Abstract
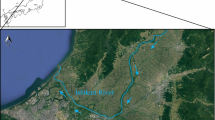
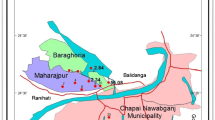
Arsenic (As) mobilization to the groundwater of Brahmaputra floodplains was investigated in Titabor, Jorhat District, located in the North Eastern part of India. The groundwater and the aquifer geochemistry were characterized in the study area. The range of As concentration in the groundwater varies from 10 to 440 μg/l with mean concentration 210 μg/l. The groundwaters are characterized by high dissolved Fe, Mn, and HCO3 − and low concentrations of NO3 − and SO4 2− indicating the reduced conditions prevailing in the groundwater. In order to understand the actual mobilization processes in the area, six core drilling surrounding the two target tube wells (T1 and T2) with high As concentration (three drill-cores surrounds each tube well closely) was done. The sediment was analyzed its chemical, mineralogical, and elemental compositions. A selective sequential extraction suggested that most of the As in the sediment is bound to Fe oxides fractions (32 to 50 %) and the competition for adsorption site by anions (PO4 3−) also accounts to significant fractions of the total arsenic extracted. High variability in the extraction as well as properties of the sediment was observed due to the heterogeneity of the sediment samples with different chemical properties. The SEM and EDX results indicate the presence of Fe, Mn coating along with As for most of the sample, and the presence of As associated minerals were calculated using PHREEQC. The mobilization of As into the groundwater was anticipated to be largely controlled by the reductive dissolution of Fe oxides and partly by the competitive anions viz. PO4 3−.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anawar, H. M., Akai, J., Komaki, K., Terao, H., Yoshioka, T., & Ishizuka, T. (2003). Geochemical occurrences of arsenic in groundwater of Bangladesh: sources and mobilization processes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 77, 109–131.
Anschutz, P., Dedieu, K., Desmazes, F., & Chaillou, G. (2005). Speciation, oxidation state, and reactivity of particulate manganese in marine sediments. Chemical Geology, 218, 265–279.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington, D.C.: American Public Health Association.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Rotterdam: Balkema.
Appelo, C. A. J., Van-Der-Weiden, M. J. J., Tournassat, C., & Charlet, L. (2002). Surface complexation of ferrous iron and carbonate on ferrihydrite and the mobilization of arsenic. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 3096–3103.
Baig, J. A., Kazi, T. G., Arain, M. B., Shah, A. Q., Sarfraz, R. A., Afridi, H. I., et al. (2009). Arsenic fractionation in sediments of different origins using BCR sequential and single extraction methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167, 745–751.
Berg, M., Stengel, C., Trang, P. T. K., Viet, P. H., Sampson, M. L., & Leng, M. (2007). Magnitude of arsenic pollution in the Mekong and Red River Deltas—Cambodia and Vietnam. Science of the Total Environment, 372, 413–425.
Berg, M., Trang, P. T. K., Stengel, C., Buschmann, J., Viet, P. H., Dan, N. V., et al. (2008). Hydrological and sedimentary controls leading to arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Hanoi area, Vietnam: the impact of iron–arsenic ratios, peat, river bank deposits and excessive groundwater abstraction. Chemical Geology, 249, 91–112.
Bhattacharya, P., Chatterjee, D., & Jacks, G. (1997). Occurrence of arsenic contaminated groundwater in alluvial aquifers from Delta plains, Eastern India: options for safe drinking water supply. Water Resources Development, 13, 79–92.
Bhattacharya, P., Jacks, G., Ahmed, K. M., Routh, J., & Khan, A. A. (2002). Arsenic in groundwater of the Bengal delta plain aquifers in Bangladesh. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 69, 538–545.
CGWB-Central Ground Water Board. (2004). Groundwater resources of Assam. Guwahati: CGWB, North East Region, Ministry of Water Resource.
Chakraborti, D., Sengupta, M. K., Rahaman, M. M., Ahamed, S., Chowdhury, U. K., & Hossain, M. A. (2004). Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in the Ganga–Megna–Brahmaputra Plain. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 6, 74–83.
Chakraborti, D., Das, B., & Murrill, M. (2011). Examining India’s groundwater quality management. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 27–33.
Charlet, L., Chakraborty, S., Appelo, C. A. J., Roman-Ross, G., Nath, B., Ansari, A. A., et al. (2007). Chemodynamics of an As “hotspot” in a West Bengal aquifer: a field and reactive transport modeling study. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 1273–1292.
Dean, W. E., Jr. (1974). Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 44, 242–248.
Dixit, S., & Hering, J. G. (2003). Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 4182–4189.
Eiche, E., Neumann, T., Berg, M., Weinman, B., van Geen, A., Norra, S., et al. (2008). Geochemical processes underlying a sharp contrast in groundwater arsenic concentrations in a village on the Red River delta, Vietnam. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 3143–3154.
Favas, P. J. C., Pratas, J., Gomes, M. E. P., & Cala, V. (2011). Selective chemical extraction of heavy metals in tailings and soils contaminated by mining activity: environmental implications. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 111, 160–171.
Goh, K. H., & Lim, T. T. (2004). Geochemistry of inorganic arsenic and selenium in a tropical soil: effect of reaction time, pH, and competitive anions on arsenic and selenium adsorption. Chemosphere, 55, 849–859.
Guo, H. M., Zhang, B., Li, Y., Berner, Z., Tang, X., Norra, S., et al. (2011). Hydrogeological and biogeochemical constrains of arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers from the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Environmental Pollution, 159, 876–883.
Halim, M. A., Majumder, R. K., Nessa, S. A., Hiroshiro, Y., Uddin, M. J., Rahman, S. H., et al. (2009). Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Ganges Delta Plain, Bangladesh. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 1335–1345.
Halim, M. A., Majumder, R. K., Nessa, S. A., Oda, K., Hiroshiro, Y., & Jinno, K. (2010). Arsenic in shallow aquifer in the eastern region of Bangladesh: insights from principal component analysis of groundwater compositions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 161, 453–472.
Harvey, C. F., Swartz, C. H., Badruzzaman, A. B. M., Keon, B. N., Yu, W., Ashraf, A. M., et al. (2002). Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science, 298, 1602–1606.
Harvey, C. F., Swartz, C. H., Badruzzaman, A. B. M., Keon, B. N., Yu, W., & Ali, M. A. (2005). Groundwater arsenic contamination on the Ganges delta: biogeochemistry, hydrology, human perturbations, and human suffering on a large scale. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 337, 285–296.
Hendershot, W. H., Lalande, H., & Duquette, M. (2008). Soil reaction and exchangeable acidity. In M. R. Carter, & E. G. Gregorich (Eds.), Soil sampling and method of analysis. 2nd Edition. Canadian Society of Soil Science. Boca Raton, CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group.
Kazi, T. G., Arain, M. B., Jamali, M. K., Jalbani, N., Afridi, H. I., Sarfraz, R. A., et al. (2009). Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 301–309.
Kirk, M. F., Roden, E. E., Crossey, L. J., Brealey, A. J., & Spilde, M. N. (2010). Experimental analysis of arsenic precipitation during microbial sulfate and iron reduction in model aquifer sediment reactors. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74, 2538–2555.
Lopez, R., Álvarez-Valero, M., Nieto, J., Sáez, R., & Matos, X. (2008). Use of sequential extraction procedure for assessing the environmental impact at regional scale of the São Domingos Mine (Iberian Pyrite Belt). Applied Geochemistry, 23, 3452–3463.
Mahanta, C., Dutta, A., Basu, S., Borah, P., Choudhury, R., Saikia, L., et al. (2010). Groundwater arsenic contamination in the Brahmaputra floodplains: outcome of a comprehensive field investigation in Assam, India. Proc. Of the ASCE - EWRI 3rd International Perspective on Current and Future State of Water Resource & the Environment at IIT Chennai from 5th January–7th January 2010.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1996). Modeling competitive adsorption of arsenate with phosphate and molybdate on oxide minerals. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 60, 121–131.
McArthur, J. M., Banerjee, D. M., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Mishra, R., Purohit, R., Ravenscroft, P., et al. (2004). Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic groundwater: the example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 1255–1293.
McArthur, J. M., Nath, B., Banerjee, D. M., Purohit, R., & Grassineau, N. (2011). Palaeosol control on groundwater flow and pollutant distribution: the example of arsenic. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 1376–1383.
Mulligan, C., Fukue, M., & Sato, Y. (2010). Sediments contamination and sustainable remediation. New York: CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group.
Nath, B., Berner, Z., Chatterjee, D., Basu Mallik, S., & Stueben, D. (2008). Mobility of arsenic in West Bengal aquifers conducting low and high groundwater arsenic Part II: comparative geochemical profile and leaching study. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 996–1011.
Nickson, R. T., McArthur, J. M., Burgess, W. G., Ahmed, K. M., Ravenscroft, P., & Rahman, M. (1998). Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater. Nature, 395, 338.
Nickson, R. T., McArthur, J. M., Ravenscroft, P., Burgess, W. G., & Ahmed, K. M. (2000). Mechanism of arsenic release to groundwater, Bangladesh and West Bengal. Applied Geochemistry, 15, 403–413.
Pal, T., Mukherjee, P. K., & Sengupte, S. (2002). Nature of arsenic pollutants in groundwater of Bengal Delta—a case study from Baruipur area, West Bengal, India. Current Science, 82, 554–561.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259.
Polizzotto, M. L., Kocar, B. D., Benner, S. G., Sampson, M., & Fendorf, S. (2008). Near surface wetland sediments as a source of arsenic release to ground water in Asia. Nature, 454, 505–508.
Postma, D., Larsen, F., Minh Hue, N. T., Thanh Duc, M., Viet, P. H., Nhan, P. Q., et al. (2007). Arsenic in groundwater of the Red River floodplain, Vietnam: controlling geochemical processes and reactive transport modeling. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71, 5054–5071.
Postma, D., Jessen, S., Minh Hue, N. T., Duc, M. T., Koch, C. B., Viet, P. H., et al. (2010). Mobilization of arsenic and iron from Red River floodplains sediments, Vietnam. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74, 3367–3381.
Sailo, L., & Mahanta, C. (2013). Hydrogeochemical factors affecting the mobilization of As into the groundwater of Brahmaputra alluvial plains of Assam, Northeast India. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 15, 1775.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Stollenwerk, K. G., Breit, G. N., Welch, A. H., Yount, J. C., Whitney, J. W., Foster, A. L., et al. (2007). Arsenic attenuation by oxidized aquifer sediments in Bangladesh. Science of the Total Environment, 379, 133–150.
Swartz, C. H., Blute, N. K., Badruzzman, B., Ali, A., Brabander, D., Jay, J., et al. (2004). Mobility of arsenic in a Bangladesh aquifer: inferences from geochemical profiles, leaching data, and mineralogical characterization. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68, 539–4557.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extractions for separation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry 51, 844–851.
Wang, S., & Mullingan, C. N. (2008). Speciation and surface structure of inorganic arsenic in solid phases: a review. Environment International, 34, 867–879.
Wenzel, W. W., Kirchbaumer, N., Prohaska, T., Stingeder, G., Lombic, E., & Adriano, D. C. (2001). Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure. Analytica Chimica Acta, 436, 309–323.
Zheng, Y., van Geen, A., Stute, M., Dhar, R., Mo, Z., Cheng, Z., et al. (2005). Geochemical and hydrogeological contrasts between shallow and deeper aquifers in two villages of Araihazar, Bangladesh: implications for deeper aquifers as drinking water sources. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, 5203–5218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Total metal concentration in the sediments analyzed using EPA-3052 digestion procedure for copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), and chromium (Cr).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sailo, L., Mahanta, C. Arsenic mobilization in the Brahmaputra plains of Assam: groundwater and sedimentary controls. Environ Monit Assess 186, 6805–6820 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3890-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3890-7