Abstract
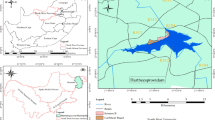
Mountainous areas, which form the largest geography of our country and are called reserves of resources owing to their difficulty of accessibility, have been increasingly under threat of exploitation and overuse in recent years. The area in question from among the mountainous areas, which are sensitive ecosystems with their environmental components, is the Bozdağ mass located in Gölcük Plateau Settlement, which has been subject to intensive construction and use. This study is intended to reveal the current uses of Gölcük Plateau (agricultural, recreation, and tourism) and determine the sources and effects of pollution as a result of these uses and aims at revealing how the permanent residents of Gölcük Plateau Settlement on Bozdağ Plateau, which is a center of attraction with respect of recreation and tourism activities, and those who go there only in certain periods, use the environment for tourism and recreational purposes, and determine their positive and negative impacts on environment through SWOT analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blangy, S., & Wood, M. E. (1991). Developing and implementing ecotourism guidelines for wildlands and neighboring communities. In K. Lindberg, & D. E. Hawkins (Eds.), Ecotourism: A guide for planners and managers (pp. 32–54). North Bennington: The Ecotourism Society.
Boyd, S. W., & Butler, R. W. (1996). Managing ecotourism: An opportunity spectrum approach. Tourism Management, 17(8), 557–566.
Butler, R. W. (1990). Alternative tourism: Pious Hope or Trojan Horse? Journal of Travel Research, 28(3), 40–45.
Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation, 18, 201–209.
Cirik, S., & Cirik, Ş. (1989). Gölcük‘ ün (Bozdağ/İzmir) planktonik algleri. İ.Ü. Su Ürünleri Yüksek Okulu. Su Ürünleri Dergisi 3(1–2), 131–150.
Countryside Working Group (1991). Tourism and the environment task force. Final Report.
Demirel, Ö. (1988). İzmir İli Yakın Çevresinde Deniz Kıyısından Uzak Dinlenme Evleri, E.Ü.Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Bornova/İzmir.
Demirel, Ö. (1992). Gölcük (Ödemiş-İzmir) Yayla Yerleşiminin Turistik ve Rekreasyonel Kullanımlar Açısından İncelenmesi, Araştırma Raporu, Ankara Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Peyzaj Mimarlığı Bölümü, Ankara, 28.
Demirel, Ö. (1998). Chevetogne (Namur-Belçika) Bölgesi Ormanı’nda Rekreasyonel ve Turistik Kullanımlar ve Bunların Olumsuz Etkileri. Peyzaj Mimarları Odası. Peyzaj Mimarlığı Dergisi (pp. 19–24).
Demirel, Ö., Sezgin, N., ve Ertuğrul, H. (1996). Gölcük Gölü (Ödemiş-İzmir)’nde Tarımsal Uygulamalar ve Rekreasyonel Kullanımlardan Kaynaklanan Kirlilik Boyutunun İrdelenmesi Üzerine Bir Araştırma, Tarım-Çevre İlişkileri Sempozyumu “Doğal Kaynakların Sürdürülebilir Kullanımı” (pp. 895–908). Türkiye: Mersin.
Doan, T. M. (2000). The effects of ecotourism in developing nations: An analysis of case studies. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 8(4), 288–304.
Farrell, B. H., & Runyan, D. (1991). Ecology and tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 18(1), 26–41.
Fennell, D., & Eagles, P. F. J. (1990). Ecotourism in Costa Rica: A conceptual framework. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration, 8(1), 23–34.
Gülez, S. (1994). Green tourism: A case study. Annals of Tourism Research, 21(2), 413–415.
Halbertsma, N. F. (1988). Proper management is a must. Naturopa, 59, 23–24.
Higgins, B. R. (1996). The global sturucture of the nature tourism industry: Ecotourists, tour operators, and local businesses. Journal of Travel Research, 35(2), 11.
Koçman, A. (1989). Uygulamalı Fiziki Coğrafya Çalışmaları ve İzmir-Bozdağlar Yöresi Üzerinde Araştırmalar. E.Ü.Edebiyat Fak.Yay:49. İzmir.
Lindberg, K., & Hawkins, D. E. (1993). Ecotourism: A guide for planners & managers. North Bennington: The Ecotourism Society.
May, U. (1991). Tourism, environment and development: Values, sustainability and stewardship. Tourism Management, 12(2), 112–118.
Montanari, A. (1994). Tourism and environment in Europe: Socio-economic aspects, report proposal for the Eurepean Environmental Bureau. Bruxelles.
Notzke, C. (1999). Indigenous tourism development in the Arctic. Annals of Tourism Research, 26(1), 55–76.
Pearce, D. G. (1985). Tourism and environmental research: A review. Journal of Environmental Studies, 25, 247–255.
Prentice, R. (1989). Environmental analysis in tourism. In S. Witt, & L. Mountinho (Eds.), Tourism marketing and management handbook Prentice Hall (pp. 131–136).
Soykan, F. (1994). Bozdağlar’da (Ege Bölgesi) Rekreatif Yaylacılık. Turizm Yıllığı (pp. 292–306).
tRAVIS, A. S. (1988). “Alternative” tourism. Naturopa, 59, 25–27.
UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) (1987). Transport/tourism. Environmental data report (Vol. 7, pp. 312–341). Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
Uysal, M., Jurowski, C., Noe, F. P., & McDonald, C. D. (1994). Environmental attitude by trip and visitor characteristics-US Virgin Islands National Park. Tourism Management, 15(4), 284–294.
Ülker, İ. (1988). Türkiye’de Sağlık Turizmi ve Kaplıca Planlaması. Kültür ve Turizm Bakanlığı Kültür Eserleri Dizisi:129, Ankara.
Var, T. (1991). Sustainable tourism development. Annals of Tourism Research, 18(2), 327–329.
Vardar, S. (2002). Bozdağlar ve Gölcük Gölü’nün (Ödemiş-İzmir) Jeomorfolojik Gelişimi. Türkiye Dağları I.Ulusal Sempozyumu. Bildiriler Kitabı;137–142, 25–27 Haziran. Ilgaz/Kastamonu.
Wall, G. (1997). Is Ecotourism sustainable? Environmental Management, 21(4), 483–491.
Yavuz, B. G. (1986). Ödemiş Yöresinin Genel Tarihi. Ödemiş Belde Yıllığı (pp. 3–13).
Yılmaz, N. (1991). Gölcük (Ödemiş) Yakın Çevresinde Yaylacılık ve Sosyo-Ekonomik Etkinlikler. Lisans Tezi. Ege Üniversitesi Edebiyat Fakültesi Beşeri ve İktisadi Coğrafya Anabilim Dalı. Bornova/İzmir.
Yonglong, L. (1991). Eco-tourism industry development—An alternative to sustainable use of landscape resources . Journal of Environmental Sciences, 8(3), 298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk Kurtaslan, B., Demirel, Ö. Pollution caused by peoples’ use for socio-economic purposes (agricultural, recreation and tourism) in the Gölcük Plain Settlement at Bozdağ Plateau (Ödemiş-İzmir/Turkey): a case study. Environ Monit Assess 175, 419–430 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1540-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1540-2