Abstract
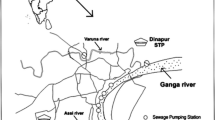
In the present study, the magnitude of contamination of vegetables with heavy metals (Pb, Zn, Cd, Cr, Cu and Zn) was determined in a long-term wastewater-irrigated agricultural land. Heavy metal concentrations in vegetables were several folds higher in wastewater-irrigated site compared to clean water-irrigated area. The wastewater-irrigated crops analysed in this study are heavily contaminated with heavy metals. Concentrations of Pb, Zn, Cd and Cr in all the sewage-fed vegetables were beyond the safe limit of FAO/WHO and Indian standard. Contamination is at its highest level in radish and spinach. Daily intake values of Pb, Cd and Ni through consumption of sewage-fed vegetables exceeded the recommended oral dose of metal for both adult and children. The study concludes that wastewater irrigation led to accumulation of heavy metals in vegetables causing potential health risk to consumers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, S. E., Grimshaw, H. M., & Rowland, A. P. (1986). Chemical analysis. In P. D. Moore & S. B. Chapman (Eds.), Methods in plant ecology (pp. 285–344). Blackwell Scientific Publication, London: Oxford.
Arora, M., Bala, K., Rani, S., Rani, A., Kaur, B., & Mittal, N. (2008). Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chemistry, 111, 811–815.
Awashthi, S. K. (2000). Prevention of food adulteration act no 37 of 1954. Central and state rules as amended for 1999 (3rd ed.). New Delhi: Ashoka Law House.
Bohn, H. L., McNeal, B. L., & O’Connor, A. G. (1985). Soil chemistry (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Codex Alimentarius Commission (FAO/ WHO) (2001). Food additives and contaminants. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, ALINORM 01/12A:1–289.
Cui, Y. J., Zhu, Y. G., Zhai, R. H., Chen, D. Y., Huang, Y. Z., Qui, Y., et al. (2004). Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables in an area near a smelter in Nanning, China. Environment International, 30, 785–791.
European Union. (2002). Heavy metals in wastes—European Commission on Environment. <http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/studies/pdf/heavymetalsreport.pdf>.
Fytianos, K., Katsianis, G., Triantafyllou, P., & Zachariadis, G. (2001). Accumulation of heavy metals in vegetables grown in an industrial area in relation to soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67, 423–430.
Ge, K. Y. (1992). The status of nutrient and meal of Chinese in the 1990s (pp. 415–434). Beijing: People’s Hygiene Press.
Itanna, F. (2002). Metals in leafy vegetables grown in Addis Ababa and toxicology implementations. The Ethiopian Journal of Health Development, 16, 295–302.
Jarup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin, 68, 167–182.
Kawatra, B. L., & Bakhetia, P. (2008). Consumption of heavy metal and minerals by adult women through food in sewage and tube well irrigated area around Ludhiana City (Punjab, India). Journal of Human Ecology, 23, 351–354.
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Zheng, Y. M., Huang, Y. Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2008). Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 152, 686–692.
Kumar, A., Sharma, I. K., Sharma, A., Varshney, S., & Verma, P. S. (2009). Heavy metals contamination of vegetable food stuffs in Jaipur (India). Electronic Journal of Environmental Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 8, 96–101.
Liu, W. H., Zhao, J. Z., Ouyang, Z. Y., Söderlund, L., & Liu, G. H. (2005). Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environment International, 31, 805–812.
Liu, W. X., Li, H. H., Li, S. R., & Wang, Y. W. (2006). Heavy metal accumulation of edible vegetables cultivated in agricultural soil in the suburb of Zhengzhou City, People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 76, 163–170.
Maleki, A., & Zarasvand, M. A. (2008). Heavy metals in selected edible vegetables and estimation of their daily intake in Sanandaj, Iran. The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 39, 335–340.
Radwan, M. A., & Salama, A. K. (2006). Market basket survey for some heavy metals in Egyptian fruits and vegetables. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 44, 1273–1278.
Rattan, R. K., Datta, S. P., Chhonkar, P. K., Suribabu, K., & Singh, A. K. (2005). Long term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and ground water—a case study. Agriculture, Ecosystem and Environment, 109, 310–322.
Sharma, R. K., Agrawal, M., & Marshall, F. M. (2006). Heavy metals contamination in vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated areas of Varanasi, India. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77, 312–318.
Sharma, R. K., Agrawal, M., & Marshall, F. M. (2007). Heavy metals contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 66, 258–266.
Sharma, R. K., Agrawal, M., & Marshall, F. M. (2009). Heavy metals in vegetables collected from production and market sites of a tropical urban area of India. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47, 583–591.
Singh, K. P., Mohon, D., Sinha, S., & Dalwani, R. (2004). Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharged by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural, and environmental quality in wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere, 55, 227–255.
Singh, A., Sharma, R. K., Agrwal, M., & Marshall, F. M. (2010). Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of food stuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 48, 611–619.
Sridhara Chary, N., Kamala, C. T., & Samuel Suman Raj, D. (2008). Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 69, 513–524.
Tandi, N. K., Nyamangara, J., & Bangira, C. (2004). Environmental and potential health effects of growing leafy vegetables on soil irrigated using sewage sludge and effluent: a case of Zn and Cu. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part B, Pesticides, Food Contaminants and Agricultural Wastes, 39, 461–471.
Türkdogan, M. K., Kilicel, F., Kara, K., Tuncer, I., & Uygan, I. (2003). Heavy metals in soil, vegetables and fruits in the endemic upper gastrointestinal cancer region of Turkey. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13, 175–179.
USEPA, IRIS (2006). United States, Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System. http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst.
Wang, X. P., Shan, X. P., Zhang, S. Z., & Wen, B. (2004). A model for evaluation of the phytoavailability of trace elements to vegetables under field conditions. Chemosphere, 55, 811–822.
Wang, X., Sato, T., Xing, B., & Tao, S. (2005). Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Science of the Total Environment, 350, 28–37.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge University of Kalyani for providing financial support and necessary facilities for the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, N., Khan, D.K. & Santra, S.C. Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables grown in a long-term wastewater-irrigated agricultural land of tropical India. Environ Monit Assess 184, 6673–6682 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2450-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2450-7