Abstract
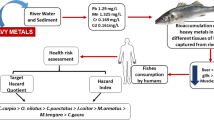
Monitoring of heavy metals was conducted in the Yamuna River considering bioaccumulation factor, exposure concentration, and human health implications which showed contamination levels of copper (Cu), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni), and chromium (Cr) and their dispersion patterns along the river. Largest concentration of Pb in river water was 392 μg L−1; Cu was 392 μg L−1 at the extreme downstream, Allahabad and Ni was 146 μg L−1 at midstream, Agra. Largest concentration of Cu was 617 μg kg−1, Ni 1,621 μg kg−1 at midstream while Pb was 1,214 μg kg−1 at Allahabad in surface sediment. The bioconcentration of Cu, Pb, Ni, and Cr was observed where the largest accumulation of Pb was 2.29 μg kg−1 in Oreochromis niloticus and 1.55 μg kg−1 in Cyprinus carpio invaded at Allahabad while largest concentration of Ni was 174 μg kg−1 in O. niloticus and 124 μg kg−1 in C. carpio in the midstream of the river. The calculated values of hazard index (HI) for Pb was found more than one which indicated human health concern. Carcinogenic risk value for Ni was again high i.e., 17.02 × 10−4 which was larger than all other metals studied. The results of this study indicated bioconcentration in fish due to their exposures to heavy metals from different routes which had human health risk implications. Thus, regular environmental monitoring of heavy metal contamination in fish is advocated for assessing food safety since health risk may be associated with the consumption of fish contaminated through exposure to a degraded environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, C. R., Johnson, A. R., & Parris, L. (2006). A framework for spatial risk assessments: potential impacts of nonindigenous invasive species on native species. Ecology and Society, 11(1), 39–42.
Allison, J.D. (2005).EPA/600/R05/074July2005 http://www.epa.gov/athens/publications/reports/Ambrose600R05074PartitionCoefficients.pdf. Accessed 10 Dec 2012.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water & wastewater. In: Mary Ann H. Franson (Eds.) American Water Works Association American Public Health Association.
Batayneh, A. T. (2010). Heavy metals in water springs of the Yarmouk Basin, North Jordan and their potentiality in health risk assessment International. Journal of the Physical Sciences, 5(7), 997–1003.
Bhargawa, D.S. (2006). Revival of Mathura's ailing Yamuna river. Environmentalists 26,111–122 Springer.
Bhattacharyya, S., Chaudhuri, P., Dutta, S., & Santra, S. C. (2010). Assessment of total mercury level in fish collected from east Calcutta wetlands and Titagarh sewage fed aquaculture in West Bengal, India. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 84(5), 618–622.
Canli, M., & Atli, G. (2003). The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environmental Pollution, 121(1), 129–136.
DeForest, D. K., Brix, K. V., & Adamsc, W. J. (2007). Assessing metal bioaccumulation in aquatic environments: the inverse relationship between bioaccumulation factors, trophic transfer factors and exposure concentration. Aquatic Toxicology, 84, 236–246.
Emmanuel, E., Pierre, G. M., & Perrodin, Y. (2009). Groundwater contamination by microbiological and chemical substances released from hospital wastewater: health risk assessment for drinking water consumers. Environment International, 35(4), 718–726.
Fiore, B. J., Anderson, H. A., Hanrahan, L. P., Olson, L. J., & Sonzogni, W. L. (1989). Sport fish consumption and body burden levels of chlorinated hydrocarbons. A study of Wisconsin anglers. Archives of Environmental Health, 44, 82–88.
Gale, N. W., Dominguez, M. G., Noguera, I., Pan, L., Hughes, V., Valenzuela, D. M., et al. (2004). Haploinsufficiency of delta-like 4 ligand results in embryonic lethality due to major defects in arterial and vascular development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(45), 15949–15954.
Harma, J. A., Jean-Paul, R., Edwin, J. C. M., Jurian, A. H., & Jos, C. S. K. (1999). Human health risk assessment in relation to environmental pollution of two artificial fresh water lake in the Netherlands. Environmental Health Perspectives, 107, 27–35.
Hawley, J. K. (1985). Assessment of health risk from exposure to contaminated soil. Risk Analysis, 5, 289–302.
Imar, M. R., & Carlose, J. R. S. (2011). Metal level in fish captured in Puerto Rico and estimation of risk from fish consumption. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60, 132–144.
Kazi, T. G., Jalbani, N., Baig, J. A., Kandhro, G. A., Afridi, H. I., Arain, B. M., et al. (2009). Assessment of toxic metals in raw and processed milk samples using electrothermal atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47, 2163–2169.
Kolluru, R. V., Bartell, S. M., Pitblado, R. M., & Stricoff, R. S. (1996). Risk assessment and management handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Kumar, B., & Mukherjee, D. P. (2011). Assessment of human health risk for arsenic, copper, nickel, mercury and zinc in fish collected from Tropical Wetlands in India. Advances in Life Science and Technology, 2, 1–13.
Lin, M. C., Cheng, H. H., Lin, H. Y., Chen, Y. C., Chen, Y. P., Liao, C. M., et al. (2004). Arsenic accumulation and acute toxicity in milkfish (Chanos chanos) from Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 248–254.
Ma, H. W., Hung, M. L., & Chen, P. C. (2007). A systemic health risk assessment for the chromium cycle in Taiwan. Environment International, 33(2), 206–218.
Mason, C. F. (1987). A survey of mercury, lead and cadmium in muscle of British fresh water fish. Chemosphere, 16, 901–906.
McGeer, J. C., Brix, K. V., Skeaf, J. M., DeForest, D. K., Brigham, S. I., Adams, W. J., et al. (2003). Inverse relationship between bioconcentration factor and exposure concentration for metals: implications for hazard assessment of metals in the aquatic environment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22(5), 1017–1037.
Michael, A. M., Matthew, R. M., & Michael, F. E. W. (2011). Elevated levels of metals and organic pollutants in fish and clams in the Cape Fear River watershed. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 61, 461–471.
Mishra, A. K. (2010). A river about to die: Yamuna. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2(4), 489–500.
Namdev, D. K., & Singh, A. K. (2012). Studies on physico-chemical properties of water in Yamuna River at Hamirpur (U.P.) with special reference to occurrence of lead (Pb). International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology, 1(3), 215–216.
Nayaka, B. M. S., Ramakrishna, S., Jayaprakash, M. R., & Delvi. (2009). Impact of heavy metals on water, fish (Cyprinus carpio) and sediments from a water tank at Tumkur, India. Oceanological and Hydrobiological Studies, 38(2), 18–28.
Oost, R. V., Jonny Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. E. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13, 57–149.
Ozden, O. (2010). Micro, macro mineral and proximate composition of Atlantic bonito and horse mackerel: a monthly differentiation. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 45, 578–586.
Rejomon, G., Nair, M., & Joseph, T. (2010). Trace metal dynamics in fishes from the southwest coast of India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 167, 243–255.
Riza. (1989). The possibility for surface water organism to survive. Rpt. no 89016a. Lelystad, The Netherlands: The Institute of Water Management and Waste Water Treatment.
Sin, S. N., Chua, H., Lo, W., & Ng, L. M. (2001). Assessment of heavy metal cations in sediments of Shing Mun River, Hong Kong. Environment International, 26, 297–301.
Singare, P. U., Mishra, R. M., & Trivedi, M. P. (2012). Heavy metal pollution in Mithi River of Mumbai. Frontiers in Science, 2(3), 28–36.
Singh, A. K., & Lakara, W. S. (2011). Risk and benefit assessment of alien fish species of the aquaculture and trade into India. Reviews in Aquaculture, 3, 3–18.
Singh, A. K., Srivastava, S. C., Ansari, A., Kumar, D., & Singh, R. (2012). Environmental monitoring and health risk assessment of African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) cultured in rural ponds, India. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 89, 1142–1147.
Singh, A. K., Kumar, D., Srivastava, S. C., Ansari, A., Jena, J. K., & Sarkar, U. K. (2013). Invasion and impacts of alien fish species in the Ganga river, India. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 16(4), 1–7.
Upadhyay, A., Shekhar, C., Ojha, P., & Singh, V. P. (2011). The Yamuna River Basin: Water Resources and Environment. Water science and Technology, Springer.
USEPA. (1998). Guidelines for ecological risk assessment http://www.epa.gov/raf/publications/pdfs/ECOTXTBX.PDF Accessed on 10 Dec 2012.
USEPA, (2004). Issue paper on the human health effects of metals. Available at: http://www.epa.gov/raf/publications/pdfs/HUMANHEALTHEFFECTS81904.PDF Accessed 10 Dec 2012.
USEPA, (2011). Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition http://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recordisplay.cfm?deid=236252 Accessed on 10 Dec 2012.
Van Wijnen, J. H. (1982). Health risk assessment in relation to soil pollution. T Soc Geneesk, 60, 555–559.
Veerkamp W, & Ten Berge W. (1990). Hazard assessment of chemical contaminants in soil. ECETOC Technical Rpt 40. Brussels:European Chemical Industry Ecology and Toxicology Centre.
WHO (2011). Guidelines for drinking water quality, 4th Edns. WHO press, 564.
Yehia, H. M., & Sebaee, E. S. (2012). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in water, sediment and fish (Oreochromis niloticus and Clarias anguillaris), in Rosetta branch of the River Nile, Egypt. African Journal of Biotechnology, 11(77), 14204–14216.
Yongli, L., Jingling, L., Zhiguo, C., Chao, L., & Zhifeng, Y. (2010). Spatial distribution and health risk of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the water of the Luanhe River Basin, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 163, 1–13.
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Dr. J.K. Jena, Director NBFGR for his encouragements and consistent support. We thankfully acknowledge the financial support of the Uttar Pradesh Biodiversity Board, Lucknow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.K., Srivastava, S.C., Verma, P. et al. Hazard assessment of metals in invasive fish species of the Yamuna River, India in relation to bioaccumulation factor and exposure concentration for human health implications. Environ Monit Assess 186, 3823–3836 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3660-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3660-6