Abstract
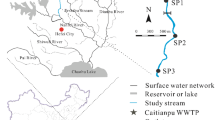
The aim of this study was to better understand the fate of nutrients discharged by sewage treatment plants into an intermittent Mediterranean river, during a low-flow period. Many pollutants stored in the riverbed during the low-flow period can be transferred to the downstream environments during flood events. The study focused on two processes that affect the fate and the transport of nutrients, a physical process (retention in the riverbed sediments) and a biological process (denitrification). A spatial campaign was carried out during a low-flow period to characterize the nutrient contents of both water and sediments in the Vène River. The results showed high nutrient concentrations in the water column downstream of the treated wastewater disposal (up to 13,315 μg N/L for ammonium and 2,901 μg P/L for total phosphorus). Nutrient concentrations decreased rapidly downstream of the disposal whereas nutrient contents in the sediments increased (up to 1,898 and 784 μg/g for total phosphorus and Kjeldahl nitrogen, respectively). According to an in situ experiment using sediment boxes placed in the riverbed for 85 days, we estimated that the proportion of nutrients trapped in the sediments represents 25% (respectively 10%) of phosphorus (respectively nitrogen) loads lost from the water column. In parallel, laboratory tests indicated that denitrification occurred in the Vène River, and we estimated that denitrification likely coupled to nitrification processes during the 85 days of the experiment was significantly involved in the removal of nitrogen loads (up to 38%) from the water column and was greater than accumulation processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin, D. S., & Mitchell, A. M. (2000). The effects of drying and re-flooding on the sediment and soil nutrient dynamics of lowland river-floodplain systems: A synthesis. Regulated Rivers: Research and Management, 16, 457–467.
Bentzen, E., Taylor, W. D., & Millard, E. S. (1992). The importance of dissolved organic phosphorus to phosphorus uptake by limnetic plankton. Limnology Oceanography, 37, 217–31.
Berenzen, N., Schulz, R., & Liess, M. (2001). Effects of chronic ammonium and nitrite contamination on the macroinvertebrate community in running water microcosms. Water Research, 35, 3478–3482.
Boström, B., Andersen, J. M., Siegfried, F., & Jansson, M. (1988). Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment water interface. Hydrobiologia, 170, 229–244.
Bowes, M. J., & House, W. A. (2001). Phosphorus and dissolved silicon dynamics in the River Swale catchment, UK: A mass-balance approach. Hydrological Processes, 15, 261–280.
Bowes, M. J., House, W. A., & Hodgkinson, R. A. (2003). Phosphorus dynamics along a river continuum. The Science of The Total Environment, 313, 99–212.
Bowes, M. J., Leach, D. V., & House, W. A. (2004). Seasonal nutrient dynamics in a chalk stream: The River Frome, Dorset, UK. The Science of The Total Environment, 336, 225–241.
Bradley, P. M., McMahon, P. B., & Chapelle, F. H. (1995). Effects of carbon and nitrate on denitrification in bottom sediments of an effluent-dominated river. Water Resource Research, 131, 1063–1068.
Brezonik, P. L. (1997). Denitrification in natural waters. Progress in Water Technology, 8, 373–972.
Bukaveckas, P. A., Guelda, D. L., Jack, J., Koch, R., Sellers, T., & Shostell, J. (2005). Effects of point source loadings, sub-basin inputs and longitudinal variation in material retention on C, N and P delivery from the Ohio River basin. Ecosystems, 8, 825–840.
Cooke, J. G., & White, R. E. (1997). The effect of nitrate in stream water on the relationship between denitrification and nitrification in a stream-sediment microcosm. Freshwater Biology, 18, 213–226.
D’Angelo, D. J., Webster, J. R., & Benfield, E. F. (1991). Mechanisms of stream phosphorus retention: An experimental study. Journal of the North American. Benthological Society, 10(3), 225–237.
Dodds, W. K. (2003). The role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow freshwater aquatic systems. Journal of Phycology, 39, 840–849.
Dorioz, J. M., Pilleboue, E., & Ferhi, A. (1989). Phosphorus dynamics in watersheds: Role of trapping processes in sediments. Water Research, 23, 147–158.
Dorioz, J. M., Pelletier, J. P., & Benoit, P. (1998). Propriétés physico-chimiques et biodisponibilité potentielle du phosphore particulaire selon l’origine des sédiments dans un bassin versant du lac Léman. (France). Water Research, 32(2), 275–286.
Drolc, A., Koncan, J. Z., & Tisler, T. (2007). Evaluation of point and diffuse sources of nutrients in a river basin on base of monitoring data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 129, 461–470.
Féray, C., & Montuelle, B. (2003). Chemical and microbial hypotheses explaining the effect of wastewater treatment plant discharges on the nitrifying communities in freshwater sediment. Chemosphere, 50, 919–928.
Garnier, J. A., Mounier, E. M., Laverman, A. M., & Billen, G. F. (2010). Potential denitrification and nitrous oxide production in the sediments of the Seine River drainage network (France). Journal of Environmental Quality, 39, 449–459. doi:10.2134/jeq2009.0299.
Gottschal, J. C. (1986). Occurrence and functioning of anaerobic bacteria in oxidized environments. In V. Jensen, A. Kjoller, & L. H. Sorensen (Eds.), Microbial communities in soil. London: Elsevier.
Grillot, C. (2006). Fonctionnement hydrologique et dynamique des nutriments d’une rivière intermittente méditerranéenne en étiage et en crues. Analyse spatiale et temporelle (p. 292). Thèse de Doctorat Thesis, Montpellier.
Haggard, B. E., Stanley, E. H., & Storm, D. E. (2005). Nutrient retention in a point-source-enriched stream. Journal of the North American. Benthological Society, 24, 29–47.
House, W. A. (2003). Geochemical cycling of phosphorus in rivers. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 739–748.
House, W. A., & Casey, H. (1989). Transport of phosphorus in rivers. In H. Tiessen, J. K. Syers, L. Ryczkowski & H. L. Golterman (Eds.), Phosphorus cycles in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Regional SCOPE workshop 1: Europe (pp. 253–82). Canada: Saskatchewan Institute of Pedology.
House, W. A., & Denison, F. H. (1997). Nutrient dynamics in a lowland stream impacted by sewage effluent: Great Ouse, England. The Science of the Total Environment, 205, 25–49.
House, W. A., & Denison, F. H. (2002). Total phosphorus content of river sediments in relationship to calcium, iron and organic matter concentrations. The Science of the Total Environment, 282–283, 341–351.
Jarvie, H. P., Neal, C., Williams, R. J., Sutton, E. J., Neal, M., Wickham, H. D., et al. (2002). Phosphorus sources, speciation and dynamics in the lowland eutrophic River Kennet, UK. The Science of the Total Environment, 282–283, 175–203.
Jarvie, H. P., Neal, C., Juergens, M. D., Sutton, E. J., Neal, M., Wickham, H. D., et al. (2006). Within-river nutrient processing in Chalk streams: The Pang and Lambourn, UK. Journal of Hydrology, 330, 101–125.
Kemp, M. J., & Dodds, W. K. (2002). Comparisons of nitrification and denitrification in prairie and agriculturally influenced streams. Ecological Applications, 12(4), 998–1009.
Keup, L. E. (1968). Phosphorus in flowing waters. Water Research, 2, 373–386.
Jacobson, P. J., Jacobson, K. M., Angermeier, P. L., & Cherry, D. S. (2004). Variation in material transport and water chemistry along a large ephemeral river in the Namid Desert. Freshwater Biology, 44, 481–491.
Lofton, D. D., Anne, Æ., Hershey, E., Steve, Æ., & Whalen, C. (2007). Evaluation of denitrification in an urban stream receiving wastewater effluent. Biogeochemistry, 86, 77–90.
Merseburger, G. C., Marti, E., & Sabater, F. (2005). Net changes in nutrient concentrations below a point source input in two streams draining catchments with contrasting land uses. The Science of the Total Environment, 347, 217–229.
Marti, E., & Sabater, F. (1996). High variability in temporal and spatial nutrient retention in Mediterranean streams. Ecology, 77, 854–869.
Marti, E., Aumatell, J., Godé, L., Pocha, M., & Sabater, F. (2004). Nutrient retention efficiency in streams receiving inputs from waste-water treatment plants. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 285–293
Martin, G. (1987). Point sur l’épuration et le traitement des effluents (Air, Eau) (Vol. 3, p. 298). Lavoisier: Phosphore.
Mulholland, P. J., Valett, H. M., Webster, J. R., Thomas, S. A., Cooper, L. W., Hamilton, S. K., et al. (2004). Stream denitrification and total nitrate uptake lengths measured using 15N tracer addition approach. Limnology Oceanography, 49, 809–820.
Némery, J., & Garnier, J. (2007). Origin and fate of phosphorus in the Seine watershed (France): Agricultural and hydrographic P budgets. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(G3), G03012.
Obermann, M., Rosenwinkel, K. H., & Tournoud, M. G. (2009). Investigation of first-flushes in a medium-sized mediterranean catchment. Journal of Hydrology, 373, 405–415.
Palmer-Felgate, E. J., Jarvie, H. P., Williams, R. J., Mortimer, R. J. G., Loewenthal, M., Neal, C. (2008). Phosphorus dynamics and productivity in a sewage-impacted lowland chalk stream. Journal of Hydrology, 351, 87–97.
Perrin, J.-L., & Tournoud, M.-G. (2009). Hydrological processes controlling flow generation in a small Mediterranean catchment under karstic influence. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 54, 1125-1140.
Peterson, B. J., Wollheim, W. M., Mulholland, P. J., Webster, J. R., Meyer, J. L., Tank, J. L., et al. (2001). Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science, 292, 86–90.
Picot, B., Andrianarison, T., Olijnyk, D. P., Wang, X., Qiu, J. P., & Brissaud, F. (2009). Nitrogen removal in wastewater stabilisation ponds. Desalination and Water Treatment, 4, 103–110.
Poulenard, J., Dorioz, J.-M., & Elsass, F. (2008). Analytical electron-microscopy fractionation of fine and colloidal particulate-phosphorus in riverbed and suspended sediments. Aquatic Geochemistry, 14, 193–210.
Reddy, K. R., Kadlec, R. H., Flaig, E., & Gale, P. M. (1999). Phosphorus retention in streams and wetlands: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 83–146.
Rigler, F. H. (1979). The export of phosphorus from Dartmoor catchments: A model to explain variations of phosphorus concentrations in streamwater. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 59, 659–687.
Ryther, J. H., & Dunstan, W. M. (1971). Nitrogen, phosphorous and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. Science, 171, 1008–1013.
Seintzinger, S. P. (1988). Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: Ecological and geochemical importance. Limnology Oceanography, 33, 702–724.
Sjodin, A. L., Lewis, W. M., & Saunders, J. F. III (1997). Denitrification as a component of the nitrogen budget for a large plains river. Biogeochemistry, 39, 327–342.
Svendsen, L. M., Kronvang, B., Kristensen, P., & Graesbol, P. (1995). Dynamics of phosphorus-compounds in a lowland river system—importance of retention and nonpoint sources. Hydological Processes, 9, 119–142.
Swank, W. T., & Caskey, W. H. (1982). Nitrate depletion in a second-order mountain stream. Journal of Environmental Quality, 11, 581–584.
Thornes, J. B. (1977). Channel changes in ephemeral streams: Observations, problems, and models. In K. J. Gregory (Ed.), River channel changes (pp. 317–335). Chichester: Wiley.
Thouvenot-Korppoo, M., Billen, G., & Garnier, J. (2009). Modelling benthic denitrification processes over a whole drainage network. Journal of Hydrology, 379, 239–250.
Todorova, Y., Belev, R., Topalova, Y., & Ribarova, I. (2009). Analogous simulation of nutrient transformation processes in stream sediments. Water SA, 35, 561–565.
Tournoud, M., Perrin, J., Gimbert, F., & Picot, B. (2005). Spatial evolution of nitrogen and phosphorus loads along a small Mediterranean river: Implications of bed sediments. Hydrological Processes, 19(18), 3581–3592.
Triska, F. J., Kennedy, V. C., Avanzino, R. J., Zellweger, G. W., & Bencala, K. E. (1989). Retention and transport of nutrients in a third-order stream. Channel Processes Ecology, 70, 1877–1892.
Wahl, M. H., McKellar, H. N., & Williams, T. M. (1997). Patterns of nutrient loading in forested and urbanized coastal streams. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 213, 111–131.
Withers, P. J. A., & Jarvie, H. P. (2008). Delivery and cycling of phosphorus in rivers: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 400, 379–395.
Whitton, B. A., Yelloly, J. M., Christmas, M., & Hernandez, I. (1998). Surface phosphatase activity of benthic algae in a stream with highly variable ambient phosphate concentrations. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie, 26, 967–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, A., Perrin, JL., Rosain, D. et al. Implication of two in-stream processes in the fate of nutrients discharged by sewage system into a temporary river. Environ Monit Assess 181, 491–507 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1844-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1844-2