Abstract
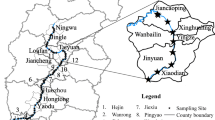
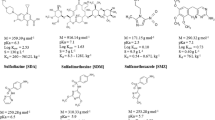
In regions with high livestock densities, the usage of antibiotics and metals for veterinary purposes or as growth promoters poses a risk in manured soils. We investigated to which degree the concentrations and depth distributions of Cu, Zn, Cr and As could be used as a tracer to discover contaminations with sulfonamides, tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones. Besides, we estimated the potential vertical translocation of antibiotics and compared the results to measured data. In the peri-urban region of Beijing, China, soil was sampled from agricultural fields and a dry riverbed contaminated by organic waste disposal. The antibiotic concentrations reached 110 μg kg−1 sulfamethazine, 111 μg kg−1 chlortetracycline and 62 μg kg−1 enrofloxacin in the topsoil of agricultural fields. Intriguingly, total concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cr and As were smaller than 65, 130, 36 and 10 mg kg−1 in surface soil, respectively, therewith fulfilling Chinese quality standards. Correlations between sulfamethazine concentrations and Cu or Zn suggest that in regions with high manure applications, one might use the frequently existing monitoring data for metals to identify potential pollution hotspots for antibiotics in topsoils. In the subsoils, we found sulfamethazine down to ≥2 m depth on agricultural sites and down to ≥4 m depth in the riverbed. As no translocation of metals was observed, subsoil antibiotic contamination could not be predicted from metal data. Nevertheless, sulfonamide stocks in the subsoil could be estimated with an accuracy of 35–200 % from fertilisation data and potential leaching rates. While this may not be sufficient for precise prediction of antibiotic exposure, it may very well be useful for the pre-identification of risk hotspots for subsequent in-depth assessment studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrich, A. P., Kistler, D., & Sigg, L. (2002). Speciation of Cu and Zn in drainage water from agricultural soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 4824–4830.
Aust, M. O., Godlinski, F., Travis, G. R., Hao, X., McAllister, T. A., Leinweber, P., & Thiele-Bruhn, S. (2008). Distribution of sulfamethazine, chlortetracycline and tylosin in manure and soil of Canadian feedlots after subtherapeutic use in cattle. Environmental Pollution, 156, 1243–1251.
Boxall, A. B. A., Blackwell, P. A., Cavallo Kay, P., & Tolls, J. (2002). The sorption and transport of a sulphonamide antibiotic in soil systems. Toxicology Letters, 131, 19–28.
Cang, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, D., & Dong, Y. (2004). Heavy metals pollution in poultry and livestock feeds and manures under intensive farming in Jiangsu Province, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 16, 371–374.
Chen, Y. S., Zhang, H. B., Luo, Y. M., & Song, J. (2012). Occurrence and assessment of veterinary antibiotics in swine manures: a case study in East China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57, 606–614.
Dalkmann, P., Broszat, M., Siebe, C., Willasheck, E., Sakinc, T., Huebner, J., Amelung, W., Grohmann, E., & Siemens, J. (2012). Accumulation of pharmaceuticals, enterococcus, and resistance genes in soils irrigated with wastewater for zero to 100 years in Central Mexico. PLoS ONE, 7, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045397
EMEA (European Medicines Agency). (2008). Revised guideline on the environmental impact assessment for veterinary medicinal products, available at: http://www.emea.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/10/WC500004386.pdf. Accessed 19 Oct 2012.
Fang, S. B., Hu, H., Sun, W. C., & Pan, J. J. (2011). Spatial variations of heavy metals in the soils of vegetable-growing land along urban–rural gradient of Nanjing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2011(8), 1805–1816.
Förster, M., Laabs, V., Lamshöft, M., Pütz, T., & Amelung, W. (2008). Analysis of aged sulfadiazine residues in soils using microwave extraction and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 391, 1029–1038.
Förster, M., Laabs, V., Lambshöft, M., Groeneweg, J., Zuehlke, S., Spiteller, M., Krauss, M., Kaupenjohann, M., & Amelung, W. (2009). Sequestration of manure-applied sulfadiazine residues in soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 1824–1830.
Golet, E. M., Strehler, A., Alder, A. C., & Giger, W. (2002). Determination of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents in sewage sludge and sludge-treated soil using accelerated solvent extraction followed by soild-phase extraction. Analytical Chemistry, 74, 5455–5462.
Golet, E. M., Xifra, I., Siegrist, H., Alder, A. C., & Giger, W. (2003). Environmental exposure assessment of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents from sewage to soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 3243–3249.
Guaita, D. P., Sayen, S., Boudesocque, S., & Guillon, E. (2011). Copper(II) influence on flumequine retention in soils: macroscopic and molecular investigations. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 357, 453–459.
Gupta, G., & Charles, S. (1999). Trace elements in soils fertilized with poultry litter. Poultry Science, 1999(78), 1695–1698.
Heimann, L. (2013). Optimization of nutrient and carbon management of agricultural land in the peri-urban region of Beijing with intensive animal husbandry. Ph.D. dissertation. Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany. Agraria - Studien zur Agrarökologie Vol. 34, Dr. Kovac (publisher), Hamburg, 198 p.
Higgins, A. J. (1984). Land application of sewage sludge with regard to cropping systems and pollution potential. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1984(13), 441–448.
Hirsch, R., Ternes, T., Haberer, K., & Kratz, K. L. (1999). Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. The Science of the Total Environment, 225, 109–118.
Hou, Y., Gao, Z., Heimann, L., Roelcke, M., Ma, W., & Nieder, R. (2012). Nitrogen balances of smallholder farms in major cropping systems in a peri-urban area of Beijing, China. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2012(92), 347–361.
Hu, X., Zhou, Q., & Luo, Y. (2010). Occurrence and source analysis of typical veterinary antibiotics in manure, soil, vegetables and groundwater from organic vegetable bases, northern China. Environmental Pollution, 158, 2992–2998.
Huang, S. W., & Jin, J. Y. (2008). Status of heavy metals in agricultural soils as affected by different patterns of land use. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 139, 317–327.
Huang, X., Liu, C., Li, K., Liu, F., Liao, D., Liu, L., Zhu, G., & Liao, J. (2013). Occurrence and distribution of veterinary antibiotics and tetracycline resistance genes in farmland soils around swine feedlots in Fujian Province, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 20, 9066–9074.
ISO 10693. (1994). Soil quality—determination of carbonate content—volumetric method. Berlin: Beuth.
ISO 11277. (2002). Soil quality—determination of soil particle size distribution in mineral soil material—method by sieving and sedimentation. Berlin: Beuth.
ISO 11466. (1995). Soil quality—extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. Berlin: Beuth.
Jacobsen, A. M., Halling-Sørensen, B., Ingerslev, F., & Hansen, S. H. (2004). Simultaneous extraction of tetracycline, macrolide and sulfonamide antibiotics from agricultural soils using pressurised liquid extraction, followed by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1038, 157–170.
Jia, D. A., Zhou, D. M., Wang, Y. J., Zhu, H. W., & Chen, J. L. (2006). Adsorption and cosorption of Cu(II) and tetracycline on two soils with different characteristics. Geoderma, 146, 224–230.
Kamphuis, B., Jongbloed, A., & van Keulen, H. (2004). Agriculture and water in Shunyi District, Beijing, available at: http://edepot.wur.nl/40559. Accessed 1 Feb 2012.
Kaschl, A., Römheld, V., & Chen, Y. (2002). The influence of soluble organic matter from municipal solid waste compost on trace metal leaching in calcareous soils. The Science of the Total Environment, 291, 45–57.
Kasteel, R., Mboh, C. M., Unold, M., Groeneweg, J., Vanderborght, J., & Vereecken, H. (2010). Transformation and sorption of the veterinary antibiotic sulfadiazine in two soils: a short-term batch study. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 4651–4657.
Kay, P., Blackwell, P. A., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2004). Fate of veterinary antibiotics in a macroporous tile drained clay soil. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23, 1136–1144.
Kay, P., Blackwell, P. A., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2005). A lysimeter experiment to investigate the leaching of veterinary antibiotics through a clay soil and comparison with field data. Environmental Pollution, 134, 333–341.
Li, X., Wu, X., Mo, C., Tai, Y., Huang, X., & Xiang, L. (2011). Investigation of sulfonamide, tetracycline, and quinolone antibiotics in vegetable farmland soil in the Pearls River Delta area, southern China. Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry, 59, 7268–7276.
Luo, L., Ma, Y., Zhang, S., Wei, D., & Zhu, Y. G. (2009). An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 2524–2530.
McBride, M., Richards, B., Steenhuis, T., & Spiers, G. (1999). Long-term leaching of trace elements in a heavily sludge-amended silty clay loam soil. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 164, 613–623.
Menzies, N. W., Donn, M. J., & Kopittke, P. M. (2007). Evaluation of extractants for estimation of the phytoavailable trace metals in soils. Environmental Pollution, 145, 121–130.
Nicholson, F., Chambers, B., Williams, J., & Unwin, R. (1999). Heavy metal contents of livestock feeds and animal manures in England and Wales. Bioresource Technology, 70, 23–31.
Nowara, A., Burhenne, J., & Spiteller, M. (1997). Binding of fluoroquinolone carboxylic acid derivated to clay minerals. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45, 1459–1463.
Ostermann, A., Siemens, J., Welp, G., Xue, Q., Lin, X., Liu, X., & Amelung, W. (2013). Leaching of veterinary antibiotics in calcareous Chinese croplands. Chemosphere, 91, 928–934.
Quevauviller, P., Lachia, M., Barahona, E., Rauret, G., Ure, A., Gomez, A., & Muntau, H. (1996). Interlaboratory comparison of EDTA and DTPA procedures prior to certification of extractable trace elements in calcareous soil. The Science of the Total Environment, 178, 127–132.
Roelcke, M., Heimann, L., Ostermann, A., Hou, Y., Müller-Hansen, K., Lu, H.Y., Knaus, M., Clemens, J., Nieder, R., Goldbach, H., Ma, W.Q., Dong, R.J., Liu, X.J. & Zhang, F.S. (2013). Organic residue management options in an Chinese peri-urban region with high nutrient and pollutant loads, In: Dong, R.J. and Raninger, B. (eds.), Biogas engineering and application, Volume 3, p. 295–309. China Agricultural University Press, Beijing, ISBN: 978-7-5655-0751-9, 361 pp.
Rosendahl, I., Siemens, J., Kindler, R., Groeneweg, J., Zimmermann, J., Czerwinski, S., Lambshoeft, M., Laabs, V., Wilke, B.-M., Vereecken, H., & Amelung, W. (2012). Persistence of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic difloxacin in soil and lacking effects on nitrogen turnover. Journal of Environmental Quality, 41, 1275–1283.
Tai, Y., Mo, C., Li, Y., Wu, X., Zou, X., Gao, P., & Huang, X. (2010). Concentration and distribution of quinolone antibiotics in long-term manure-amended soil. China Environmental Science, 30, 816–821. in Chinese.
Tai, Y., Mo, C., Li, Y., Wu, X., Duan, X., Qu, X., & Huang, X. (2011). Concentrations and distribution of tetracycline antibiotics in vegetable field soil chronically fertilized with manures. Environmental Science, 2011(32), 1182–1187. in Chinese.
Tamtam, F., van Oort, F., Le Bot, B., Dinh, T., Mompelat, S., Chevreuil, M., Lamy, I., & Thiry, M. (2011). Assessing the fate of antibiotic contaminants in metal contaminated soils four years after cessation of long-term waste water irrigation. The Science of the Total Environment, 409, 540–547.
Teng, Y., Ni, S., Wang, J., Zuo, R., & Yang, J. (2010). A geochemical survey of trace elements in agricultural and non-agricultural topsoil in Dexing area, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 104, 118–127.
Thiele-Bruhn, S. (2003). Pharmaceutical antibiotic compounds in soil—a review. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 166, 145–167.
Tong, L., Li, P., Wang, Y., & Zhu, K. (2009). Analysis of veterinary antibiotic residues in swine wastewater and environmental water samples using optimized SPE-LC/MS/MS. Chemosphere, 74, 1090–1097.
Vasudevan, D., Bruland, G. L., Torrance, B. S., Upchurch, V. G., & MacKay, A. A. (2009). PH-dependent ciprofloxacin sorption to soils. Geoderma, 2009(151), 68–76.
Wei, R., Ge, F., Huang, S., Chen, M., & Wang, R. (2011). Occurrence of veterinary antibiotics in animal wastewater and surface water around farms in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere, 2011(82), 1408–1414.
Welp, G., & Brümmer, G. (1999). Adsorption and solubility of ten metals in soil samples of different composition. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 162, 155–161.
WHO (World Health Organization), 2001, Monitoring antimicrobial usage in food animals for the protection of human health, available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2002/WHO_CDS_CSR_EPH_2002.11.pdf. Accessed 28 May 2012.
Wu, L., Pan, X., Chen, L., Huang, Y., Teng, Y., Luo, Y., & Christie, P. (2013). Occurrence and distribution of heavy metals and tetracyclines in agricultural soils after typical land use change in east China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 20, 8342–8354.
Xiong, X., Li, Y., Li, W., Lin, C., Han, W., & Yang, M. (2010). Copper content in animal manures and potential risk of soil copper pollution with animal manure use in agriculture. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 54, 985–990.
Zhang, S., Zhang, F., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Zou, S., & He, X. (2005). Determination and analysis on main harmful composition in excrement of scale livestock and poultry feedlots. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizing Science, 11, 822–829. in Chinese.
Zhang, Z., Sun, K., Gao, B., Zhang, G., Liu, X., & Zhao, Y. (2011). Adsorption of tetracycline on soil and sediment: effects of pH and the presence of Cu(II). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190, 856–862.
Zhao, L. Y., Schulin, R., & Nowack, B. (2009). Cu and Zn mobilisation in soil columns percolated by different irrigation solutions. Environmental Pollution, 157, 823–833.
Zhao, L., Dong, Y. H., & Wang, H. (2010). Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. The Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1069–1075.
Zhu, Y., Johnson, T. A., Su, J., Qiao, M., Guo, G., Steadtfeld, R. D., Hashsham, S. A., & Tiedje, J. M. (2013). Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistant genes in Chinese swine farms. PNAS, 110, 3435–3440.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Hou Yong for his help during field work, the filling in of the questionnaires during the farmers’ survey and their translation. Furthermore, we want to express our gratitude to Manfred Grote and his group, who carried out first orienting tetracycline and fluoroquinolone extractions and measurements of manure samples. Also, we thank Martin Krauss for analysing the concentrations of various sulfonamides in preliminary experiments. The study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (FKZ: 0330847D) and the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) (grant no. 2009DFA32710).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
(PDF 81 kb)
Online Resource 2
(PDF 84 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ostermann, A., Gao, J., Welp, G. et al. Identification of soil contamination hotspots with veterinary antibiotics using heavy metal concentrations and leaching data—a field study in China. Environ Monit Assess 186, 7693–7707 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3960-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3960-x