Abstract
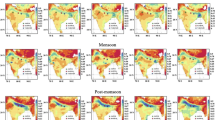
Satellite-retrieved data on aerosol optical depth (AOD) and Ångström exponent (AE) using a moderate resolution imaging spectrometer (MODIS) were used to analyze large-scale distributions of atmospheric aerosols in East Asia. AOD was relatively high in March (0.44 ± 0.25) and low in September (0.24 ± 0.21) in the East Asian region in 2009. Sandstorms originating from the deserts and dry areas in northern China and Mongolia were transported on a massive scale during the springtime, thus contributing to the high AOD in East Asia. However, whereas PM10 with diameters ≤10 μm was the highest in February at Anmyon, Cheongwon, and Ulleung, located leeward about halfway through the Korean Peninsula, AOD rose to its highest in May. The growth of hygroscopic aerosols attendant on increases in relative humidity prior to the Asian monsoon season contributed to a high AOD level in May. AE typically appears at high levels (1.30 ± 0.37) in August due to anthropogenic aerosols originating from the industrial areas in eastern China, while AOD stays low in summer due to the removal process caused by rainfall. The linear correlation coefficients of the MODIS AOD and ground-based mass concentrations of PM10 at Anmyon, Cheongwon, and Ulleung were measured at 0.4~0.6. Four cases (6 days) of mineral dustfall from sandstorms and six cases (12 days) of anthropogenically polluted particles were observed in the central area of the Korean Peninsula in 2009. PM10 mass concentrations increased at both Anmyon and Cheongwon in the cases of mineral dustfall and anthropogenically polluted particles. Cases of dustfall from sandstorms and anthropogenic polluted particles, with increasing PM10 mass concentrations, showed higher AOD values in the Yellow Sea region.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acker, J. G., & Leptoukh, G. (2007). Online analysis enhances use of NASA earth science data. Eos, Transactions of American Geophysical Union, 88, 14–17.
Al-Saadi, J., Szykman, J., Pierce, R. B., Kittaka, C., Neil, D., Chu, D. A., Remer, L., Gumley, L., Prins, E., Weinstock, L., MacDonald, C., Wayland, R., Dimmick, F., & Fishman, J. (2005). Improving national air quality forecasts with satellite aerosol observations. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 86, 1249–1261.
Chan, C. K., & Yao, X. (2008). Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmospheric Environment, 42, 1–42.
Chu, D. A., Kaufman, Y. J., Ichoku, C., Remer, L. A., Tanre, D., & Holben, B. N. (2002). Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth retrieval over land. Geophysical Research Letters, 29, 8007. doi:10.1029/2001GL013205.
Chu, D. A., Kaufman, Y. J., Zibordi, G., Cherm, J. D., Mao, J., Li, C., & Holben, N. (2003). Global monitoring of air pollution over the land from the Earth observing system-terra moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). Journal of Geophysical Research, 108, 4661. doi:10.1029/2002JD003179.
Chung, Y. S., & Le, H. V. (1984). Detection of forest-fire smoke plumes by satellite image. Atmospheric Environment, 18, 2143–2151.
Chung, Y. S., Kim, H. S., Jugder, D., Natsagdorj, L., & Chen, S. J. (2003). On sand and duststorms and associated significant dustfall observed in Chongju-Cheongwon, Korea during 1997–2000. Water, Air and Soil Pollution: Focus, 3, 5–19.
Chung, Y. S., & Kim, H. S. (2008). Observations of massive-air pollution transport and associated air quality in the Yellow Sea region. International Journal Air Quality, Atmosphere and Health, 1, 69–70.
Engel-Cox, J. A., Hoff, R. M., & Haymet, D. J. (2004). Recommendations on the use of satellite remote sensing data for urban air quality. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 54, 1306–1371.
Herman, J. R., Bhartia, P. K., Torres, O., Hsu, C., Seftor, C., & Celarier, E. (1997). Global distribution of UV-absorbing aerosols from Nimbus7/TOMS data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102, 16911–16922.
Kim, S. W., Yoon, S. C., Kim, J., & Kim, S. Y. (2007). Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over East Asia determined from multi-year MODIS, LIDAR, and AERONET Sun/sky radiometer measurements. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 1634–1651.
Kim, H. S., & Chung, Y. S. (2008). Satellite and ground observations for large-scale air pollution transport in the Yellow Sea Region. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 60, 103–116.
Kim, Y. K., Song, S. K., Lee, H. W., Kim, C. H., & Oh, I. B. (2006). Characteristics of Asian dust transport based on synoptic meteorological analysis over Korea. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 56, 306–316.
Kurosaki, Y., & Mikami, M. (2003). Recent frequent dust events and their relation to surface wind in East Asia. Geophysical Research Letters, 30, 1736–1739.
Lee, D. H., Lee, K. H., & Kim, Y. J. (2006). Application of MODIS aerosol data for aerosol type classification. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, 22, 495–505.
Lee, J. H., Kim, J. H., Lee, H. C., & Takemura, T. (2007). Classification of aerosol type from MODIS and OMI over East Asia. Journal of the Korean Meteorological Society, 43, 343–357.
Li, J., Zhuang, G., Huang, K., Lin, Y., Xu, C., & Yu, S. (2007). Characteristics and sources of air-born particulate in Urumqi, China, the upstream area of Asia dust. Atmospheric Environment, 42, 776–787.
Liu, Y., Park, R. J., Jacob, D. J., Li, Q., Kilaru, V., & Samat, J. A. (2004). Mapping annual mean ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using Multi-angle Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical thickness over the contiguous United Sates. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, D22206. doi:10.1029/2004JD005025.
Menon, S., Hansen, J., Nazarenko, L., & Luo, Y. (2002). Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science, 27, 2250–2253.
Remer, L. A., Kaufman, Y. J., Tanre, D., Mattoo, S., Chu, D. A., Martins, J. V., Li, R. R., Ichoku, C., Levy, R. C., Kleidman, R. G., Eck, T. F., Vermote, E., & Holben, B. N. (2005). The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 62, 947–973.
Smirnov, A., Yershov, O., & Villevalde, Y. (1995). Measurement of optical depth in the Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea. Proceedings of SPIE The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2582, 203–325.
Song, C. K., Ho, C. H., Park, R. J., Choi, Y. S., Kim, J., Gong, D. Y., & Lee, Y. B. (2009). Spatial and seasonal variations of surface PM10 concentration and MODIS aerosol optical depth over China. Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 45, 33–43.
Takemura, A et al. (2001). Simulation of future aerosol distribution, radiative forcing, and long-range transport in East Asia. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 79, 1139–1155.
Wang, J., & Christopher, S. A. (2003). Inter-comparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2.5 mass: Implications for air quality studies. Geophysical Research Letters, 30, 2095. doi:10.1029/2003GL018174.
Wang, M. X., Zhang, R. J., & Pu, Y. F. (2001). Recent researches on aerosol in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 576–586.
Ye, B., Ji, X., Yang, H., Yao, X. H., Chan, C. K., Cadle, S. H., Chan, T., & Mulawa, P. A. (2003). Concentration and chemical composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai for 1-year period. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 499–510.
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank the Korea Meteorological Administration (CATER 2006-3103) for providing subvention for scientific research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HS., Chung, YS. & Lee, SG. Analysis of spatial and seasonal distributions of MODIS aerosol optical properties and ground-based measurements of mass concentrations in the Yellow Sea region in 2009. Environ Monit Assess 185, 369–382 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2559-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2559-3