Abstract
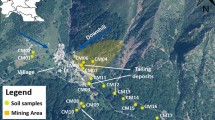
This study analyses the pedological environment of the area near a municipal waste incinerator that has been operating in the south-east district of Pisa for approximately 20 years. There are many other industrial activities in the area besides the incinerator, which represent possible sources of pollution, as well as heavy road traffic. The study area was defined by a 0–4-km zone around the site with a population of approximately 12,000 residents. The study included the physical and chemical characterisation of 100 samples of soil and an analysis of trace metals such as Cr, Ni, Pb, Zn, Hg, As and Cd. The samples were grouped into soil use categories. The results showed Zn, Pb and Hg correlated with their potentially mobile fractions, and suggested an anthropic contribution to their presence in the soil. Ni, Cr and As showed values attributable to a lithological origin. This was consistent with the PCA results. The aim was to define the environmental state of the soil of the area in order to create a reference for future research and to verify the possible presence of pollution from other sources (local industrial activities and traffic).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino, A., Aceto, M., Malandrino, M., Mentasti, E., Sarzanini, C., & Petrella, F. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils from Piedmont, Italy. Distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment. Chemosphere, 49, 545–557. PII: S00 4 5-6 5 35 (0 2) 0 03 5 2-1.
Alloway, B. J., & Jackson, A. P. (1991). The behaviour of heavy metals in sewage sludge amended soils. Science of the Total Environment, 100, 151–176.
ASA-SSSA (1996). Methods of Analysis, Part 1 and 3 physical and chemical methods (2nd ed.). Madison, Wisconsin, USA: ASA-SSSA.
Backstrom, M., Karlsson, S., & Allard, B. (2004). Metal leachability and anthropogenic signal in roadside soils estimated from sequential extraction and stable lead isotopes. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 90, 135–160.
Barbafieri, M., Lubrano, L., & Petruzzelli, G. (1996). Characterization of pollution in sites contaminated by heavy metals. Annali di Chimica, 86, 585–594.
Bech, J., Tume, P., Logan, L., & Reverter, F. (2005). Baseline concentrations of trace elements in surface soils of the Torrelles and Sant Clement Municipal Districts (Catalonia, Spain). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 108, 309–322. doi:10.1007/s10661-005-4331-4.
Beesley, L., Moreno-Jimenez, E., & Gomez-Eyles, J. (2010). Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil. Environmental Pollution, 158, 2282–2287. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.02.003.
Bermudez, G. M. A., Moreno, M., Invernizzi, R., Plà, R., & Pignata, M. L. (2010). Heavy metal pollution in topsoil near a cement plant: The role of organic matter and distance to the source to predict total and HCl-extracted heavy metal concentrations. Chemosphere, 78, 375–381. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.11.012.
Biasioli, M., Barberis, R., & Ajmon-Marsan, F. (2005). The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals content. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 154–164. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.04.033.
Biasioli, M., Greman, H., Kralij, T., Madrid, F., Diaz-Barrientos, E., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2007) Potentially toxic elements in urban soils: a comparison of three European cities. Journal of Environmental Quality, 36(1), 70–79.
Boyd, H. B., Pedersen, F., Cohr, K., Damborg, A., Jakobsen, B. M., Kristensen, P., et al. (1999). Exposure scenarios and guidance values for urban soil pollutants. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 30, 197–208.
Brazauskiene, D., Paulauskas, V., & Sabiene, N. (2008). Speciation of Zn, Cu and Pb in the soil depending on soil texture and fertilization with sewage sludge compost. Journal of Soil and Sediment, 8, 184–192. doi:10.1007/s11368-008-0004-6.
Bretzel, F., & Calderisi, M. (2006). Metal contamination in urban soils of coastal Tuscany (Italy). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 319–335. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-1495-5.
Bridges, E. M. (1991). Waste materials in urban soils. In P. Bullock & P. J. Gregory (Eds.), Soils in the Urban Environment (pp. 28–46). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Cangialosi, F., Intini, G., Liberti, L., Notarnicola, M., & Stellacci, P. (2008). Health risk assessment of air emissions from a municipal solid waste incinerator plant—A case study. Waste Management, 28, 885–895. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2007.05.006.
Carlon, C., Critto, A., Marcomini, A., & Nathanil, P. (2001). Risk based characterization of contaminated industrial site using multivariate and geostatistical tools. Environmental Pollution, 111, 417–427. PII: S0269-7491(00)00089-0.
Carlosena, A., Andrade, J. M., & Prada, D. (1998). Searching for heavy metals grouping roadside soils as a function of motorized traffic influence. Talanta, 47, 753–767. PII S0039-9140(98)00117-9.
Cattell, R. B. (1966). The Scree test for the number of factors. Multivariate Behavioural Research, 1, 245–276.
Collett, R. S., Oduyemi, K., & Lill, D. E. (1998). An investigation of environmental levels of cadmium and lead in airbone matter and surface soils within the locality of a municipal waste incinerator. Science of the Total Environment, 209, 157–167.
Critto, A., Carlon, C., & Marcomini, A. (2003). Characterization of contaminated soil and groundwater surrounding an illegal landfill (S.Giuliano, Venice, Italy) by principal components analysis and kriging. Enivironmental Pollution, 122, 235–244. PII: S0269-7491(02)00296-8.
Einax, J. W., Zwanziger, H. W., & Geib, S. (1997). Chemometrics in Environmental Analysis. Weinheim: VCHWiley.
Feng, X., Melander, A. P., & Klaue, B. (2000). Contribution of municipal waste incineration to trace metal deposition on the vicinity. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 119, 295–316.
Gee, G. W., & Bauder, J. W. (1986). Particle-size analysis. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods (2nd ed., pp. 399–404). Madison: ASA-SSSA.
Li, X., Lee, S., Wong, S., Shi, W., & Thornton, I. (2004). The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environmental Pollution, 129, 113–124. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2003.09.030.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of DTPA test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 421–428.
Llobet, J. M., Schuhmacher, M., & Domingo, J. L. (2002). Spatial distribution and temporal variation of metals in the vicinity of a municipal solid waste incinerator after a modernization of the flue gas cleaning system of the facility. Science of the Total Environment, 284, 205–214. PII: S 0 0 4 8-9 6 9 7 Ž 0 1 . 0 0 8 8 6-5.
Maio, S., Nuvolone, D., della Maggiore, R., Fresco, R., Baldacci, S., Martini, F., et al. (2006). GIS for epidemiological studies, 8th Agile Conference on GIS Sciences, 26–28 May, Estoril Portugal.
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 300, 229–243
Morselli, L., Bartoli, M., Brusoni, B., & Passarini, F. (2002). Application of an integrated environment al monitoring system to an incineration plant. Science of the Total Environment, 289, 117–188. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00170-3.
Nadal, M., Bocio, A., Schumacher, M., & Domingo, J. L. (2005). Trends in the levels of metals in soils and vegetation samples collected near a hazardous waste incinerator. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 49, 290–298. doi:10.1007/s00244-004-0262-2.
Petruzzelli, G. (1989). Recycling wastes in agriculture: Heavy metal bioavailability. Agriculture Ecosystem and Environment, 27, 493–503.
Reimann, C., & Filzmoser, P. (2000). Normal and lognormal distribution in geochemistry: Death of a myth. Consequences for the statistical treatment of geochemical and environmental data. Environmental Geology, 39(9), 1001–1014.
Rimmer, D. L., Vizard, C. G., Pless-Mulloli, T., Singleton, I., Air, V. S., & Keatinge, Z. A. F. (2006). Metal contamination of urban soils in the vicinity of a municipal waste incinerator: One source among many. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 207–216. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.04.037.
Rovira, J., Mari, M., Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M., & Domingo, J. L. (2010). Environmental monitoring of metals, PCDD/Fs and PCB as a complementary tool of biological surveillance to assess human health risks. Chemosphere, 80, 1183–1189. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.06.016.
Sillanpää, M., & Jansson, H. (1992). Status of cadmium, lead, cobalt and selenium in soils and plants of thirty countries. FAO.
Theocharopoulos, S. P., Wagner, G., Sprengart, J., Mohr, M.-E., Desaules, A., Muntau, H., et al. (2001). European soil sampling guidelines for soil pollution studies. The Science of the Total Environment, 264, 51–62.
Wright, R. J., & Stuczynski, T. I. (1996). Atomic absorption and flame emission spectrometry. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis: Part 3. Chemical methods and processes. Science Society of America Journal Book Series 5, SSSA, Madison, WI, pp. 65–90.
Yongming, H., Peixuan, D., Junji, C., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355, 176–186. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.02.026.
Zhang, G. (2006). Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Pollution, 142, 501–511. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bretzel, F.C., Calderisi, M. Contribution of a municipal solid waste incinerator to the trace metals in the surrounding soil. Environ Monit Assess 182, 523–533 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1894-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1894-0