaga and Hurghada Harbours, Red Sea Coast, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 31, 92–103.
Müller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins-Vernderungen seit 1971. Umschau, 24, 778–783.
Murray, J. W. (1970). Foraminifers of the western approaches to the English Channel. Micropaleontology, 16, 471–485.
Murray, J. W. (1973). Distribution and ecology of living benthic foraminiferids (pp. 1–288). London: Heinemann Educational Books.
Murray, J. W. (1991). Ecology and paleoecology of benthic foraminifera. Harlow: Longman.
Norton, S. A., & Kahl, J. S. (1991). Progress in understanding the chemical stratigraphy of metals in lake sediments in relation to acidic deposition. Hydrobiologia, 214, 77–84.
Nour, H. (2001). Quaternary sea shells and their environmental significance in the area between Gebel Zeit and El-Hamarawein Red Sea Coast, Egypt.M. Sc. Zagazig University, 320 pp.
Praveena, M. S., Radojevic, M., & Abdullah, M. H. (2007). The assessment of mangrove sediment quality in Mengkabong Lagoon: an index analysis approach. International Journal of Environmental & Science Education, 2(3), 60–68.
Rao, K., & Rao, T. (1979). Studies on pollution ecology of foraminifera of the Trivandrum coast. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 8, 31–35.
Reiss, Z., & Hottinger, L. (1984). The Gulf of Aqaba: ecological micropaleontology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 354 p.
Romano, E., Bergamin, L., Ausili, A., Pierfranceschi, G., Maggi, C., Sesta, G., & Gabellini, M. (2009). The impact of the Bagnoli industrial site (Naples, Italy) on sea-bottom environment. Chemical and textural features of sediments and the related response of benthic foraminifera. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 59(8), 245–256.
Samir, A. M. (2000). The response of benthic foraminifera and ostracods to various pollution sources: a study from two lagoons in Egypt. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 30(2), 83–98.
Samir, A., & El-Din, A. (2001). Benthic foraminiferal assemblages and morphological abnormalities as pollution proxies in two Egyptian bays. Marine Micropaleontology, 41(3), 193–227.
Shannon, C. E. (1948). A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379–423.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoland Marine Research, 33(1–4), 566–575.
Yang, H., & Rose, N. (2005). Trace metals pollution records in some UK lake sediments, their history, influence factors and regional differences. Environment International, 31(1), 63–75.
Yanko, V., Ahmad, M., & Kaminski, M. (1998). Morphological deformities of benthic foraminiferal tests in response to pollution by heavy metals: implications for pollution monitoring. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 28, 177–200.
Youssef, M. (2015). Heavy metals contamination and distribution of benthic foraminifera from the Red Sea coastal area, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Oceanologia, 57, 1–15.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the National Oceanography and Fisheries Institute, Hurghada Branch, for the help during sampling. Also, the authors are gratitude to Prof. Dr. Neil Sturchio (the head of the Geoscience Department, Delaware’s University College of Earth Science, USA) for revising this manuscript. Thanking should be extended to the anonymous reviewers for evolving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Appendix 1
(GIF 365 kb)
Appendix 2
(GIF 175 kb)
Appendix 3
(GIF 190 kb)
Appendix 4
(GIF 63 kb)
Appendix 5
(GIF 389 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Kahawy, R., El-Shafeiy, M., Helal, S.A. et al. Morphological deformities of benthic foraminifera in response to nearshore pollution of the Red Sea, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 190, 312 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6695-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6695-2