Abstract
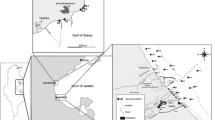
The response of benthic foraminiferal assemblages to trace element pollution in the marine sediments of the Gulf of Milazzo (north-eastern Sicily) was investigated. Since the 1960s, this coastal area has been a preferred site for the development of two small marinas and a commercial harbour as well as for heavy industry. Forty samples collected in the uppermost 3–4 cm of an undisturbed layer of sediment in the littoral environment were used for this benthic foraminiferal analysis. The enrichment factors (EFs) of selected trace elements (As, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) were also calculated. Changes both in benthic foraminiferal assemblages and in some trace elements concentrations have provided evidence that the gulf’s littoral zone can be subdivided into three sectors characterised by environmental changes in the marine ecosystem. In the sector unpolluted, close to the Milazzo Cape, foraminiferal assemblages exhibit high values of species richness and foraminiferal density while trace element concentrations and their EFs are very low. Here, the highest densities of Miliolids and epiphytic species are present. On the contrary, in the sector polluted, from the marinas to the crude oil refinery, foraminiferal density and species diversity are low, and assemblages are dominated, albeit with very low densities, by species that tolerate stressed environmental conditions, such as LOFAs, agglutinants and Ammonia spp. Here, the highest trace elements concentrations of Pb, Zn and Cu and related EFs were detected. Eastwards, in the sector moderately polluted, foraminiferal populations are quite poor. They are characterised by low values of species richness and foraminiferal densities, nevertheless trace element concentrations become lower than in the other sectors and their EFs are often below 1. Deformed foraminifera, with percentages up to 7.14 %, were found in all three of the sectors. Differences in benthic foraminiferal assemblages, coupled with results from statistical analysis, indicate that anthropogenic trace element pollution could be considered as one of the most important causes of the modifications of foraminiferal assemblages in the study area.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alagarsamy, R., & Zhang, J. (2010). Geochemical characterization of major and trace elements in the coastal sediments of India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 161, 161–176.
Alve, E. (1991). Benthic foraminifera in sediment cores reflecting heavy metal pollution in Sørfjord, Western Norway. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 21, 1–19.
Alve, E., & Nagy, J. (1986). Estuarine foraminiferal distribution in Sandebukta, a branch of the Oslo Fjord. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 16, 261–284.
Amodio-Morelli, L., Bonardi, G., Colonna, V., Dietrich, D., Giunta, G., Ippolito, F., et al. (1976). L’Arco Calabro-Peloritano nell’orogene Appenninico-Maghrebide. Memorie della Società Geologica Italiana, 17, 1–60.
Armynot du Châtelet, E. A., Debenay, J. P., & Soulard, R. (2004). Foraminiferal proxies for pollution monitoring in moderately polluted harbors. Environmental Pollution, 127, 27–40.
Bernhard, J. M. (2000). Distinguishing live from dead foraminifera: methods review and proper applications. Micropaleontology, 46, 38–46.
Bonardi, G., Cavazza, W., Perrone, V., & Rossi, S. (2001). Calabria-Peloritani terrane and northern Ionian Sea. In: Vai, G.B., Martini, P.I. (Eds.). Anatomy of an orogen: the Apennines and the adjacent Mediterranean basins (pp. 287–306). Norwell: Kluwer Academic
Carral, E., Villares, R., Puente, X., & Carballeira, A. (1995). Influence of watershed lithology on heavy metal levels in estuarine sediments and organisms in Galicia (North-West Spain). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 30, 604–608.
Caruso, A., Cosentino, C., Tranchina, L., & Brai, M. (2011). Response of benthic foraminifera to heavy metal contamination in marine sediments (Sicilian coasts, Mediterranean Sea). Chemistry and Ecology, 27, 9–30.
Cearreta, A., Irabien, M. J., Leorri, E., Yusta, I., Croudace, I. W., & Cundy, A. B. (2000). Recent anthropogenic impacts on the Bilbao estuary, Northern Spain: geochemical and microfaunal evidence. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 50, 571–592.
Chatterjee, A., & Banerjee, R. N. (1999). Determination of lead and other metals in a residential area of greater Calcutta. The Science of the Total Environment, 227, 175–185.
Cimerman, F., & Langer, M. R. (1991). Mediterranean foraminifera. Ljubljana: Slovenska Akademija Znanosti in Umetnosti.
Coccioni, R. (2000). Benthic foraminifera as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution—a case study from the Goro Lagoon (Italy). In R. E. Martin (Ed.), Environmental micropaleontology (pp. 71–103). New York: Kluwer Academic.
Daskalakis, K. D., & O’Connor, T. P. (1995). Normalization and elemental sediment contamination in the coastal US. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 470–477.
Debenay, J. P., Della Patrona, L., Herbland, A., & Goguenheim, H. (2009). Colonization of coastal environments by Foraminifera: insight from shrimp ponds in New Caledonia. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 39, 249–266.
Decembrini F., Azzaro F., Galletta M., Raffa F. (2004). Short-term changes of hydrobiological features in the Gulf of Milazzo (Tyrrhenian Sicily). Rapp. 511 Comm. int. Mer Médit., 37, 511.
Di Leonardo, R., Bellanca, A., Capotondi, L., Cundy, A., & Neri, R. (2007). Possible impacts of Hg and PAH contamination on benthic foraminiferal assemblages: an example from the Sicilian coast, central Mediterranean. Science of the Total Environment, 388, 168–183.
Di Leonardo, R., Adelfio, G., Bellanca, A., & Chiodi, M. (2013). Multivariate statistical study of trace elements in the offshore sediments of Augusta (SE Sicily). Journal of Sea Research (in press)
Ernst, S. R., Morvan, J., Geslin, E., Le Bihan, A., & Jorissen, F. J. (2006). Benthic foraminiferal response to experimentally induced Erika oil pollution. Marine Micropaleontology, 61, 76–93.
Ferraro, L., Sprovieri, M., Alberico, I., Lirer, F., Prevedello, L., & Marsella, E. (2006). Benthic foraminifera and heavy metals distribution: a case study from the Naples Harbour (Tyrrhenian Sea, Southern Italy). Environmental Pollution, 142, 274–287.
Ferraro, L., Sammartino, S., Feo, M. L., Rumolo, P., Salvagio Manta, D., Marsella, E., et al. (2009). Utility of benthic foraminifera for biomonitorig of contaminant in marine sediments: a case study from the Naples harbour (Southern Italy). Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11, 1226–1235.
Fisher, R. A., Corbet, A. S., & Williams, C. B. (1943). The relationship between the number of species and the number of individuals in a random sample of an animal population. Journal of Animal Ecology, 12, 42–58.
Frontalini, F., & Coccioni, R. (2008). Benthic foraminifera for heavy metal pollution monitoring: a case study from the central Adriatic Sea coast of Italy. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 76, 404–417.
Frontalini, F., Buosi, C., Da Pelo, S., Coccioni, R., Cherchi, A., & Bucci, C. (2009). Benthic foraminifera as bio-indicators of trace element pollution in the heavily contaminated Santa Gilla lagoon (Cagliari, Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 858–877.
Frontalini, F., Armynot du Châtelet, E., Debenay, J.P., Coccioni, R., & Bancalà, G. (2010). Benthic foraminifera in coastal lagoons: Distributional patterns and biomonitoring implications. In: Friedman, A.G. (Ed.). Lagoons: Biology, Management and Environmental Impact (pp. 1–34). Hauppauge: Nova Publishers
Gerardi, F., Smedile, A., Pirrotta, C., Barbano, M. S., De Martini, P. M., Pinzi, S., et al. (2012). Geological record of tsunami inundations in Pantano Morghella (south-eastern Sicily) both from near and far-field sources. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 12(1185–1200), 2012. doi:10.5194/nhess-12-1185-2012.
Geslin, E., Debenay, J. P., Duleba, W., & Bonetti, C. (2002). Morphological abnormalities of foraminiferal tests in Brazilian environments: comparison between polluted and non-polluted areas. Marine Micropaleontology, 45, 151–168.
Goineau, A., Fontanier, C., Jorissen, F. J., Lansard, B., Buscail, R., Mouret, A., et al. (2011). Live (stained) benthic foraminifera from the Rhône prodelta (Gulf of Lion, NW Mediterranean): environmental controls on a river-dominated shelf. Journal of Sea Research, 65, 58–75.
Gustafsson, M., Dahllfà, I., Blanck, H., Hall, P., Molander, S., & Nordberg, K. (2000). Benthic foraminiferal tolerance to tri-n-butyltin (TBT) pollution in an experimental mesocosm. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(12), 1072–1075.
Hallock, P. (1999). Symbiont bearing foraminifera. In B. K. Sen Gupta (Ed.), Modern Foraminifera (pp. 123–139). London: Kluwer Academic.
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D. A. T., & Ryan, P. D. (2001). PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica, 4, 1–9.
Hayward, B. W., Holzmann, M., Grenfell, H. R., Pawlowski, J., & Triggs, C. M. (2004). Morphological distinction of molecular types in Ammonia towards a taxonomic revision of the world’s most commonly misidentified foraminifera. Marine Micropaleontology, 50, 237–271.
Insinga, D., Calvert, A.T., Lanphere, M.A., Morra, V., Perrotta, A., Sacchi, M., Scarpati, C., Saburomaru, J., and Fedele, L., (2006). The Late-Holocene evolution of the Miseno area (southwestern Campi Flegrei) as inferred by stratigraphy, petrochemistry and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology. In: B. De Vivo (Ed.), Volcanism in the Campania Plain: Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei and Ignimbrites (pp. 97–124). Amsterdam: Elsevier
Jorissen, F. J. (1988). Benthic Foraminifera from the Adriatic Sea; principles of phenotypic variation. Utrecht Micropaleontological Bulletin, 37, 1–174.
Langer, M. R. (1993). Epiphytic foraminifera. Marine Micropaleontology, 20, 235–265.
Le Cadre, V., & Debenay, J. P. (2006). Morphological and cytological responses of Ammonia (foraminifera) to copper contamination: implication for the use of foraminifera as bioindicators of pollution. Environmental Pollution, 143, 304–317.
Lee, J. J., & Anderson, O. R. (1991). Biology of Foraminifera. London: Academic.
Loeblich, A. R., & Tappan, H., Jr. (1987). Foraminiferal genera and their classification vol. 4. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Martinez-Colon, M., Hallock, P., & Green-Ruiz, C. (2009). Strategies for using shallow-water benthic foraminifers as bioindicators of potentially toxic elements: a review. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 39, 278–299.
Messina, A., Somma, R., Macaione, E., Carbone, G., & Careri, G. (2004). Peloritani continental crust composition (Southern Italy): geological and petrochemical evidence. Bollettino della Societa Geologica Italiana, 123, 405–441.
Morford, J. L., Russell, A. D., & Emerson, S. (2001). Trace metal evidence for changes in the redox environment associated with the transition from terrigenous clay to diatomaceous sediment, Saanlich Inlet, BC. Marine Geology, 174, 355–369.
Morvan, J., Debenay, J. P., Jorissen, F., Redois, F., Bénéteau, E., Delplancke, M., et al. (2006). Patchiness and life cycle of intertidal foraminifera: implication for environmental and paleoenvironmental interpretation. Marine Micropaleontology, 61, 131–154.
Murray, J. W. (1973). Distribution and ecology of living benthic foraminiferids. London: Heinemann Educational Books.
Murray, J. W. (2000). The enigma of the continued use of total assemblages in ecological studies of benthic foraminifera. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 30, 244–245.
Parker, W. C., & Arnold, A. J. (1999). Quantitative methods of data analysis in foraminiferal ecology. In B. K. Sen Gupta (Ed.), Modern Foraminifera (pp. 71–89). London: Kluwer Academic.
Pepe, F., Scopelliti, G., Di Leonardo, R., & Ferruzza, G. (2010). Granulometry, mineralogy and trace elements of marine sediments from the Gulf of Milazzo (NE Sicily): evaluation of anthropogenic impact. Italian Journal of Geoscience, 129, 385–394.
Polovodova, I., & Schönfeld, J. (2008). Foraminiferal test abonormalities in the western Baltic Sea. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 38, 318–336.
Sacchi, M., Pepe, F., Corradino, M., Insinga, D., Molisso F. (2013) Architecture and 15 kyr to present evolution of the Pozzuoli Bay: a perspective on the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff caldera off the Campi Flegrei, Eastern Tyrrhenian Margin. Marine Geology (in press)
Samir, A. M., & El-Din, A. B. (2001). Benthic foraminiferal assemblages and morphological abnormalities as pollution proxies in two Egyptian bays. Marine Micropaleontology, 41, 193–227.
Saraswat, R., Kurtarkar, S. R., Mazumder, A., & Nigam, R. (2004). Foraminifers as indicators of marine pollution: a culture experiment with Rosalina leei. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 91–96.
Scott, D. B., Tobin, R., Williamson, M., Medioli, F. S., Latimer, J. S., Boothman, W. A., et al. (2005). Pollution monitoring in two North American estuaries: historical reconstruction using benthic foraminifera. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 35, 65–82.
Sen Gupta, B. K. (1999a). In B. K. Sen Gupta (Ed.), Modern Foraminifera. London: Kluwer Academic.
Sen Gupta, B. K. (1999b). Systematics of Modern Foraminifera. In B. K. Sen Gupta (Ed.), Modern Foraminifera. London: Kluwer Academic.
Sgarrella, F., & Montcharmont Zei, M. (1993). Benthic Foraminifera of the Gulf of Naples (Italy): systematics and autoecology. Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana, 32, 145–264.
Sharifi, A. R., Croudace, T. W., & Austin, R. L. (1991). Benthonic foraminiferids as pollution indicators in Southampton water, Southern England, UK. Journal of Micropaleontology, 10, 109–113.
Shepard, F. P. (1954). Nomenclature based on sand, silt, clay ratios. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 24, 151–158.
Smart, C. (2002). Environmental applications of deep-sea benthic foraminifera. Quaternary environmental micropaleontology. In: Haslett SK (Ed.), Quaternary Environmental Micropaleontology (pp 14–58). London: Arnold Publisher
Thibodeau, B., deVernal, A., & Mucci, A. (2006). Recent eutrophication and consequent hypoxia in the bottom waters of the Lower St. Lawrence Estuary: micropaleontological and geochemical evidence. Marine Geology, 231, 37–50.
Tranchida, G., Bellanca, A., Angelone, M., Bonanno, A., Langone, L., Mazzola, S., et al. (2010). Chronological records of metal deposition in sediments from the Strait of Sicily, central Mediterranean: assessing natural fluxes and anthropogenic alteration. Journal of Marine System, 79, 157–172.
Tranchina, L., Basile, S., Brai, M., Caruso, A., Cosentino, C., & Miccichè, S. (2008). Distribution of heavy metals in marine sediments of Palermo Gulf (Sicily, Italy). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 191, 245–256.
Valenti, D., Tranchina, L., Brai, M., Caruso, A., Cosentino, C., & Spagnolo, B. (2008). Environmental metal pollution considered as noise: effects on the spatial distribution of benthic foraminifera in two coastal marine areas of Sicily (Southern Italy). Ecological Modelling, 213, 449–462.
Yanko, V., & Flexer, A. (1991). Foraminiferal benthonic assemblages as indicators of pollution (an example of Northwestern shelf of the Black Sea). In: Proceedings of Third Annual Symposium on the Mediterranean Margin of Israel, Institute Oceanography and Limnology, Haifa, Israel, Abstract Volume, 5 pp.
Yanko, V., Kronfeld, J., & Flexer, A. (1994). Response of benthic foraminifera to various pollution sources: implications for pollution monitoring. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 24, 1–17.
Yanko, V., Ahmad, M., & Kaminski, M. (1998). Morphological deformities of benthic foraminiferal tests in response to pollution by heavy metals: implications for pollution monitoring. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 28, 177–200.
Yanko, V., Arnold, A. J., & Parker, W. C. (1999). Effects of marine pollution on benthic foraminifera. In B. K. Sen Gupta (Ed.), Modern Foraminifera (pp. 217–235). London: Kluwer Academic.
Yawar, W., Naeem, K., Akhter, P., Rehana, I., & Saeed, M. (2010). Assessment of three digestion procedures for Zn contents in Pakistani soil by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 14, 125–129.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Cassandra Funsten for reviewing the text's English. We are very grateful to the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. The research was funded by MIUR grants n. 2010RMTLYR_001 (A. Caruso team leader) and by grants from F. Pepe.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cosentino, C., Pepe, F., Scopelliti, G. et al. Benthic foraminiferal response to trace element pollution—the case study of the Gulf of Milazzo, NE Sicily (Central Mediterranean Sea). Environ Monit Assess 185, 8777–8802 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3292-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3292-2