Abstract
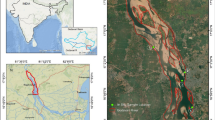
Monitoring surface water velocity during flood events is a challenging task. Techniques based on deploying instruments in the flow are often unfeasible due to high velocity and abundant sediment transport. A low-cost and versatile technology that provides continuous and automatic observations is still not available. Among remote methods, large-scale particle image velocimetry (LSPIV) is an optical method that computes surface water velocity maps from videos recorded with a camera. Here, we implement and critically analyze findings obtained from a recently introduced LSPIV experimental configuration during a flood event in the Tiber River at a cross section located in the center of Rome, Italy. We discuss the potential of LSPIV observations in challenging environmental conditions by presenting results from three tests performed during the hydrograph flood peak and recession limb of the event for different illumination and weather conditions. The obtained surface velocity maps are compared to the rating curve velocity and to benchmark velocity values. Experimental findings show that optical methods should be preferred in extreme conditions. However, their practical implementation may be associated with further hurdles and uncertainties.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R. J. (1991). Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid-mechanics. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 23, 261–304.
Alessandrini, V., Bernardi, G., & Todini, E. (2013). An operational approach to real-time dynamic measurement of discharge. Hydrology Research, 44, 953–964.
Bechle, A. J., & Wu, C. H. (2014). An entropy-based surface velocity method for estuarine discharge measurement. Water Resources Research, 50(7), 6106–6128.
Bechle, A., Wu, C., Liu, W., & Kimura, N. (2012). Development and application of an automated river-estuary discharge imaging system. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 138(4), 327–339.
Bradley, A. A., Kruger, A., Meselhe, E. A., & Muste, M. V. I. (2002). Flow measurement in streams using video imagery. Water Resources Research, 38(12), 1–8.
Buchanan, T. J., and W. P. Somers (1969), Discharge measurements at gaging stations: U.S. geological survey techniques of water-resources investigations, Tech. rep., U.S. Geological Survey.
Chow, V. T. (1959). Open-Channel Hydraulics. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Creutin, J. D., Muste, M., Bradley, A. A., Kim, S. C., & Kruger, A. (2003). River gauging using PIV techniques: a proof of concept experiment on the Iowa River. Journal of Hydrology, 277(3-4), 182–194.
deLima, J. L. M. P., & Abrantes, J. R. C. B. (2014). Using a thermal tracer to estimate overland and rill flow velocities. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 39(10), 1293–1300.
Dramais, G., LeCoz, J., Camenen, B., & Hauet, A. (2011). Advantages of a mobile LSPIV method for measuring flood discharges and improving stage-discharge curves. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 5(4), 301–312.
Fujita, I., & Hino, T. (2003). Unseeded and seeded PIV measurements of river flows video from a helicopter. Journal of Visualization, 6(3), 245–252.
Fujita, I., & Kunita, Y. (2011). Application of aerial LSPIV to the 2002 flood of the Yodo River using a helicopter mounted high density video camera. Journal of Hydro-environment Research, 5(4), 323–331.
Fujita, I., Muste, M., & Kruger, A. (1997). Large-scale particle image velocimetry for flow analysis in hydraulic engineering applications. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 36(3), 397–414.
Fulton, J., & Ostrowski, J. (2008). Measuring real-time streamflow using emerging technologies: radar, hydroacoustics, and the probability concept. Journal of Hydrology, 357(1-2), 1–10.
Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., Alonso, G., & Nardi, F. (2010). Flow time estimation with variable hillslope velocity in ungauged basins. Advances in Water Resources, 33(10), 1216–1223.
Gui, L. (2014), EDPIV—evaluation software for digital particle image velocimetry, http://lcgui.net.
Gunawan, B., Sun, X., Sterling, M., Shiono, K., Tsubaki, R., Rameshwaran, P., Knight, D., Chandler, J., Tang, X., & Fujita, I. (2012). The application of LS-PIV to a small irregular river for inbank and overbank flows. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 24, 1–12.
Hauet, A., Kruger, A., Krajewski, W. F., Bradley, A., Muste, M., Creutin, J.-D., & Wilson, M. (2008a). Experimental system for real-time discharge estimation using an image-based method. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 13(2), 105–110.
Hauet, A., Creutin, J. D., & Belleudy, P. (2008b). Sensitivity study of large-scale particle image velocimetry measurement of river discharge using numerical simulation. Journal of Hydrology, 349(1-2), 178–190.
Hauet, A., Muste, M., & Ho, H.-C. (2009). Digital mapping of riverine waterway hydrodynamic and geomorphic features. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 34(2), 242–252.
Hilgersom, K. P., & Luxemburg, W. M. J. (2012). Technical note: how image processing facilitates the rising bubble technique for discharge measurement. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 16, 345–356.
Hrachowitz, M., Savenije, H. H. G., Bogaard, T., Tetzlaff, D., & Soulsby, C. (2013a). What can flux tracking teach us about water age distribution patterns and their temporal dynamics? Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 17, 533–564.
Hrachowitz, M., Savenije, H. H. G., Blöschl, G., McDonnell, J. J., Sivapalan, M., Pomeroy, J. W., Arheimer, B., Blume, T., Clark, M. P., Ehret, U., Fenicia, F., Freer, J. E., Gelfan, A., Gupta, H. V., Hughes, D. A., Hut, R. W., Montanari, A., Pande, S., Tetzlaff, D., Troch, P. A., Uhlenbrook, S., Wagener, T., Winsemius, H. C., Woods, R. A., Zehe, E., & Cudennec, C. (2013b). A decade of predictions in ungauged basins (PUB)—a review. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 58(6), 1198–1255.
Jodeau, M., Hauet, A., Paquier, A., Le Coz, J., & Dramais, G. (2008). Application and evaluation of LS-PIV technique for the monitoring of river surface velocities in high flow conditions. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 19(2), 117–127.
Kantoush, S. A., Schleiss, A. J., Sumi, T., & Murasaki, M. (2011). LSPIV implementation for environmental flow in various laboratory and field cases. Journal of Hydro-environment Research, 5(4), 263–276.
Kim, Y. (2006), Uncertainty analysis for non-intrusive measurement of river discharge using image velocimetry, Ph.D. thesis, Graduate College of the University of Iowa.
Kreibich, H., Piroth, K., Seifert, I., Maiwald, H., Kunert, U., Schwarz, J., Merz, B., & Thieken, A. H. (2009). Is flow velocity a significant parameter in flood damage modelling? Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 9(5), 1679–1692.
LeCoz, J., Hauet, A., Pierrefeu, G., Dramais, G., & Camenen, B. (2010). Performance of image-based velocimetry LSPIV applied to flash-flood discharge measurements in mediterranean rivers. Journal of Hydrology, 394(1–2), 42–52.
Leibundgut, C., Maloszewski, P., & Külls, C. (2009). Tracers in Hydrology. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Manoj, K. C., & Fang, X. (2015). Estimating time parameters of overland flow on impervious surfaces by the particle tracking method. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 60(2), 294–310.
Manzo, M., Ioppolo, T., Ayaz, U. K., LaPenna, V., & Ötügen, M. V. (2012). A photonic wall pressure sensor for fluid mechanics applications. Review of Scientific Instruments, 83, 105003.
McMillan, H., Freer, J., Pappenberger, F., Krueger, T., & Clark, M. (2010). Impacts of uncertain river flow data on rainfall-runoff model calibration and discharge predictions. Hydrological Processes, 24(10), 1270–1284.
Montanari, A., Young, G., Savenije, H. H. G., Hughes, D., Wagener, T., Ren, L. L., Koutsoyiannis, D., Cudennec, C., Toth, E., Grimaldi, S., Blöschl, G., Sivapalan, M., Beven, K., Gupta, H., Hipsey, M., Schaefli, B., Arheimer, B., Boegh, E., Schymanski, S. J., Di Baldassarre, G., Yu, B., Hubert, P., Huang, Y., Schumann, A., Post, D. A., Srinivasan, V., Harman, C., Thompson, S., Rogger, M., Viglione, A., McMillan, H., Characklis, G., Pang, Z., & Belyaev, V. (2013). Panta Rhei—everything flows: change in hydrology and society—The IAHS scientific decade 2013-2022. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 58(6), 1256–1275.
Muste, M., Fujita, I., & Hauet, A. (2008). Large-scale particle image velocimetry for measurements in riverine environments. Water Resources Research, 44(4), W00D19.
Planchon, O., Silvera, N., Gimenez, R., Favis-Mortlock, D., Wainwright, J., Le Bissonnais, Y., & Govers, G. (2005). An automated salt-tracing gauge for flow-velocity measurement. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 30(7), 833–844.
Quénot, G. M., Pakleza, J., & Kowalewski, T. A. (1998). Particle image velocimetry with optical flow. Experiments in Fluids, 25, 177–189.
Raffel, M., Willert, C. E., Wereley, S. T., & Kompenhans, J. (2007). Particle image velocimetry. A practical guide. New York: Springer.
Centro Funzionale Regionale – Regione Lazio (2015), http://www.idrografico.roma.it.
Sassi, M. G., Hoitink, A. J. F., Vermeulen, B., and Hidayat (2011), Discharge estimation from H-ADCP measurements in a tidal river subject to sidewall effects and a mobile bed, Water Resources Research, 47(6), W06504.
Tang, H.-W., Chen, C., Chen, H., & Huang, J.-T. (2008). An improved PTV system for large-scale physical river model, Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 20(6), 669–678.
Tarpanelli, A., Barbetta, S., Brocca, L., & Moramarco, T. (2013). River discharge estimation by using altimetry data and simplified flood routing modeling. Remote Sensing, 5(9), 4145–4162.
Tauro, F., Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., & Porfiri, M. (2012). Fluorescent particle tracers in surface hydrology: a proof of concept in a natural stream. Water Resources Research, 48(6), W06528.
Tauro, F., Porfiri, M., & Grimaldi, S. (2013a). Fluorescent eco-particles for surface flow physics analysis. AIP Advances, 3(3), 032108.
Tauro, F., Rapiti, E., Al-Sharab, J. F., Ubertini, L., Grimaldi, P., & Porfiri, M. (2013b). Characterization of eco-friendly fluorescent nanoparticle doped-tracers for environmental sensing. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 15(9), 1884.
Tauro, F., Porfiri, M., & Grimaldi, S. (2014a). Orienting the camera and firing lasers to enhance large scale particle image velocimetry for stream flow monitoring. Water Resources Research, 50(9), 7470–7483.
Tauro, F., Porfiri, M., & Grimaldi, S. (2014b). Unraveling flow patterns through nonlinear manifold learning. PLoS One, 9(3), e91131.
Tauro, F., A. Petroselli, and E. Arcangeletti (2015a), Assessment of drone-based surface flow observations, Hydrological Processes, 10.1002/hyp.10698
Tauro, F., Pagano, C., Phamduy, P., Grimaldi, S., & Porfiri, M. (2015b). Large-scale particle image velocimetry from an unmanned aerial vehicle. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 20(6), 3269–3275.
Tazioli, A. (2011). Experimental methods for river discharge measurements: comparison among tracers and current meter [Méthodes expérimentales pour mesurer le débit des cours d’eau: Comparaison entre les traceurs artificiels et le courantomètre]. Hydrol Sci J, 56(7), 1314–1324.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2004). Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(4), 600–612.
Yorke, T. H., & Oberg, K. A. (2002). Measuring river velocity and discharge with acoustic Doppler profilers. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 13(5–6), 191–195.
Zeng, J., Constantinescu, G., Blanckaert, K., & Weber, L. (2008). Flow and bathymetry in sharp open-channel bends: experiments and predictions. Water Resources Research, 44(9), W09401.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the American Geophysical Union Horton (Hydrology) Research Grant for Ph.D. students, by the Ministero degli Affari Esteri project 2015 Italy-USA PGR00175, by the UNESCO Chair in Water Resources Management and Culture, and by the National Science Foundation under grant number BCS-1124795. The authors thank Roberto Rapiti and Giuliano Cipollari for help with the experiments and Francesco Mele, Domenico Spina, and Luigi D’Aquino from UIM for providing water level measurements and rating curves.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tauro, F., Olivieri, G., Petroselli, A. et al. Flow monitoring with a camera: a case study on a flood event in the Tiber River. Environ Monit Assess 188, 118 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5082-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5082-5