Abstract
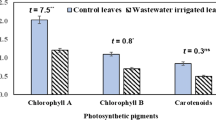
The present study was conducted to determine the heavy metal contamination in soil with accumulation in edible parts of plants and their subsequent changes in biochemical constituents due to wastewater irrigation. Though the wastewater contains low levels of the heavy metals (Fe, Mn, Pb, Cd, and Cr), the soil and plant samples show higher values due to accumulation. The trend of metal accumulation in wastewater-irrigated soil is in the order: Fe > Pb > Mn > Cr > Cd. Of the three species Colocasia esculentum, Brassica nigra, and Raphanus sativus that are grown, the order of total heavy metal accumulation in roots is Raphanus sativus > Colocasia esculentum, while in shoots the order is Brassica nigra > Colocasia esculentum > Raphanus sativus. The enrichment factor (EF) of the heavy metals in contaminated soil is in the sequence of Cd (3) > Mn (2.7) > Cr (1.62) > Pb (1.46) > Fe (1.44), while in plants EF varies depending upon the species and plant part. C. esculentum and R. sativus show a higher EF for Cr and Cd. All plants show a high transfer factor (TF > 1) for Cd signifying a high mobility of Cd from soil to plant whereas the TF values for Pb are very low as it is not bioavailable. Results of the biochemical parameters show decrease in total chlorophyll and total amino acid levels in plants and an increase in amounts of soluble sugars, total protein, ascorbic acid, and phenol except B. nigra for protein in plants grown in soil irrigated with wastewater as compared to control site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmal, M., Ahmad, A., & Nomani, A. A. (1982). Microbial uptake of cadmium and its effects on the biochemical oxygen demand. Water Research, 16, 1611–1614. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(82)90238-X.
Ajmal, M., Ahmad, A., & Nomani, A. A. (1983). Influence of toxic metals on the repression of carbonaceous oxygen demand. Water Research, 17, 799–802. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(83)90074-X.
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (20th ed.). Washington: APHA.
Barman, S. C., & Lal, M. M. (1994). Accumulation of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Cd and Pb) in soils and cultivated vegetables and weeds grown in industrially polluted fields. Journal of Environmental Biology, 15, 107–115.
Barman, S. C., Sahu, R. K., Bhargava, S. K., & Chatterjee, C. (2000). Distribution of heavy metals in wheat, mustard and weed grown in fields irrigated with industrial effluents. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64, 489–496. doi:10.1007/s001280000030.
Berg, H., Kiibus, M., & Kautsky, N. (1995). Heavy metals in tropical kariba, Zimbabwe. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 83, 237–252. doi:10.1007/BF00477355.
Bordin, G., McCourt, J., & Rodriguez, A. (1992). Trace element in the marine bivalve Macoma balthica in the Westrschelde estuary. The Science of the Total Environment, 127, 225–280. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(92)90507-O.
Cao, Z. H., & Hu, Z. Y. (2000). Copper contamination in paddy soils irrigated with wastewater. Chemosphere, 41, 3–6. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00383-5.
Chamberlin, A. C. (1983). Fallout of lead and uptake by crops. Atmospheric Environment, 17, 693–706. doi:10.1016/0004-6981(83)90416-X.
Dučić, T., Maksimović, V., & Radotić, K. (2008). Oxalate oxidase and non-enzymatic compounds of the antioxidative system in young Serbian spruce plants exposed to cadmium stress. Archives of Biological Sciences (Belgrade), 60(1), 67–76.
Farooq, M., Hans, R. K., Viswanathan, P. N., & Joshi, P. C. (1999). Health hazard from dry river bed agriculture. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 62, 555–562. doi:10.1007/s001289900911.
Fazeli, M. S., Sathyanarayan, S., Satish, P. N., & Mutanna, L. (1991). Effects of paper mill effluents on the accumulation of heavy metals in coconut trees near Najangud, Mysore District, Karnataka, India. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences, 17, 47–50. doi:10.1007/BF01716073.
Feign, A., Ravina, I., & Shalhevet, J. (1991). Irrigation with wastewater irrigated sewage effluents: Management for environmental protection. Berlin: Springer.
Giertych, M. J., & Karolewski, P. (1993). Changes in phenolic compounds content in needles of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) seedlings following short-term exposition to sulphur dioxide. Arboretum Kórnickie, 38, 43–51.
Godson, R. E., Ana, E., & Sridhar, M. K. C. (2002). Soil quality near a chemical fertilizer industry at Port Harcourt, Nigeria. AJEAM/RAGEE, 4(2), 50–57.
Guo, Z., Tan, H., Zhu, Z., Lu, S., & Zhou, B. (2005). Effect of intermediates on ascorbic acid and oxalate biosynthesis of rice and in relation to its stress resistance. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 43(10–11), 955–962. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2005.08.007.
Gupta, S., Nayek, S., Saha, R. N., & Satpati, S. (2007). Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in macrophyte, agricultural soil, and crop plants adjacent to discharge zone of sponge iron factory. Environmental Geology, 55, 731–739. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1025-y.
Harrison, R., & Chirgawi, M. B. (1989). The assessment of air and soil as contributors of some trace metals to vegetable plants I. Use of a filtered air growth cabinet. The Science of the Total Environment, 83, 13–34. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(89)90003-X.
Hsu, Y. T., & Kao, C. H. (2003). Role of abscisic acid in cadmium tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant, Cell & Environment, 26, 867–874. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.01018.x.
Karolewski, P., & Giertych, M. J. (1995). Changes in the level of phenols during needle development in Scot pine populations in a control and polluted environment. European Journal of Forest Pathology, 25, 297–306. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0329.1995.tb01345.x.
Laperche, V., Logan, T. J., Gaddam, P., & Traina, S. J. (1997). Effect of apatite amendments on plant uptake of lead from contaminated soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 2745–2753. doi:10.1021/es961011o.
Madoni, P., Davoli, D., Gorbi, G., & Vescoli, L. (1996). Toxic effects of heavy metals on the activated sludge Protozoan community. Water Research, 30, 135–141. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(95)00124-4.
Mapanda, F., Mangwayana, E. N., Myamangara, J., & Giller, K. E. (2005). The effect of long term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 107, 151–165. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2004.11.005.
Monni, S., Uhlig, C., Hansen, E., & Magel, E. (2001). Ecophysiological responses of Empetrum nigrum to heavy metal pollution. Environmental Pollution, 112, 121–129. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00125-1.
Nan, Z., Li, J., & Zhang, C. G. (2002). Cadmium and zinc interaction and their transfer in soil—crop system under actual field conditions. The Science of the Total Environment, 285, 187–195. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00919-6.
Nyamangara, J., & Mzezewa, J. (1999). The effects of long-term sewage sludge application on Zn, Cu, Ni and Pb levels in clay loam soil under pasture grass in Zimbabwe. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 73, 199–204. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(99)00056-0.
Patsikka, E., Kairavuo, M., Sersen, F., Aro, E.-M., & Tyystjarvi, E. (2002). Excess copper predisposes photosystem II to photoinhibition in vivo by outcompeting iron and causing decrease in leaf chlorophyll. Plant Physiology, 129, 1359–1367. doi:10.1104/pp.004788.
Rong Guo, T., Guo Ping, Z., & Yan Hua, Z. (2007). Physiological changes in barley plants under combined toxicity of aluminum, copper and cadmium. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 57, 182–188. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.01.013.
Sadasivam, S., & Manikam, A. (2005). Biochemical methods (2nd ed.). India: New Age International.
Sharma, R. K., Agrawal, M., & Marshal, F. (2007). Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 66(2), 258–266. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.11.007.
Sheng, P. H., Zhou, A. X., & Li, P. J. (2001). Pollution ecology. Beijing: Science Press.
Singh, K. P., Mohem, D., Sinha, S., & Dalwani, R. (2004). Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharged by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural, and environmental quality in the wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere, 55, 227–255. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.050.
Sinha, S., Gupta, A. K., Bhatt, K., Pandey, K., Rai, U. N., & Singh, K. P. (2006). Distribution of metals in the edible plants grown at Jajmau, Kanpur (India) receiving wastewater irrigated tannery wastewater: Relation with physico-chemical properties of the soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 115, 1–22. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-5036-z.
Verma, S., & Dubey, R. S. (2001). Effect of cadmium on soluble sugars and enzymes of their metabolism in rice. Biologia Plantarum, 44(1), 117–123. doi:10.1023/A:1017938809311.
Voutsa, D., Grimanis, A., & Samara, C. (1996). Trace elements in vegetables grown in an industrial area in relation to soil and air particulate matter. Chemosphere, 94, 325–335.
Wang, Q., Dong, Y., Cui, Y., & Liu, X. (2001). Instances of soil and crop heavy metal contamination in china. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 10, 497–510. doi:10.1080/20015891109392.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Satpati, S., Nayek, S. et al. Effect of wastewater irrigation on vegetables in relation to bioaccumulation of heavy metals and biochemical changes. Environ Monit Assess 165, 169–177 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0936-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0936-3