Abstract
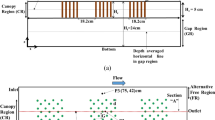
River bed scourings are a major environmental problem for fish and aquatic habitat resources. In this study, to prevent river bed and banks from scouring, different types of bed sills including convex, concave and linear patterns were installed in a movable channel bed in a laboratory flume. The bed sills were tested with nine different arrangements and under different flow conditions. To find the most effective bed sill pattern, the scouring depth was measured downstream of the bed sill for a long experimental duration. The scour depth was measured at the middle and at the end of each experimental test for different ratios of the arch radius to the channel width \((r/\emph{w})\). The experimental results indicated that the convex pattern with \(r/\emph{w}=0.35\) produced minimum bed scouring depth at the center line whereas the concave pattern with \(r/\emph{w}=0.23\) produced the minimum scour depth at the wall banks. Therefore, the convex pattern was the most effective configuration for prevention of scouring at the center line of the river while the concave pattern was very effective to prevent scouring at the river banks. These findings can be suggested to be used in practical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlinghaus, R., Engelhardt, C., Sukhodolov, A., & Wolter, C. (2002). Fish recruitment in a canal with intensive navigation: Implications for ecosystem management. Journal of Fish Biology, 61, 1386–1402.
Armstrong, J. D., Kemp, P. S., Kennedy, G. J. A., Ladle, M., & Milner, N. J. (2003). Habitat requirements of Atlantic salmon and brown trout in rivers and streams. Fisheries Research, 62(6), 143–170.
Ben Meftah, M., & Mossa, M. (2004). Experimental study of the scour hole downstream of bed sills. In M. Greco, A. Carravetta, & R. Della Morte (Eds.), RiverFlow 2004 (Vol. 2, pp. 585–592), 23–25 June, Napoli, Italy.
Bormann, N. E., & Julien, P. Y. (1991). Scour downstream of grade-control structures. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 117(5), 579–594.
Breusers, H. N. C. (1966). Conformity and time scale in two dimensional local scour. In Proc. symposium on model and prototype conformity (pp. 1–8). Poona: Hydraulic Research Laboratory.
Farhoudi, J., & Smith, K. V. H. (1982). Time scale for scour downstream of hydraulic jump. Journal of the Hydraulics Division, ASCE, 108(HY10), 1147–1162.
Farhoudi, J., & Smith, K. V. H. (1985). Local scour profiles downstream of hydraulic jump. Journal of Hydraulic Research, IAHR, 23(4), 343–358.
Gaudio, R., & Marion, A. (2003). Time evolution of scouring downstream of bed sills. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 41(3), 271–284.
Gaudio, R., Marion, A., & Bovolin, V. (2000). Morphological effects of bed sills in degrading rivers. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 38(2), 89–96.
Habib, E., Mossa, M., & Petrillo, A. (1994). Scour downstream of hydraulic jump. In Modeling, testing & monitoring for hydro power plants conference (pp. 561–602). Budapest, Hungary.
Hassan, N. M. K. N., & Narayanan, R. (1985). Local scour downstream of an apron. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 111(11), 1371–1385.
Hoffmans, G. J. C. M., & Pilarczyk, K. W. (1995). Local scour downstream of hydraulic structures. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 121(4), 326–340.
Hoffmans, G. J. C. M., & Verheij, H. J. (1997). Scour manual. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema.
Lenzi, M. A., Marion, A., Comiti, F., & Gaudio, R. (2002). Local scouring in low and high gradient streams at bed sills. Journal of Hydraulic Research, IAHR, 40(6), 731–739.
Marion, A., & Gaudio, R. V. (1998). Scour down stream of bed sills. HR Wallingford Research Report TR7. United Kingdom: Wallingford.
Van der Meulen, T., & Vinji, J. J. (1995). Three-dimensional local scour in non-cohesive sediments. In Proc. 16th IAHR congress. Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Volkart, P., Tshopp, J., & Bisaz, E. (1973). The effect of sills on river bed. In Proc. of int. symp. on river mechanics, IAHR, 1 (pp. 167–178). Bangkok.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshavarzi, A., Khaje Noori, L. Environmental protection stability of river bed and banks using convex, concave, and linear bed sills. Environ Monit Assess 171, 621–631 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1306-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1306-x