Abstract
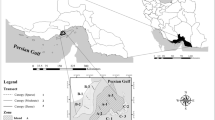
This paper deals with the spatial distribution and diversity of macrobenthos and their relationships between physico-chemical parameters of the water and sediment in different mangrove habitats of Tamil Nadu, India during different seasons (2008). Among the different ecosystems of mangrove benthic faunal assemblages, macrofauna species number, density, richness, and Shannon–Wiener index were the highest and the Simpson dominance index was medial at riverine mangrove community. However, the Pielou Evenness index of riverine mangrove community was slightly lower than other communities. The similarities among the macrobenthic communities at different sampling sites were determined using Bray–Curtis similarity coefficient and ordinations of non-metric multidimensional scaling (MDS). Thirty-one species were recorded in developing (16 polychaetes, six bivalves, seven gastropods, and two crustaceans), 35 species were recorded in riverine (20 polychaetes, six bivalves, five gastropods, and four crustaceans) and 31 species were recorded in island mangrove ecosystem (19 polychaetes, four bivalves, five gastropods, and three crustaceans). Among the three ecosystems, a total of 46 benthic macrofauna consisting of 27 species of polychaetes, eight species of gastropods, seven species of bivalves, and four species of crustaceans were recorded. However, there were obvious differences among the community structures in the three mangrove habitats. This result implied that the different mangrove ecosystem had different effects on the macrofauna communities and shed light on the macrofauna adaptation capability to specific habitats.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller, J. Y., Woodin, S. A., & Aller, R. C. (2001). Organism–sediment interactions. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press.
Ansari, Z. A., Ingole, B. S., Banerjee, G., & Parulekar, A. H. (1986). Spatial and temporal changes in benthic macrofauna from Mandovi & Zuari estuaries of Goa, West coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 15, 223–229.
Ashton, E. C. (1999). Biodiversity and community ecology of mangrove plants, molluscs and crustaceans in two mangrove forests in Peninsular Malaysia in relation to management practices. Ph.D. thesis. University of York, UK.
Athalye, R. P., & Gokhale, K. S. (1998). Macrobenthos from the mudflats of Thane creek, Maharashtra, India. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society, 95, 259–266.
Bloom, S. A., Simon, J. L., & Hunter, V. D. (1972). Animal–sediment relations and community analysis of a Florida estuary. Marine Biology, 13, 43–56.
Chandran, R. (1987). Hydrobiological studies in the gradient zone of the Vellar estuary. IV. Benthic fauna. Mahasagar—Bulletin of the National Institute of Oceanography, 20(1), 1–13.
Day, J. H. (1967). A monograph on the polychaeta of Southern Africa, Part I (Errantia) & II (Sedentaria). London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History).
English, S., Wilkinson, C., & Baker, V. (l994). Survey manual for tropical marine resources (2nd edition), Australian Institute of Marine Science, 238.
Fauvel, P. (1953). The fauna of India including Pakistan, Ceylon, Burma and Malaya. Allahabad: The Indian Press.
Fenchel, T., Kofoed, L. H., & Lappalainen, A. (1975). Particle size-selection of two deposit feeders: the amphipod Corophium volututor and the prosobranch Hydrobiu ulvae. Marine Biology, 30, 119–128.
Goldin, Q., Mishra, V., Ullal, V., Athalye, A. R., & Gokhale, K. S. (1996). Meiobenthos of mangrove mudflats from shallow region of Thane Creek, Central westcoast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 25, 137–141.
Gray, J. (1974). Animal–sediment relationships. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review, 12, 223–261.
Harikantra, S. N., Nair, A., Ansari, Z. A., & Parulekar, A. H. (1980). Benthos of shelf region along the west coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Pollution and Bulletin, 14(2), 41–46.
Hearld, C. L., & Odum, E. P. (1970). Mechanisms maintaining high productivity in Georgia estuaries. In Proceedings of the Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 14th Annual Session, 75–80.
Jackson, M. L. (1958). Soil chemical analysis. New Delhi: Prentice Hall.
Kathiresan, K. (2000). A review of studies on Pichavaram mangroves, southeast India. Hydrobiologia, 430, 185–205.
Kathiresan, K., & Quasim, S. Z. (2005). Biodiversity of mangrove ecosystems (p. 251). New Delhi: Hindustan Publishing Corporation.
Kathiresan, K., Rajendran, N., & Palaniselvam, V. (2000). Growth of Rhizophora apiculata in degraded areas of Ariyankuppam estuary along Pondicherry coastline, southeast coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 29, 86–88.
KondalaRao, B., & Ramanamurthy, K. V. (1988). Ecology of intertidal meiofauna of the Kakin Bay (Gautam–Godavari Estuarine System), east coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 17, 40–47.
Krom, M. D., & Berner, R. A. (1980). Adsorption of phosphate in anoxic marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 25(5), 797–806.
Krumbein, W. C., & Pettijohn, F. J. (1938). Manual of sedimentary petrography. New York: Appleton Century Crofts.
Kumar, R. S. (2001). Macrobenthos in the mangrove ecosystem of Cochin backwaters, Kerala (southwest coast of India). Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 24, 56–61.
Kundu, S., Mondal, N., Lyla, P. S., & Ajmal Khan, S. (2009). Biodiversity and seasonal variation of macro-benthic infaunal community in the inshore waters of Parangipettai Coast. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0817-9.
Macintosh, D. J. (1984). Ecology and productivity of Malaysian mangrove crab populations (Decapoda: Brachyura). Proceedings of the Asian Symposium on Mangrove Environmental Research and Management, 354–377.
Manson, F. J., Loneragan, N. R., Skilleter, G. A., & Phinn, S. R. (2005). An evaluation of the evidence for linkages between mangroves and fisheries: a synthesis of the literature and identification of research directions. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review, 43, 483–513.
Maurer, D. (1969). Diversity of soft-bottom benthos in a tropical estuary: Gulf of Nicoya, Costa Rica. Marine Biology, 81, 97–106.
Mishra, A., & Choudhury. (1985). Polychaetes annalids from the mangrove swamps of Sundarbans, India. Proceedings on the National Symposium on Biological Utilization and Conservation of Mangroves, 448–452.
Mohammed, S. Z. (1995). Observation on the benthic macrofauna of the soft sediment on Western side of the Arabian Gulf (ROPME sea area) with respect to 1991 Gulf War oil spill. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 24, 147–152.
Olsen, S. R., Cole, C. V., Watanabe, F. S., & Dean, L. (1954). USDA Circ., 939. Washington DC: U.S. Govt. Printing Office.
Parulekar, A. H., & Ansari, Z. A. (1981). Spatial and temporal changes in benthic macrofauna from Mandovi & Zuari estuaries of Goa, West coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Science, 15, 223–229.
Parulekar, A. H., & Waugh. (1975). Benthos studies in Goa estuaries III. Annual cycle of macrofaunal distributional production and trophic relations. Indian Journal of Marine Science, 1, 189–200.
Pearson, T. H., & Rosenberg, R. (1978). Macrobenthos secession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review, 16, 229–234.
Postma, H. (1954). Hydrography of the Dutch Wadden sea. Thesis Groningen. Arch. Neerland. Zoologie, X, 4e Livraison, 106.
Prabha Devi, L. (1994). Ecology of Coleroon estuary: studies on benthic fauna. Journal Marine Biology Assessment of India, 36(1–2), 260–266.
Prabha Devi, L., & Ayyakkannu, K. (1989). Ecology of benthic macrofauna in Cuddalore—Uppanar backwater, southeast coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Science, 20, 200–203.
Qasim, S. Z. (1970). Some problems related to the food chain a tropical estuary. In J.H. Steele (Ed.), Marine food chains (pp. 45–51). Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd.
Raveenthiranath Nehru (1990). Ecology of macrobenthos in and around Mahandrapalli region of Coleroon estuary, Southeast coast of India. Ph.D. thesis, Annamalai University, India, 231
Reid, G. K. (1961). Ecology of inland waters and estuaries. New York: Reinhold.
Rhoads, D. (1974). Organism–sediment relations on the muddy sea floor. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review, 12, 263–300.
Sanders, H. L. (1956). Benthic studies in Buzzards Bay. Animal sediment relationships. Limnology and Oceanography, 3, 245–258.
Sankar, G. (1998). Studies on the hydrobiology, benthic ecology and fisheries of Muthupet lagoon. Ph.D. thesis, Annamalai University, India, 105
Sasekumar, A. (1974). Distribution of macrofauna on a Malayan mangrove shore. Journal of Animal Ecology, 43, 51–69.
Schelske, C. L., & Odum, E. P. (1961). Mechanisms maintaining high productivity in Georgia estuaries. In: Proceedings of the Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 14th Annual Session, 75–80.
Smith, T. J., Boto, K. G., Frusher, S. D., & Giddins, R. L. (1991). Keystone species and mangrove forest dynamics: the influence of burrowing by crabs on soil nutrient status and forest productivity. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 33, 19–32.
Snelgrove, P. V. R., & Butman, C. A. (1994). Animal–sediment relationships revisited: cause versus effect. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review, 32, 111–177.
Stone, A. N., & Reish, D. J. (1965). The effect of fresh water run-off on a population of estuarine polychaetous annelids. Bulletin of the Southern California Academy of Sciences, 64, 111.
Strickland, J. D. H., & Parsons, T. R. (1972). A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Fishery Research Board, Canada, 310p.
Subba Rao, N. V., Surya Rao, K. V., & Maitra, S. (1991). Marine molluscs. State Fauna Series. Fauna of Orissa (pp. 1–175). Kolkata: Zoological Survey of India, 1(3), 1–175.
Subbiah, B. V., & Asija, G. L. (1956). A rapid procedure for the determination of available nitrogen in soils. Current Science, 31, 196.
Sunilkumar, R. (1995). Macrobenthos in the mangrove ecosystem of Cochin backwaters, Kerala (Southwest coast of India). Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 24, 56–61.
Sunilkumar, R., & Antony, A. (1994). Preliminary studies on the polychaete fauna of the mangrove areas of Cochin. In: Proceedings of The 6th Kerala Science Congress, Thiruvanthapuram, Kerala. R. Ravikumar (Eds.), State Committee on Science, Technology and Environment, 74–77.
Thorson, G. (1966). Some factors influencing the requirement and establishment of marine benthic communities. Journal of Sea Research, 3, 267–293.
Viijayakumar, S., Rajesh, K. M., Mridula, R. M., & Hariharan, V. (2000). Seasonal distribution and behaviour of nutrients with reference to tidal rhythm in the Mulki estuary, Southwest coast of India. Journal of Marine Biology Assessment of India, 42(1–2), 21–31.
Warren, J. H., & Underwood, A. J. (1986). Effects of burrowing crabs on the topography of mangroves swamps in New South Wales. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 102, 223–235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samidurai, K., Saravanakumar, A. & Kathiresan, K. Spatial and temporal distribution of macrobenthos in different mangrove ecosystems of Tamil Nadu Coast, India. Environ Monit Assess 184, 4079–4096 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2245-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2245-x