Abstract
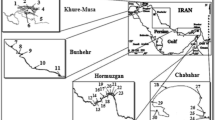
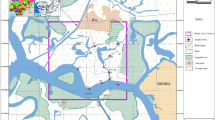
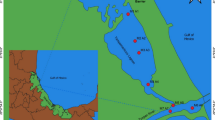
The quantification of 14 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) was carried out in sediment samples collected from Akaki River, Lake Awassa, and Lake Ziway, Ethiopia. The concentration of PAHs in the samples was determined using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode, after microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), using acetone/n-hexane (1:1, v/v) mixture. The accuracy of the method was determined by extracting and analyzing New York/New Jersey waterway sediment standard reference material (SRM 1944). The measured concentrations of PAHs in SRM 1944 agreed well with the certified values. In samples from Akaki River, Lake Awassa, and Lake Ziway, the total content of PAHs determined ranged from 0 to 3070 ng/g (average 534 ng/g), 24.9 to 413 ng/g (average 169 ng/g), and 15.0 to 305 ng/g (average 175 ng/g), respectively. Source ratios indicated that the PAHs were mainly from petrogenic origin. Sediments from all sampling sites indicated negligible levels of toxicity with no risk of adverse biological effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, T., Khillare, P. S., & Shridhar, V. (2006). PAHs contamination in bank sediment of the Yamuna River, Delhi, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 123(1–3), 151–166.
Alvarez-Aviles, O., Cuadra-Rodriguez, L., Gonzalez-Illan, F., Quinones-Gonzalez, J., & Rosario, O. (2007). Optimization of a novel method for the organic chemical characterization of atmospheric aerosols based on microwave-assisted extraction combined with stir bar sorptive extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 597(2), 273–281.
Awulachew, S. B., Yilma, A. D., Loulseged, M., Loiskandl, W., Ayana, M., & Alamirew, T. (2007). Water resources and irrigation development in Ethiopia. Colombo: International Water Management Institute. 78p. (Working Paper 123).
Boonyatumanond, R., Wattayakorn, G., Togo, A., & Takada, H. (2006). Distribution and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in riverine, estuarine, and marine sediments in Thailand. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(8), 942–956.
Cardellicchio, N., Buccolieri, A., Giandomenico, S., Lopez, L., Pizzulli, F., & Spada, L. (2007). Organic pollutants (PAHs, PCBs) in sediments from the Mar Piccolo in Taranto (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55(10), 451–458.
Chan, C. H., Yusoff, R., Ngoh, G. C., & Kung, F. W. L. (2011). Microwave-assisted extractions of active ingredients from plants. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218(37), 6213–6225.
Culotta, L., de Stefano, C., Gianguzza, A., Mannino, M. R., & Orecchio, S. (2006). The PAH composition of surface sediments from Stagnone coastal lagoon, Marsala, Italy. Marine Chemistry, 99(1–4), 117–127.
Dean, J. R., & Xiong, G. (2000). Extraction of organic pollutants from environmental matrices: selection of extraction technique. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 19(9), 553–564.
Denis, E. H., Toney, J. L., Tarozo, R., Anderson, R. S., Roach, L. D., & Huang, Y. (2012). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in lake sediments record historic fire events: validation using HPLC-fluorescence detection. Organic Geochemistry, 45(1), 7–17.
Doong, R., & Lin, Y. (2004). Characterization and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminations in surface sediment and water from Gao-ping River, Taiwan. Water Research, 38(7), 1733–1744.
Duke, O., & Albert, I. O. (2007). Carcinogenic potency of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Ethiopia, 21(3), 437–443.
Guo, W., Pei, Y., Yang, Z., & Chen, H. (2011). Historical changes in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) input in Lake Baiyangdian related to regional socio-economic development. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 187(1–3), 441–449.
Hahladakis, J., Smaragdaki, E., Vasilaki, G., & Gidarakos, E. (2013). Use of sediment quality guidelines and pollution indicators for the assessment of heavy metal and PAH contamination in Greek surficial sea and lake sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(3), 2843–2853.
Kumar, K. S., Sajwan, K. S., Richardson, J. P., & Kannan, K. (2008). Contamination profiles of heavy metals, organochlorine pesticides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and alkyl phenols in sediment and oyster collected from marsh/estuarine Savannah GA, USA. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(1), 136–162.
Ledgard, J. (2007). The preparatory manual of explosives. 3rd ed. ISBN: 978-0-6151-4290-6 South Bend, IN: Paranoid Publications Group, USA.
Li, X. H., Ma, L. L., Liu, X. F., Fu, S., Cheng, H. X., & Xu, X. B. (2006). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in urban soil from Beijing, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 8(5), 944–950.
Li, J., Shang, X., Zhao, Z., Tanguay, R. L., Dong, Q., & Huang, C. (2010). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, sediment, soil, and plants of the Aojiang River waterway in Wenzhou, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173(1–3), 75–81.
Li, J., Dong, H., Zhang, D., Han, B., Zhu, C., Liu, S., Liu, X., Ma, Q., Li. X. (2015). Sources and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in surface sediments from Bohai Sea and northern part of the Yellow Sea, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin. xxx (2015) xxx–xxx (Article in Press). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.002.
Liang, Y., Tse, M. F., Young, L., & Wong, M. H. (2007). Distribution pattern of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the sediments and fish at Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Water Research, 41(6), 1301–1311.
Long, E. R., & MacDonald, D. D. (1998). Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 4(5), 1019–1039.
Long, E. R., Macdonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects with ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19(1), 81–97.
Long, E. R., Field, L. J., & Macdonald, D. D. (1998). Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17(4), 717–727.
Macdonald, D. D., Carr, R. S., Calder, F. D., Long, E. R., & Ingersoll, C. G. (1996). Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 5(1), 253–278.
Martinez, E., Gros, M., Lacorte, S., & Barcelo, D. (2004). Simplified procedures for the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, sediments and mussels. Journal of Chromatography A, 1047(2), 181–188.
Mekonnen, K. N., Ambushe, A. A., Chandravanshi, B. S., Redi-Abshiro, M., & McCrindle, R. I. (2014). Assessment of potentially toxic elements in Swiss chard and sediments of Akaki River, Ethiopia. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 96(10), 1501–1515.
Mekonnen, K. N., Ambushe, A. A., Chandravanshi, B. S., Redi-Abshiro, M., & McCrindle, R. I. (2015). Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in surface sediments of Lake Awassa and Lake Ziway, Ethiopia, Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 50(1), 90–99.
Nikolaou, A., Kostopoulou, M., Lofrano, G., & Meric, S. (2009). Determination of PAHs in marine sediments: analytical methods and environmental concerns. Global NEST Journal, 11(4), 391–405.
Orecchio, S., & Papuzza, V. (2009). Levels, fingerprint and daily intake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in bread baked using wood as fuel. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(2–3), 876–883.
Orecchio, S., Ciotti, V. P., & Culotta, L. (2009). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coffee brew samples: analytical method by GC–MS, profile, levels and sources. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47(4), 819–826.
Perez-Fernandez, B., Vinas, L., Franco, M. A., Bargiela, J. PAHs in the Ría de Arousa (NW Spain): a consideration of PAHs sources and abundance Marine Pollution Bulletin xxx (2015) xxx–xxx (Article in Press). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.04.028.
Prabu, P. C. (2009). Impact of heavy metal contamination of Akaki River of Ethiopia on soil and metal toxicity on cultivated vegetable crops. Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 8(9), 818–827.
Prasse, C., Zech, W., Itanna, F., & Glaser, B. (2012). Contamination and source assessment of metals, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils from Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 94(10), 1954–1979.
Qiao, M., Wang, C., Huang, S., Wang, D., & Wang, Z. (2006). Composition, sources, and potential toxicological significance of PAHs in the surface sediments of the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. Environment International, 32(1), 28–33.
Ricklund, N., Kierkegaard, A., & McLachlan, M. S. (2008). An international survey of decabromodiphenyl ethane (deBDethane) and decabromodiphenyl ether (decaBDE) in sewage sludge samples. Chemosphere, 73(11), 1799–1804.
Sany, S. B. T., Hashim, R., Salleh, A., Safari, O., Mehdinia, A., & Rezayi, M. (2014). Risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the West Port semi-enclosed basin (Malaysia). Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(10), 4319–4332.
Shu, Y. Y., Lao, R. C., Chiu, C. H., & Turle, R. (2000). Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediment reference materials by microwave-assisted extraction. Chemosphere, 41(11), 1709–1716.
Shu, Y. Y., Tey, S. Y., & Wu, D. K. S. (2003). Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in airborne particles using open-vessel focused microwave-assisted extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 495(1–2), 99–108.
Soclo, H. H., Garrigues, P. H., & Ewald, M. (2000). Origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal marine sediments: case studies in Cotonou (Benin) and Aquitaine (France) areas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(5), 387–396.
Sverdrup, L. E., Nielsen, T., & Krogh, P. H. (2002). Soil ecotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in relation to soil sorption, lipophilicity, and water solubility. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(11), 2429–2435.
Svoboda, M. L., Yang, J. J., Falletta, P., & Lee, H. B. (2007). A microwave-assisted extraction method for the determination of synthetic musks in sewage sludge. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 42(1), 11–19.
Villar, P., Callejon, M., Alonso, E., Jimenez, J. C., & Guiraum, A. (2004). Optimization and validation of a new method of analysis for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sewage sludge by liquid chromatography after microwave assisted extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 524(1–2), 295–304.
Wang, W., Meng, B., Lu, X., Liu, Y., & Tao, S. (2007). Extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides from soils: a comparison between Soxhlet extraction, microwave-assisted extraction and accelerated solvent extraction techniques. Analytica Chimica Acta, 602(2), 211–222.
Wenning, R. J., & Ingersoll, C. G. (2002). Summary of the SETAC Pellston workshop on use of sediment quality guidelines and related tools for the assessment of contaminated sediments; 17-22 August 2002; Fairmont, Montana, USA. Pensacola: Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC).
Xu, Y., & Usher, B. (2006). Groundwater pollution in Africa. London: Taylor and Francis Group plc.
Yamada, T. M., Souza, D. A., Morais, C. R., & Mozeto, A. A. (2009). Validation of a method for the analysis of PAHs in bulk lake sediments using GC–MS. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 47(9), 794–799.
Yim, U. H., Hong, S. H., & Shim, W. J. (2007). Distribution and characteristics of PAHs in sediments from the marine environment of Korea. Chemosphere, 68(1), 85–92.
Yohannes, Y. B., Ikenaka, Y., Nakayama, S. M. M., Saengtienchai, A., Watanabe, K., & Ishizuka, M. (2013a). Organochlorine pesticides and heavy metals in fish from Lake Awassa, Ethiopia: insights from stable isotope analysis. Chemosphere, 91(6), 857–863.
Yohannes, Y. B., Ikenaka, Y., Saengtienchai, A., Watanabe, K. P., Nakayama, S. M. M., & Ishizuka, M. (2013b). Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of DDTs and heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Awassa-Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1821-8.
Zhang, Y., Guo, C. S., Xu, J., Tian, Y. Z., Shi, G. L., & Feng, Y. C. (2012). Potential source contributions and risk assessment of PAHs in sediments from Taihu Lake, China: comparison of three receptor models. Water Research, 46(9), 3065–3073.
Acknowledgments
The financial assistances of the Office of Research and Graduate Programs of Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and Mekelle University, Mekelle, Ethiopia, are gratefully acknowledged. Moreover, the Department of Chemistry of Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and Department of Chemistry of Tshwane University of Technology, Pretoria, South Africa, are duly acknowledged for allowing us to use the laboratory facilities.
Compliance with ethical standards
ᅟ
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mekonnen, K.N., Chandravanshi, B.S., Redi-Abshiro, M. et al. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Akaki River, Lake Awassa, and Lake Ziway, Ethiopia. Environ Monit Assess 187, 474 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4669-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4669-1