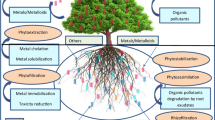
Abstract
Multifaceted issues or paradigm of sustainable development should be appropriately addressed in the discipline of environmental management. Pollution of the biosphere with toxic metals has accelerated dramatically since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. In present review, comparative assessment of traditional chemical technologies and phytoremediation has been reviewed particularly in the context of cost-effectiveness. The potential of phytoremediation and green chemicals in heavy metals management has been described critically. Further, the review explores our work on phytoremediation as green technology during the last 6 years and hand in hand addresses the various ecological issues, benefits and constraints pertaining to heavy metal pollution of aquatic ecosystems and its phytoremediation as first case study. Second case study demonstrates the possible health implications associated with use of metal contaminated wastewater for irrigation in peri-urban areas of developing world. Our researches revealed wetland plants/macrophytes as ideal bio-system for heavy metals removal in terms of both ecology and economy, when compared with chemical treatments. However, there are several constraints or limitations in the use of aquatic plants for phytoremediation in microcosm as well as mesocosm conditions. On the basis of our past researches, an eco-sustainable model has been proposed in order to resolve the certain constraints imposed in two case studies. In relation to future prospect, phytoremediation technology for enhanced heavy metal accumulation is still in embryonic stage and needs more attention in gene manipulation area. Moreover, harvesting and recycling tools needs more extensive research. A multidisciplinary research effort that integrates the work of natural sciences, environmental engineers and policy makers is essential for greater success of green technologies as a potent tool of heavy metals management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, M.G.M., Snow, E. T., & Tanaka, A. (2003). Arsenic and heavy metal contamination of vegetables grown in Samta village, Bangladesh. Science of the Total Environment, 308, 83–96.
Alloway, B. J., & Ayres, D. C. (1993). Chemical principles of environmental pollution. Oxford: Blackie. An imprint of Chapman and Hall.
APHA (2000). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, (10th ed.). Washington, D.C.: APHA.
Awashthi, S. K. (2000). Prevention of food adulteration act no 37 of 1954. Central and state rules as amended for 1999, (3rd edn.). New Delhi: Ashoka Law House.
Babel, S., & Kurniawan, T. A. (2003). Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B97, 219–243.
Bailey, S. E., Olin, T. J., Bricka, R. M., & Adrian, D. D. (1999). A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Research, 33, 2469–2479.
Barker, R. (1997). And the waters turned to blood. New York: Simon and Schuster.
Batty, L. C. (2003). Wetland plants—more than just a pretty face? Land Contamination & Reclamation, 112, 173–180.
Bean, H., Schuler, C., Leggett, R. E., & Levin, R. M. (2009). Last update 2010. Antioxidant levels of common fruits, vegetables, and juices versus protective activity against in vitro ischemia/reperfusion. International Urology and Nephrology, 42(2), 409–415, doi:10.1007/s11255-009-9639-5.
Bohn, H. L., McNeal, B. L., & O’Connor, A. G. (1985). Soil chemistry, 2nd (ed.). New York: Wiley.
Borah, S., Baruah, A. M., Das, A. K., & Borah, J. (2009). Determination of mineral content in commonly consumed leafy vegetables. Food Anayitical Methods, 2, 226–230.
Borenstein, S. (1998). Coastal waters have big problems, Harvard study says. The Buffalo News, 25 August.
Boyd, R. S., & Martens, S. N. (1992). The raison d’etre for metal hyperaccumulation in plants. In A. J. M. Baker, J. Proctor, & R. D. Reeves (Eds.), The vegetation of ultramafic (Serpentine) soils (pp. 279–289). Andover: Intercept.
Boyd, R. S., & Martens, S. N. (1998). The significance of metal hyperaccumulation for biotic interactions. Chemoecology, 8, 1–7.
Brix, H. (1997). Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Science and Technology, 35, 11–17.
Brown, L. (1999). China’s water crisis linked to global security. Population Press, 5(5), 5.
Bruner, A. J., Gullison, R. E., & Balmford, A. (2004). Financial costs and shortfalls of managing and expanding protected-area systems in developing countries. BioScience, 54(12), 1119–1126.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS; 1983). General standards for discharge of environment pollutants effluents. IS: 10500–1983 (http://hppcb.nic.in/standard.htm).
Cao, Z. H., & Hu, Z. Y. (2000). Copper contamination in paddy soils irrigated with wastewater. Chemosphere, 41(1–2), 3–6.
Center for New American Dream (2000). [Online] http://www.newdream.org/monthly/aug00.html.
Centi, G., & Perathoner, S. (2003). Catalysis and sustainable (green) chemistry. Catalysis Today, 77, 287–297.
Cobb, G. P., Sands, K., Waters, M., Wixson, B. J., & Dorward-King, E. (2000). Accumulation of heavy metals by vegetables grown in mine wastes. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 19(3), 600–607.
Cochrane, E. L., Lua, S., Gibb, S. W., & Villaescusa, I. (2006). A comparison of low-cost biosorbents and commercial sorbents for the removal of copper from aqueous media. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B137, 198–206.
Collier, C. (1999). Save some for tomorrow. Environment News Service. Available at http://ens.lycos.com/ewire/July99/20july9903.html.
Concas, A., Ardau, C., Cristini, A., Zuddas, P., & Cao, G. (2006). Mobility of heavy metals from tailings to stream waters in a mining activity contaminated site. Chemosphere, 63, 244–253.
CPCB (1998). Permissible limit for the discharge of Industrial effluents (inland water surface). New Delhi: CPCB.
Demir, A., & Arisoy, M. (2007). Biological and chemical removal of Cr (VI) from waste water: cost and benefit analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 275–280.
Demrbaş, A. (2003). Trace metal concentrations in ashes from various types of biomass species. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 25(7), 743–751.
Duda, A. M. (1993). Addressing non-point sources of water pollution must become an international priority. Water Research, 28(3–5), 1–11.
E.N.N. (2003). Malaysian leader defends government’s campaign against Singapore over water use. Available at http://www.enn.com/news/2003-07-18?s_6707.asp.
Eapen, S., & D’Souza, S. F. (2005). Prospects of genetic engineering of plants for phytoremediation of toxic metals. Biotechnology Advances, 23, 97–114.
Eccles, H. (1999). Treatment of metal-contaminated wastes: why select a biological process? Trends in Biotechnology, 17, 462–465.
Edie Summaries (2000). Israel: Water not land is key to shepherdstown talks. Available at http://www.edie.net/news/Archive/2223.html.
ENS (Environment News Service) (1999a). Canada, U.S. Consider great lakes water export ban. Available at http://ens.lycos.com/ens/aug99/1999L-08-24-06.html.
ENS (1999b). Growing population faces shrinking water supply. Available at http://ens.lycos.com/ ens/jul99/1999L-07-20-01.html.
ENS (2003). Threats rising for U.S. Public water supplies. Available at http://ens-news.com/ens/ jun2003/2003-06-11-10.asp.
EPA US (2002). Integrated risk information system. Available at http:www.epa.govyirisygloss8.htm.
Evangelou, M. W. H., Ebel, M., & Schaeffer, A. (2007). Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents. Chemosphere, 68, 989–1003.
Feigin, A., Ravina, I., & Shalhevet, J. (1991). Irrigation with treated sewage effluent. Berlin: Springer.
Finkelman, R. B., & Gross Peggy, M. K. (1999). The types of data needed for assessing the environmental and human health impacts of coal. International Journal of Coal Geology, 40, 91–101.
Fleischer, T., & Grunwald, A. (2008). Making nanotechnology developments sustainable. A role for technology assessment? Journal of Cleaner Production, 16, 889–898.
Flint, R. W. (2003). Sustainable development: What does sustainability mean to the individual in the conduct of their life and business. In G. M. Mudacumura (Ed.), Handbook of development policy strategies. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Flint, R. W. (2004). The sustainable development of water resources. Water Resources Update, 127, 41–51.
Flint, R. W., & Houser, W. L. (2001). Living a sustainable lifestyle for our children’s children. Campbell: IUniverse.
Fuller, D. A., & Ottman, J. A. (2004). Moderating unintended pollution: the role of sustainable product design. Journal of Business Research, 57, 1231–1238.
Garćıa-Serna, J., Pérez-Barriǵon, L., & Cocero, M. J. (2007). New trends for design towards sustainability in chemical engineering: green engineering. Chemical Engineering Journal, 133, 7–30.
Gavrilescua, M., & Chisti, Y. (2005). Biotechnology—A sustainable alternative for chemical industry. Biotechnology Advances, 23, 471–499.
Gisbert, C., Ros, R., De, H. A., Walker, D. J., Bernal, M. P., Serrano, R., et al. (2000). A plant genetically modified that accumulates Pb is especially promising for phytoremediation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 303, 440–445.
Gladden, J. B., Specht, W. L., & Nelson, E. A. (2002). Comparison of constructed Wetland Mesocosms designed for treatment of copper-contaminated wastewater. Aiken: Westinghouse Savannah River Company (Contract no. DE-AC09-96SR18500 with the U.S. Department of Energy).
GreenBiz.com (2003). Humanity wages war with nature for water. Environmental News Network, New York. Available at http://www.enn.com/news/2003-02-05/s_2417.asp.
Grossman, R. (1998). Can corporations be held accountable? Part I. Rachel’s Environment and Health Weekly, 609. Available at http://www.rachel.org.
Hanninen, H., & Lindstrom, H. (1979). Behavioral test battery for toxic psychological studies used at the institute of occupational health in Helsinki. Helsinki: Institute of Occupational Health.
Hanson, B., Lindbom, S. D., Loeffler, M. L., & Pilon-Smits, E. A. H. (2004). Selenium protects plants from phloem feeding aphids due to both deterrence and toxicity. The New Phytologist, 162, 655–662.
Ho, K. C., Chow, Y. L., & Yau, J. T. S. (2003). Chemical and microbiological qualities of The East River (Dongjiang) water, with particular reference to drinking water supply in Hong Kong. Chemosphere, 52, 1441–1450.
Khan, A. G. (2005). Role of soil microbes in the rhizospheres of plants growing on trace metal contaminated soils in phytoremediation. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 18, 355–364.
Khan, G., Kuek, C., Chaudhary, T., Fhoo, C., & Hayes, W. (2000). Role of mycorrhizae and phytochelators in heavy metal contaminated land remediation. Chemosphere, 41, 197–207.
Kirchhoff, M. M. (2005). Promoting sustainability through green chemistry. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 44, 237–243.
Knasmuller, S., Gottmann, E., Steinkellner, H., Fomin, A., Pickl, C., Paschke, A., et al. (1998). Detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metal contaminated soils with plant bioassay. Mutation Research, 420, 37–48.
Koefoed, M., & Buckley, C. (2008). Clean technology transfer. A case study from the South African metal finishing industry 2000–2004. Journal of Cleaner Production, 16, 78–84.
Korhonen, J. (2004). Industrial ecology in the strategic sustainable development model: strategic applications of industrial ecology. Journal of Cleaner Production, 12, 809–823.
Kratochvil, D., & Volesky, B. (1998). Advances in the biosorption of heavy metals. TIBTECH, 16, 291–300.
Kudo, A., & Miyahara, S. (1991). A case history—Minamata mercury pollution in Japan-from loss of human lives to decontamination. Water Science and Technology, 23, 283.
Kumar, P. B. A. N., Dushenkov, V., Motto, H., & Raskin, I. (1995). Phytoextraction—the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 29, 1232–1238.
Kurniawan, T. A., Chan, G. Y. S., Lo, W.-H., & Babel, S. (2006). Comparisons of low-cost adsorbents for treating wastewaters laden with heavy metals. The Science of the Total Environment, 366, 409–426.
Lazaroff, C. (2000). Growing population faces diminishing resources. In Environment news service. Available at http://ens.lycos.com/ens/jan2000/2000L-01-18-06.html.
Lee, S. M., & Tiwari, D. (2009). Application of ferrate (VI) in the treatment of industrial wastes containing metal complexed cyanides: a green treatment. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2, 1347–1352.
Lewandowski, I., Schmidt, U., Londo, M., & Faaij, A. (2006). The economic value of the phytoremediation function—Assessed by the example of cadmium remediation by willow (Salix ssp). Agricultural Systems, 89, 68–89.
Mapanda, F., Mangwayana, E. N., Nyamangara, J., & Giller, K. E. (2005). The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare. Zimbabwe Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 107, 151–165.
McLellan, B. C., Corder, G. D., Giurco, D., & Green, S. (2009). Incorporating sustainable development in the design of mineral processing operations—Review and analysis of current approaches. Journal of Cleaner Production, 17, 1414–1425.
Miller, J. R., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Lechler, P. J., Preston, D., & Macklin, M. G. (2004). Heavy metal contamination of water, soil and produce with in riverine communities of the Rıo Pilcomayo basin. Bolivia Science Total Environment, 320, 189–209.
Millis, P. R., Ramsey, M. H., & John, E. A. (2004). Heterogeneity of cadmium concentration in soil as a source of uncertainity in plant uptake and its implication for human health risk assessment. The Science of the Total Environment, 326, 49–53.
Mireles, A., Solis, C., Andrade, E., Lagunas-Solar, M., Pina, C., & Flocchini, R. G. (2004). Heavy metal accumulation in plants and soil irrigated with wastewater from Mexico City. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research, B, 1(219–220), 187–190.
Mohan, D., & Pittman, C. U., Jr. (2007). Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents-A critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 142, 1–53.
Montague, P. (1998). Landfills are dangerous. Rachel’s environment and health weekly, #617, p. 2. [Online] http://www.rachel.org.
Muggiati, A. (2003). Four nations guard giant South American aquifer. In Environment news service. Available at http://ens-news.com/ens/may2003/2003-05-29-03.asp.
Murozono, K., Ishii, K., Yamazaki, H., Matsuyama, S., & Iwasaki, S. (1999). PIXE spectrum analysis taking into account bremsstrahlung spectra. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research, B., 150, 76–82.
Mustikhan, A. (1999). Pakistan provinces feud over water. In Environment news service (ENS), 7/28/99. Available at http://www.ens.lycos.com/ens/jul99/1999L-07-28-02.html.
Nan, Z., Li, J., Zhang, J., & Cheng, G. (2002). Cadmium and zinc interaction and their transfer in soil–crop system under actual field conditions. The Science of the Total Environment, 285, 187–195.
Ngah, W. S. W., & Hanafiah, M. A. K. M. (2008). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: a review. Bioresource Technology, 99, 3935–3948.
Nies, D. H. (1999). Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 51, 730–750.
Nordberg, G. F. (1996). Current issues in low-dose cadmium toxicology: nephrotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Environmental Sciences, 4(3), 133–147.
Nriagu, J. O. (1979). Global inventory of natural and anthropogenic emission of trace metals to the atmosphere. Nature, 279, 409–411.
Nriagu, J. O. (1996). A history of global metal pollution. Science, 272, 273–274.
Nyamangara, J., & Mzezewa, J. (1999). The effects of long-term sewage sludge application on Zn, Cu, Ni and Pb levels in clay loam soil under pasture grass in Zimbabwe. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 73, 199–204.
Olguín, E. J. (2002). Phycoremediation: Key issues for cost-effective nutrient removal processes. Biotechnology Advances, 22, 81–91.
Omer, A. M. (2008). Energy, environment and sustainable development. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 12, 2265–2300.
Palme, U., Lundin, M., Tillman, A. M., & Molander, S. (2005). Sustainable development indicators for wastewater systems—Researchers and indicator users in a co-operative case study. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 43, 293–311.
Pandey, V. C., Abhilash, P. C., & Singh, N. (2009). The Indian perspective of utilizing fly ash in phytoremediation, phytomanagement and biomass production. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 2943–2958.
Pehlivan, E., & Arslan, G. (2007). Removal of metal ions using lignite in aqueous solution—Low cost biosorbents. Fuel Processing Technology, 88, 99–106.
Pendias, H., & Pendias, K. (1989). Trace elements in soil and plants. Florida: CRC.
Pescod, M. B. (1992). Wastewater treatment and use in agriculture (p 125). Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, FAO irrigation and drainage paper 47.
Pilon-Smits, E., & Pilon, M. (2002). Phytoremediation of metals using transgenic plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 21(5), 439–456.
Press Notice (1998). Government launches first ever business plan for environment industries. Joint Environmental Markets Unit, P/98/212, 18 March.
Quaid, L. (2003). Missouri river ruling could hinder water quality. In Environmental news network. Available at http://www.enn.com/news/2003-07-15/s_6555.asp.
Queirlo, F., Stegen, S., Restovic, M., Paz, M., Ostapczuk, P., Schwuger, M. J., et al. (2000). Total arsenic, lead, and cadmium levels in vegetables cultivated at the Andean villages of Northern Chile. The Science of the Total Environment, 255, 75–84.
Rai, P. K. (2007a). Phytoremediation of Pb and Ni from industrial effluents using Lemna minor: An eco-sustainable approach. Bullettin Bioscience, 5(1), 67–73.
Rai, P. K. (2007b). Wastewater management through biomass of Azolla pinnata: An eco-sustainable approach. Ambio, 36(5), 426–428.
Rai, P. K. (2008a). Heavy-metal pollution in aquatic ecosystems and its phytoremediation using wetland plants: An eco-sustainable approach. International Journal Phytoremediation, 10(2), 133–160.
Rai, P. K. (2008b). Mercury pollution from chlor-alkali industry in a tropical lake and its biomagnification in aquatic biota: Link between chemical pollution, biomarkers and human health concern. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 14, 1318–1329.
Rai, P. K. (2008c). Phytoremediation of Hg and Cd from industrial effluents using an aquatic free floating macrophyte Azolla pinnata. International Journal Phytoremediation, 10(5), 430–439.
Rai, P. K. (2008d). Ecological investigation on heavy metal pollution of G.B. Pant Sagar and its phytoremediation. PhD Dissertation. Varanasi, India: Banaras Hindu University.
Rai, P. K. (2009a). Heavy metal phytoremediation from aquatic ecosystems with special reference to macrophytes. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 39(9), 697–753.
Rai, P. K. (2009b). Last update 2010. Phytoremediation of heavy metals in a tropical impoundment of industrial region. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 165, 529–537, doi:10.1007/S10661-009-0964-2.
Rai, P. K. (2009c). Last update 2010. Seasonal monitoring of heavy metals and physico-chemical characteristics in a lentic ecosystem of sub-tropical industrial region, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 165, 407–433. doi:10.1007/S10661-009-0956-2.
Rai, P. K. (2009d). Heavy metals in water, sediments and wetland plants in an aquatic ecosystem of tropical industrial region, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 158, 433–457. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0595-9.
Rai, P. K. (2010a). Microcosm investigation on Phytoremediation of Cr using Azolla pinnata. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 12, 96–104.
Rai, P. K. (2010b). Heavy metal pollution in lentic ecosystem of sub-tropical industrial region and its phytoremediation. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 12(3), 226–242.
Rai, P. K., Mishra, A., & Tripathi, B. D. (2010). Heavy metals and microbial pollution of river Ganga: A case study on water quality at Varanasi. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 13(4), 352–361.
Rai, P. K., Sharma, A. P., & Tripathi, B. D. (2007). Urban environment status in singrauli industrial region and its eco-sustainable management: A case study on heavy metal pollution. In V. Lakshmi (Ed.) Urban planing and environment, strategies and challenges (pp. 213–217). London: McMillan.
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2007a). Heavy metals removal using nuisance blue green alga Microcystis in continuous culture experiment. Environmental Sciences, 4(1), 53–59.
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2007b). Microbial contamination in vegetables due to irrigation with partially treated municipal wastewater in a tropical city. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 17(5), 389–395.
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2008). Heavy metals in industrial wastewater, soil and vegetables in Lohta Village, India. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 90(2), 247–257.
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2009). Comparative assessment of Azolla pinnata and Vallisneria spiralis in Hg removal from G.B. Pant Sagar of Singrauli Industrial region, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 148, 75–84.
Rai, U. N., Sinha, S., Tripathi, P., & Chandra, P. (1995). Wastewater treatability potential of some aquatic macrophytes: Removal of heavy metals. Ecological Engineering, 5, 5–12.
Rai, U. N., Tripathi, R. D., Vajpayee, P., Vidyanath, Jha., & Ali, M. B. (2002). Bioaccumulation of toxic metals (Cr, Cd, Pb and Cu) by seeds of Euryale ferox Salisb (Makhana). Chemosphere, 46, 267–272.
Ramakrishnan, P. S. (1993). Evaluating sustainable development with peoples’ participation. In F. Moser (Ed.), Sustainability—where do we stand? Proc. Intl. Symposium (pp. 165–182). Graz, Austria: Technische Universität.
Ramakrishnan et al. (1994). In M. Hadley (Ed.), Ecosystem rehabilitation of the rural landscape in south and central Asia: An analysis of issues (pp. 1–33). MAB series UNESCO.
Reddy, K. R., Patrick, W. H., & Lindau, C. W. (1989). Nitrification–denitrification at the plant root-sediment interface in wetlands. Limnology and Oceanography, 34, 1004–1013.
Roche, M., & Toyne, P. (2004). Green lead—oxymoron or sustainable development for the lead–acid battery industry? Journal of Power Sources, 133, 3–7.
Ross, S. M. (1994). Sources and forms of potentially toxic metals in soil–plant systems. In S. M. Ross (Ed.), Toxic metals in soil–plant systems (pp. 3–26). England: Wiley.
Rupert, L. H., Neil, B., Scott, D. Y., Neil, M. J. C., Andrew, M. T., Ann, M. M., et al. (2004). Assessing potential risk of heavy metal exposure from consumption of home-produced vegetables by urban populations. Environmental Health Perspective, 112, 215–221.
Salt, D. E., Blaylock, M., Kumar, P. B. A. N., Dushenkov, V., Ensley, D., Chet, I., et al. (1995). Phytoremediation: A novel strategy for the removal of toxic elements from the environment using plants. Bio/Technology, 13, 468–474.
Salt, D. E., Smith, R. D., & Raskin, I. (1998). Phytoremedietion. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 49, 643–648.
Scholz, M. (2006). Wetland systems to control urban runoff. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Serrano, E., Rus, G., & García-Martínez, J. (2009). Nanotechnology for sustainable energy. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 13, 2373–2384.
Shah, P. B., Schreier, H., Brown, S. J., & Riley, K. W. (1991). Soil fertility and erosion issues in the middle mountains of Nepal: Workshop proceedings (p 285). Jhiku Khola Watershed. Integrated Survey Section, HMG, Kathmandu.
Sharma, D. C. (2003). Concern over mercury pollution in India. Lancet, 362, 1030.
Shukla, V. K., Prakash, A., Tripathi, B. D., & Reddy, D. C. S. (1998). Biliary heavy metal concentration in carcinoma of the gall bladder: case-control study. BMJ, 317, 1288–1289.
Singh, K. P., Mohan, D., Sinha, S., & Dalwani, R. (2004). Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharged by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural, and environmental quality in the wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere, 55, 227–255.
Singh, R. P. B. (2005). Life in historic urban landscape of Varanasi, a heritage city of India. Varanasi: Geography Department, Banaras Hindu University.
Sridhara, C. N., Kamala, C. T., & Samuel, S. R. D. (2008). Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 69, 513–524.
Stalikas, C. D., Mantalovas, A. C., & Pilidis, G. A. (1997). Multielement concentrations in vegetable species grown in two typical agricultural areas of Greece. The Science of the Total Environment, 206, 17–24.
Stevenson, M. (2003). The “Other” gulf war, dispute over water rights threatens environment. In Environmental news network (ENN) (Online).
Stottmeister, U., Wiesner, A., Kuschk, P., Kappelmeyer, M., & Kaster, M. (2003). Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnology Advances, 22, 93–117.
Sutherland, D. (1999). Tug-o-War: Cancer kids vs. water pollution. Environment News Service. Available at http://ens.lycos.com/ens/sep99/1999L-09-27-01.html.
Syers, J. K., & Goldfeld, M. (2001). Introduction. In: J. K. Syers & M. Goldfeld (Eds.) Environmental cadmium in the food chain: Source, pathways and risks (pp. iv–v). Proceeding of the SCOPE workshop. Scientific committee on problems of the environment/international council of scientific unions (SCOPE/ICSU). Sep. 13–16, 2000. Brussels, Belgium. Paris’ SCOPE.
Thompson, H. C., & Kelly, E. C. (1990). Vegetable crops (5th ed). New Delhi: McGraw Hill.
Tiwari, D., Yang, J. K., & Lee, S. M. (2005). Applications of ferrate (VI) in the treatment of wastewaters. Environmental Engineering Research, 10, 269–282.
Tiwari, D., Kim, H. U., Choi, B. J., Lee, S. M., Kwon, O. H., Choi, K. M., et al. (2007). Ferrate (VI): A green chemical for the oxidation of cyanide in aqueous/waste solutions. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, A4, 803–810.
Tiwari, D., Yang, J. K., Chang, Y. Y., & Lee, S. M. (2008). Application of ferrate (VI) on the decomplexation of Cu(II)-EDTA. Environmental Engineering Research, 13, 131–135.
UNESCO (2003). Water for people, water for life: The world water development report. World Water Assessment Programme, United Nations, NY. [On-line]. Available at http://ens-news.com/ens/mar2003/2003-03-05-02.asp.
Urie, D. H. (1986). The status of wastewater irrigation of forest. In D. W. Cole, C. L. Henry, & W. L. Nutter (Eds.), The forest alternative for treatment and utilization of municipal and industrial wastes (pp. 26–40). Seattle: University of Washington Press.
Volesky, B. (2003). Potential of biosorption. In: B. Volesky (Ed.), Sorption and biosorption. Montreal: BVSorbex.
Vymazal, C., Jaroslav, S., Lenka, K., & Vladislav, C. (2007). Trace metals in Phragmites australis and Phalaris arundinacea growing in constructed and natural wetlands. Ecological Engineering, 30(4), 320–325.
Vymazal, J. (2002). The use of sub-surface constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in the Czech Republic: 10 years experience. Ecological Engineering, 18, 633–646.
Wagner, A., & Boman, J. (2003). Biomonitoring of trace elements in muscle and liver tissue of freshwater fish. Spectrochimica Acta Part B, 58, 2215–2226.
Wang, S., Soudi, M., Lib, L., & Zhu, Z. H. (2006). Coal ash conversion into effective adsorbents for removal of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B133, 243–251.
Wang, W. H., Lin, S. H., & Juang, R. S. (2003). Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using various low-cost adsorbents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B102, 291–302.
Wang, X., Sato, T., Xing, B., & Tao, S. (2005). Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. The Science of the Total Environment, 350, 28–37.
Warner, J. C., Cannon, A. S., & Dye, K. M. (2004). Green chemistry. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 24, 775–799.
Wenzel, W. W., et al. (2003). Chelate-assisted phytoextraction using canola (Brassica napus L) in outdoors pot and lysismeter experiments. Plant and Soil, 249, 83–96.
WHO (1993). Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. Forty-first report of the joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives, WHO Technical series no. 837. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO).
WHO (1996). Trace elements in human nutrition and health. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO).
WHO (1997). Health and environment in sustainable development. Geneva: WHO.
Wilson, A., & Yost, P. (2001). Buildings and the environment: The numbers. Environmental Building News, 1 May.
Wu, G., Kanga, H., Zhang, X., Shaob, H., Chuc, L., & Ruan, C. (2010). A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174, 1–8.
Yadav, S. K., Juwarkar, A. A., Kumar, G. P., Thawale, P. R., Singh, S. K., & Chakrabarti, T. (2009). Bioaccumulation and phyto-translocation of arsenic, chromium and zinc by Jatropha curcas L.: Impact of dairy sludge and biofertilizer. Bioresource Technology, 100, 4616–4622.
Yavuz, M., Godea, F., Pehlivan, E., Ozmert, S., & Sharma, Y. C. (2008). An economic removal of Cu2 + and Cr3 + on the new adsorbents: pumice and polyacrylonitrile/pumice composite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 137, 453–461.
Yngard, R. A., Damrongsiri, S., Osathaphan, K., & Sharma, V. K. (2007). Ferrate (VI) oxidation of zinc-cyanide complex. Chemosphere, 69, 729–735.
Zhuang, P., McBride, M. B., Xia, H., Li, N., & Li, Z. (2009). Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. The Science of the Total Environment, 407, 1551–1651.
Zietz, B. P., Dieter, H., Lakomek, M., Schneider, H., Gaedtke, K. B., & Dunkelberg, H. (2003). Epidemiological investigation on chronic copper toxicity to children exposed via the public drinking water supply. The Science of the Total Environment, 302, 127–144.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, P.K. An eco-sustainable green approach for heavy metals management: two case studies of developing industrial region. Environ Monit Assess 184, 421–448 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1978-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1978-x