Abstract
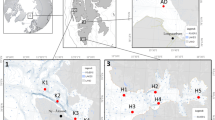
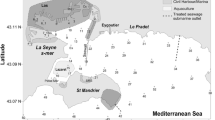
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) were measured in two dated salt marsh cores of the Venice Lagoon to assess their input chronology and to evaluate the importance of atmospheric deposition as a source. Sampling sites were chosen in order to evidence the differences between areas located leeward and windward with respect to inputs originating in both the city of Venice and the industrial area. Concentrations of PCB indicators (0.13–15.6 ng g − 1) increased gradually from the 1930s, reached maxima from the 1950s to the late 1970s, and then decreased. PCB loadings to marshes are driven by both the atmospheric deposition and the resuspension of subtidal sediments, this latter being more important for heavier congeners. The downwind marsh recorded higher fluxes (0.06–9.72 ng cm − 2 year − 1) than the upwind one (0.01–0.53 ng cm − 2 year − 1). Recent fluxes are rather consistent with bulk deposition measurements. A higher contribution of CB-101 and CB-118 was detected in the intermediate layers of the downwind site, suggesting a different PCB source for the corresponding time interval. In the other marsh, PCBs showed a rather constant composition at all levels (mostly CB-153, CB-138 and CB-180), accounting for a regional influence. Deep layers showed an enrichment of higher chlorinated congeners at both sites, whereas recent samples conserve the patterns typical of surficial and subsurficial subtidal sediments. The scientific approach adopted in this research can be considered as a sort of methodological procedure for the determination of fluxes and pathways of PCBs through the study of marsh cores.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleby, P. G. & Oldfield, F (1978). The calculation of lead-210 dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. Catena, 5, 1–8.
Battiston, G. A., Degetto, S., Gerbasi, R., Sbrignadello, G., & Tositti, L. (1988). The use of 210Pb and 137Cs in the study of sediment pollution in the lagoon of Venice. Science of the Total Environment, 77, 15–23.
Bedard, D. L., & May, R. J. (1996). Characterization of the polychlorinated biphenyls in the sediments of woods pond: Evidence for microbial dechlorination of Aroclor 1260 in situ. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 237–245.
Bellucci, L. G., Frignani, M., Raccanelli, S., & Carraro, C. (2000). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in surficial sediments of the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 65–76.
Bellucci, L. G., Frignani, M., Cochran, J. K., Albertazzi, S., Zaggia, L., Cecconi, G., (2007). 210Pb and 137Cs as chronometers for salt marsh accretion in the Venice Lagoon – Links to flooding frequency and climate change. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 97, 85–102.
Bozlaker, A., Odabasi, M., & Muezzinoglu, A. (2008). Dry deposition and soil-air gas exchange of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in an industrial area. Environmental Pollution, 156, 784–793.
Breivik, K., Sweetman, A., Pacyna, J. M., & Jones, K. C. (2002). Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners — A mass balance approach. 2. Emissions. Science of the Total Environment, 290, 199-224.
Brown, J. F., Bedard, D. L., Brennan, M. J., Carnahan, J. C., Feng, H., & Wagner, R. E. (1987). Polychlorinated biphenyl dechlorination in aquatic sediments. Science, 236, 709–712.
Bzdusek, P. A., Lu, J., & Christensen, E. R. (2006). PCB congeners and dechlorination in sediments of Sheboygan River, Wisconsin, determined by matrix factorization. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 109–119.
Callaway, J. C., Delaune, R. D., & Patrick, W. H. (1998). Heavy metal chronologies in selected coastal wetlands from Northern Europe. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 36, 82–96.
Casado-Martinez, M. C., Buceta, J. L., Belzunce, M. J., & Delvalls, T. A. (2006). Using sediment quality guidelines for dredged material management in commercial ports from Spain. Environment International, 32, 388–396.
Castro-Jimenez, J., Deviller, G., Ghiani, M., Loos, R., Mariani, G., Skejo, H., (2008). PCDD/F and PCB multi-media ambient concentrations, congener patterns and occurrence in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Etang de Thau, France). Environmental Pollution, 156, 123–135.
CNR-IGM (2000). Progetto Orizzonte 2023. Linea C. Inquinamento e dinamica dei sedimenti. Technical Report, MAV/CVN, Venice, Italy.
Cochran, J. K., Frignani, M., Salamanca, M., Bellucci, L. G., & Guerzoni, S. (1998a). Lead-210 as a tracer of atmospheric input of heavy metals in the northern Venice Lagoon. Marine Chemistry, 62, 15–29.
Cochran, J. K., Hirschberg, D. J., Wang, J., & Dere, C. (1998b). Atmospheric deposition of metals to coastal waters (Long Island Sound, New York U.S.A.): Evidence from saltmarsh deposits. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 46, 503–522.
Cundy, A. B., & Croudace, I. W. (1995). Sedimentary and geochemical variations in a salt marsh/mud flat environment from the mesotidal Hamble estuary, Southern England. Marine Chemistry, 51, 115–132.
Cundy, A. B., Croudace, I. W., Thomson, J., & Lewis, J. T. (1997). Reliability of salt marshes as “geochemical recorders” of pollution input: A case study from contrasting estuaries in Southern England. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 1093–1101.
Day, J. W., Scarton, F., Rismondo, A., & Are, D. (1998). Rapid deterioration of a salt marsh in Venice Lagoon. Journal of Coastal Research, 14, 583–590.
Degetto, S., & Cantaluppi, C. (2004). Radiochemical methodology for the determination of the mass balance of suspended particulate materials exchanged at the inlets of the Venice Lagoon. Journal of Marine Systems, 51, 77–94.
Diamond, M. L., Melymuk, L., Csiszar, S. A., & Robson, M. (2010). Estimation of PCB stocks, emissions and urban fate: Will our policies reduce concentrations and exposures? Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 2777–2783.
Di Domenico, A., Turrio Baldassarri, L., Ziemaki, G., De Felip, E., La Rocca, C., Ferrari, G., (1998). Priority microcontaminants in sediment samples from the Venice Lagoon: A selection of concentration data and predominant analytical features. Organohalogen Compouds, 39, 205–210.
Duinker, J. C., & Bruchertall, F. (1989). On the distribution of atmospheric polychlorinated congeners between vapor, aerosols, and rain. Environmental Science and Technology, 23, 57–62.
EFSA (2005). Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the commission related to the presence of non dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in feed and food. EFSA Journal, 284, 1–137. http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/scdocs/scdoc/284.htm. Accessed on 3 February 2010.
Fängmark, I., Stromberg, B., Berge, N., & Rappe, C. (1994). Influence of postcombustion temperature profiles on the formation of PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBzs, and PCBs in a pilot incinerator. Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 624–629.
Fox, W. M., Connor, L., Copplestone, D., Johnson, M. S., & Leah, R. T. (2001). The organochlorine contamination history of the Mersey estuary, U.K., revealed by analysis of sediment cores from salt marshes. Marine Environmental Research, 51, 213–227.
França, S., Vinagre, C., Caçador, I., & Cabral, H. N. (2005). Heavy metal concentrations in sediment, benthic invertebrates and fish in three salt marsh areas subjected to different pollution loads in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 998–1003.
French, P. W. (1996). Implications of a saltmarsh chronology for the Severn Estuary based on independent lines of dating evidence. Marine Geology, 135, 115–125.
Frignani, M., Bellucci, L. G., Carraro, C., & Favotto, M. (2004). Accumulation of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Venice Lagoon and the industrial area of Porto Marghera. Chemosphere, 54, 1563–1572.
Frignani, M., Bellucci, L. G., Carraro, C., & Raccanelli, S. (2001). Polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Venice Lagoon. Chemosphere, 43, 567–575.
Frignani, M., Piazza, R., Bellucci, L. G., Cu, N. H., Zangrando, R., Albertazzi, S., (2007). Polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Tam Giang-Cau Hai lagoon, Central Vietnam. Chemosphere, 67, 1786–1793.
Gevao, B., Hamilton-Taylor, J., Murdoch, C., Jones, K. C., Kelly, M., & Tabner, B. J. (1997). Depositional time trends and remobilization of PCBs in lake sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 3274–3280.
Guebuem, K., Alleman, L. Y., & Church, T. M. (2004). Accumulation records of radionuclides and trace metals in two contrasting Delaware salt marshes. Marine Chemistry, 87, 87–96.
Guerzoni, S. (2000). Project “Orizzonte 2023” section A. Contribution of the atmospheric fallout to the inputs to the Venice Lagoon. Final Report, Magistrato alle Acque di Venezia – Consorzio Venezia Nuova, Venice.
Guerzoni, S., Rossini, P., Sarretta, A., Raccanelli, S., Ferrari, G., & Molinaroli, E. (2007). POPs in the Lagoon of Venice: Budgets and pathways. Chemosphere, 67, 1776–1785.
Harner, T., Mackay, D., & Jones, K. C. (1995). Modeling the long term exchange of PCBs between soil and the atmosphere in the Southern UK. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 1200–1209.
Herrick, R. F., McClean, M. D., Meeker, J. D., Baxter, L. K., & Waymouth, G. A. (2004). An unrecognized source of PCB contamination in schools and other buildings. Environmental Health Perspectives, 112, 1051–1053.
Hung, G. A., & Chmura, G. L. (2006). Mercury accumulation in surface sediments of salt marshes of the Bay of Fundy. Environmental Pollution, 142, 418–431.
Hyun-Gu, Y., Minkyu, C., Man-Young, C., & Young, S. (2003). Gas/particle concentrations and partitioning of PCBs in the atmosphere of Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 3561–3570.
ICES (2002). Committee on toxicity of chemicals in food, consumer products and the environment. In Meeting held on Wednesday 27 February 2002 at the De Vere Dunton Hall, Norwich. Available online at http://cot.food.gov.uk/pdfs/200201feb.pdf. Accessed on 3 February 2010.
Kohler, M., Tremp, J., Zennegg, M., Seiler, C., Minder-Kohler, S., Beck, M., (2005). Joint sealants: An overlooked diffuse source of polychlorinated biphenyls in buildings. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 1967–1973.
Mai, B., Zeng, E. Y., Luo, X., Yang, Q., Zhang, G., Li, X., (2005). Abundances, depositional fluxes, and homologue patterns of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in dated sediment cores from the Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 49–56.
Marani, C. (1999). Determinazione del Flusso di 210 Pb mediante analisi dei depositi al suolo. Ph.D. Thesis, Environmental Chemistry, University of Bologna, Italy.
Marcomini, A., Zanette, M., D’ Andrea, F., Della Sala, S. (1997). Diossine, ambiente e salute (p. 102). Venezia: Arsenale Editrice.
Masque, P., Sanchez-Cabeza, J. A., Bruach, J. M., Palacios, E., & Canals, M. (2002). Balance and residence times of 210Pb and 210Po in surface waters of the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 22, 2127–2146.
McCaffrey, R. J., & Thomson, J. (1980). A record of the accumulation of sediment and trace metals in a Connecticut salt marsh. In B. Saltzman (Ed.), Estuarine physics and chemistry: Studies in Long Island sound. Advances in geophysics (Vol. 22, pp. 165–235). New York: Academic Press.
Moret, I., Piazza, R., Benedetti, M., Gambaro, A., Barbante, C., & Cescon, P. (2001). Determination of polychloro biphenyls in Venice Lagoon sediments. Chemosphere, 43, 559–565.
Orson, R. A. (1996). Some applications of paleoecology to the management of tidal marshes. Estuaries, 19, 236–246.
Pandelova, M., Stanev, I., Henkelmann, B., Lenoir, D., & Schramm, K. W. (2009). Correlation of PCDD/F and PCB at combustion experiments using wood and hospital waste. Influence of (NH4)2SO4 as additive on PCDD/F and PCB emissions. Chemosphere, 75, 685–691.
Quensen, J. F., Tiedje, J. M., & Boyd, S. A. (1988). Reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls by anaerobic microorganisms from sediments. Science, 242, 752–754.
Robbins, J. A. (1978). Geochemical and geophysical application of radioactive lead. In J. O. Nriagu (Ed.), The biogeochemistry of lead in the environment (pp. 285–393). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Robson, M., & Harrad, S. (2004). Chiral PCB signatures in air and soil: Implications for atmospheric source apportionment. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 1662–1666.
Rossini, P., Guerzoni, S., Matteucci, G., Gattolin, M., Ferrari, G., & Raccanelli, S. (2005a). Atmospheric fall-out of POPs (PCDD-Fs, PCBs, HCB, PAHs) around the industrial district of Porto Marghera, Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 349, 190–200.
Rossini, P., Guerzoni, S., Molinaroli, E., Rampazzo, G., De Lazzari, A., & Zancanaro, A. (2005b). Atmospheric bulk deposition to the lagoon of Venice. Part I. Fluxes of metals, nutrients and organic contaminants. Environment International, 31, 959–974.
Secco, T., Pellizzato, F., Sfriso, A., & Pavoni, B. (2005). The changing state of contamination in the Lagoon of Venice. Part 1: Organic pollutants. Chemosphere, 58, 279–290.
Selliah, S. S., Cussion, S., MacPherson, K. A., Reiner, E. J., & Toner, D. (2001). Development of a reference material for routine performance monitoring of methods measuring polychorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 370, 208–212.
Spencer, K. L., Cundy, A. B., & Croudace, I. W. (2003). Heavy metal distribution and early-diagenesis in salt marsh sediments from the Medway Estuary, Kent, UK. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 57, 43–54.
Sprovieri, M., Feo, M. L., Prevedello, L., Manta, D. S., Sammartino, S., Tamburrino, S., (2007). Heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of the Naples harbour (southern Italy). Chemosphere, 67, 998–1009.
Turekian, K. K., Nozaki, Y., Benninger, L., & Thomson, J. (1977). Geochemistry of atmospheric radon and radon products. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 5, 227–255.
Yamashita, N., Kannan, K., Imagawa, T., Villeneuve, D. L., Hashimoto, S., Miyazaki, A., (2000). Vertical profile of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, naphthalenes, biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and alkylphenols in a sediment core from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 3560–3567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mugnai, C., Giuliani, S., Bellucci, L.G. et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls in two salt marsh sediments of the Venice Lagoon. Environ Monit Assess 181, 243–254 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1826-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1826-4