Abstract
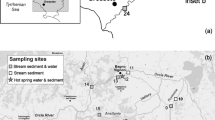
The Iron Quadrangle has been one of the most important gold production regions in Brazil since the end of the seventeenth century. There, arsenic occurs in close association with sulfide-rich auriferous rocks. The most abundant sulfide minerals are pyrite and arsenopyrite, yet trace metal sulfides occur in subordinate phases as well. Historical mining activities have been responsible for the release of As and trace metals to both aquatic and terrestrial environments close to mining sites in the region. Therefore, this study was aimed to evaluate the distribution and mobility of As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in streams in the southeast portion of the Iron Quadrangle between the municipalities of Ouro Preto and Mariana, the oldest Brazilian Au mining province. Total concentrations of some trace metals and arsenic in water were determined. The four-stage sequential extraction procedure proposed by the commission of the European Communities Bureau of Reference (BCR) was used to investigate the distribution of these elements in stream sediments. Arsenic concentration in water was >10 μg L − 1 (maximum limit permitted by Brazilian environmental regulations for water destined for human consumption) at all sampling sites, varying between 36.7 and 68.3 μg L − 1. Sequential extraction in sediments showed high concentrations of As and trace metals associated with easily mobilized fractions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basílio, M. S., Friese, K., Lena, J. C., Nalini Júnior, H. A., & Roeser, H. M. P. (2005). Adsorption of As, Cu, Pb and Cr for the assessment of metal retention by two different residues from iron ore mines. Química Nova, 28, 822–828.
Borba, R. P., Figueiredo, B. R., & Matschullat, J. (2003). Geochemical distribution of arsenic in waters, sediments and weathered gold mineralized rocks from Iron Quadrangle, Brazil. Environmental Geology, 44, 39–52.
Cidu, R., Biddau, R., & Fanfani, L. (2009). Impact of past mining activity on the quality of groundwater in SW Sardinia (Italy). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 100, 125–132.
CONAMA—Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (2005). Resolução No. 357. Brasil: Ministério do Desenvolvimento Urbano e Meio Ambiente, Brasília.
Craw, D., Falconer, D., & Youngson, J. H. (2003). Environmental arsenopyrite stability and dissolution: Theory, experiment and field observations. Chemical Geology, 199, 71–82.
Davidson, C. M., Thomas, R. P., McVey, S. E., Littlejohn, D. & Ure, A. M. (1994). Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of heavy metals in sediments. Analitica Chimica Acta, 291, 277–286.
Davidson, C. M., Duncan, A. L., Littlejohn, D., Ure, A. M. & Garden, L. M. (1998). A critical evaluation of the three-stage BCR sequential extraction procedure to assess the potential mobility and toxicity of heavy metals in industrially contaminated land. Analitica Chimica Acta, 363, 45–55.
Deschamps, E., & Matschullat, J. (2007). Arsênio antropogênico e natural: um estudo em regiões do Quadrilátero Ferrífero (p. 330). Belo Horizonte: FEMA.
Deschamps, E., Cimineli, V. S. T., Lange, F. T., Matschullat, J., Raue, B., & Schmidt, H. (2002). Soil and sediment geochemistry of the Iron Quadrangle, Brazil: The case of arsenic. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2, 216–222.
Deschamps, E., Carneiro, M. E. D. P., Ciminelli, V. S. T., Peter, W. & Ramos, A. (2003). Arsenic sorption onto soils enriched in Mn and Fe minerals. Clays and Clay Minerals, 51, 198–205.
Dhoum, R. T., & Evans, G. J. (1998). Evaluation of uranium and arsenic retention by soil from a low-level radioactive waste management site, using sequential extraction. Applied Geochemistry, 13, 415–420.
EMBRAPA (1997). Manual de métodos de análise do solo. Rio de Janeiro: Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos.
Figueiredo, M. A., Varajão, A. F. D. C., Fabris, J. D., Loutfi, I. F., & Carvalho, A. P. (2004). Superficial alteration and pedogeomorphology in the south of the Bação Complex–Quadrilátero Ferrífero–MG, Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Ciências do Solo, 28, 713–729.
Filgueiras, A. V., Lavilla, I., & Bendicho, C. (2004). Chemical sequential extraction for metal partitioning in environmental solid samples. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 4, 823–857.
Fontes, M. P. F., & Gomes, P. C. (2003). Simultaneous competitive adsorption of heavy metals by the mineral matrix of tropical soils. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 795–804.
Giménez, J., Martínez, M., Pablo, J., Rovira, M., & Duro, L. (2007). Arsenic sorption onto natural hematite, magnetite and goethite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 575–580.
Gismera, M. J., Lacal, J., Silva, P., Garcia, R., Sevilla, M. T., & Procópio, J. R. (2004). Study of metal fractionation in river sediments. A comparison between kinetic and sequential extraction procedures. Environmental Pollution, 127, 175–182.
Gleyzes, C., Tellier, S., & Astruc, M. (2002). Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: A review of sequential extraction procedures. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 21, 451–467.
Gomes, P. C., Fontes, M. P. F., Silva, A. G., Mendonça, E. S., & Rodrigues Netto, A. (2001). Selectivity sequence and competitive adsorption of heavy metals by Brazilian soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 1115–1121.
Gonçalves, J. A. C., Lena, J. C., Paiva, J. F., Nalini, H. A. Jr., & Pereira, J. C. (2007). Arsenic in the groundwater of Ouro Preto (Brazil): Its temporal behavior as influenced by hydric regime and hydrology. Environmental Geology, 53, 785–794.
Jain, C. K., Gupta, H., & Chakrapani, G. J. (2008). Enrichment and fractionation of heavy metals in bed sediments of River Narmada, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 14, 35–47.
Kumaresan, M., & Riyazuddin, P. (2001). Overview of speciation chemistry of arsenic. Current Science, 80, 837–846.
Lakshmipathiraj, P., Narasimhan, B. R. V., Prabhakar, S., & Raju, G. B. (2006). Adsorption studies of arsenic on Mn-substituted iron oxyhydroxide. Journal of Colloids and Interface Science, 304, 317–322.
Long, G. L., & Winefordner, J. D. (1983). Limit of detection. A closer look at the IUPAC definition. Analytical Chemistry, 55, 712–724.
Marguí, E., Salvadó, V., Queralt, I., & Hidalgo, M. (2004). Comparison of three-stage sequential extraction and toxicity characteristic leaching test to evaluate metal mobility in mining wastes. Analitica Chimica Acta, 524, 151–159.
Matschullat, J., Borba, R. P., Deschamps, E., Figueiredo, B. R., Gabrio, T., & Schwenk, M. (2000). Human and environmental contamination in the Iron Quadrangle, Brazil. Applied Geochemistry, 15, 193–202.
Mello, J. W. V., Roy, W. R., Talbott, J. L. & Stucki, J. W. (2006). Mineralogy and arsenic mobility in arsenic-rich Brazilian soils and sediments. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 6, 9–19.
Mello, J. W. V., Talbott, J. L., Scott, J., Roy, W. R., & Stucki, J. W. (2007). Arsenic speciation in arsenic-rich Brazilian soils from gold mining sites under anaerobic incubation. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 14, 388–396.
Oliveira, F. R. (1998). Contribuicão ao estudo da geologia estrutural e da gênese do depósito aurífero de Passagem de Mariana-MG. M.Sc. Thesis, Unicamp, São Paulo.
Pereira, J. C., Guimarães-Silva, A. K., Nalini, H. A. Jr., Pacheco-Silva, E., & Lena, J. C. (2007). Distribution, fractionation and mobility of trace elements in stream sediments. Química Nova, 30, 1249–1255.
Pertsemli, E., & Voutsa, D. (2007). Distribution of heavy metals in lakes Doirani and Kerkini, Northen Greece. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148, 529–537.
Pueyo, M., Sastre, J., Hernández, E., Vidal, M., López-Sanchez, J. F., & Rauret, G. J. (2003). Prediction of trace element mobility in contaminated soils by sequential extraction. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 2054–2066.
Raposo, J. C., Zuloaga, O., Sanz, J., Villanueva, U., Crea, P., Extrebaria, N., et al. (2006). Analytical and thermodynamical approach to understand the mobility retention of arsenic species from river to estuary. Marine Chemistry, 99, 42–51.
Rauret, G., López-Sanchez, J. F., Sahuquillo, A., Rubio, R., Davidson, C., Ure, A., et al. (1999). Improvement of the BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 57–61.
Rimstidt, J. D., & Vaughan, D. J. (2003). Pyrite oxidation: A state-of-the-art assessment of the reaction mechanism. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67, 873–880.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Sracek, O., Bhattacharya, P., Jacks, G., Gustafsson, J.-P., & Von Brömssen, M. (2004). Behavior of arsenic and geochemical modeling of arsenic enrichment in aqueous environments. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 169–180.
Templeton, D. M., Ariese, F., Cdornelis, R., Danielsson, L. G., Muntau, H., Van Leeuwen, H. P., et al. (2000). Guidelines for terms related to chemical speciation and fractionation of elements. Definitions, structural aspects, and methodological approaches. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 72, 1453–1470.
Terlecka, E. (2005). Arsenic speciation analysis in water samples: A review of the hyphenated techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 107, 259–284.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–851.
Thomas, J. E., Smart, R. S. C., & Skinner, W. M. (2000). Kinetic factors for oxidative and non-oxidative dissolution of iron sulfides. Minerals Engineering, 13, 1149–1159.
Tokalioglu, S., Kartal, S., & Elçi, L. (2000). Determination of heavy metal and their speciation in lake sediments by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after a four-stage sequential extraction procedure. Analitica Chimica Acta, 413, 33–40.
Ure, A. M., Quevauviller, Ph., Muntau, H., & Griepink, B. (1993). Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 51, 133–151.
Varejão, E. V. V., Bellato, C. R., & Fontes, M. P. F. (2009a). Mercury fractionation in stream sediments from the Quadrilátero Ferrífero gold mining region, Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 157, 125–135.
Varejão, E. V. V., Bellato, C. R., Mello, J. W. V. & Fontes, M. P. F. (2009b). Optimization of pre-reduction conditionof As(V) in BCR extracts to quantify arsenic by Hg-AAS. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 33, 875–883.
Veado, M. A. R. V., Arantes, I. A., Oliveira, A. H., Almeida, M. R. M. G., Miguel, R. A., Severo, M. I., et al. (2006). Metal pollution in the environment of Minas Gerais State–Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 117, 157–172.
Vial, D. S. (1988). Mina de ouro de Cuiabá, QF, Minas Gerais. In: C. Schobbenhaus & C. E. S. Coelho (Eds.), Principais depósitos minerais do Brasil (Vol. 3, pp. 413–419). DNPM/CVRD, Brazil.
Vial, D. S., Duarte, B. P., Fuzikawa, K., & Vieira, M. B. H. (2007). An epigenetic origin of the Passagem de Mariana gold deposit, Quadrilátero Ferrífero, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Ore Geology Reviews, 32, 596–613.
Vink, B. W. (1996). Stability relations of antimony and arsenic compounds in the light of revised and extended Eh–pH diagrams. Chemical Geology, 130, 21–30.
Weisz, M., Polyák, K., & Hlavay, J. (2000). Fractionation of elements in sediment samples collected in rivers and harbors at Lake Balaton and its catchment’s area. Microchemical Journal, 67, 207–217.
Wilkie, J. A., & Hering, J. G. (1996). Adsorption of arsenic onto hydrous ferric oxide: Effects of adsorbate/adsorbent ratios and co-occurring solutes. Colloids and Surfaces A, 107, 97–110.
Žemberyová, M., Barteková, J., & Hagarová, I. (2006). The utilization of modified BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure for the fractionation of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in soil reference materials of different origins. Talanta, 70, 973–978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varejão, E.V.V., Bellato, C.R., Fontes, M.P.F. et al. Arsenic and trace metals in river water and sediments from the southeast portion of the Iron Quadrangle, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 172, 631–642 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1361-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1361-3