Abstract
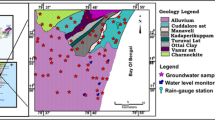
The study area Rameswaram, a holy island, is famous for the sacred Ramanathaswamy temple, which cements people of the country regardless of their place, residence, or their religion or creed. This coastal tract is experiencing a chronic fresh water shortage, despite a few spring sources. The study area is selected for the characterization of physico-chemical parameters viz., pH, EC, TDS, salinity, TA, TH, CH, MH, chloride, and fluoride for 150 groundwater samples and the impact of pre- and post-monsoons on the groundwater quality is studied. The water quality index advocates the transfer of groundwater quality from unacceptable status in the pre-monsoon into an acceptable status in the post-monsoon. The Langelier saturation index reflects the scaling tendency of groundwater in the study area. The Karl Pearson correlation matrix has approved the maximum influence of calcium and chloride on the total dissolved solids. It is interesting to conclude that the groundwater in the study area has very had nature, especially of non-carbonate type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarawal, V., & Jegetia, M. (1997). Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality in Udaipur City, Rajasthan, India. In Proceedings of national conference on “Dimensions of Environmental Stress in India” (pp. 151–154). Baroda, India: Department of Geology, MS University.
APHA (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington D.C: American Public Health Association.
Billings, R. J., Berkowitz, R. J., & Watson, G. (2004). Teeth. Pediatrics, 113, 1120–1127.
Chow, V. T. (1964). Handbook of applied hydrology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Durvey, V. S., Sharma, L. L., Saini, V. P., & Sharma, B. K. (1991). Handbook on the methodology of water quality assessment. India: Rajasthan Agriculture University.
Fetter, C. W. (1990). Applied hydrogeology. New Delhi: CBS.
Khurshid, S. H., Hasan, N., & Zaheeruddin (2002). Water quality status and environmental hazards in parts of Yamuna-Karwan sub-basin of Aligarh-Mathura District, Uttar Pradesh, India. Journal of Applied Hydrology, XV, 30–37.
Kulasekaran, A., & Balakrishnan, P. (2002). Status of fluoride in groundwater in Tamil Nadu. Chennai: Tamil Nadu Water Administrative Department.
Langelier, W. F. (1946). Chemical equilibria in water treatment. Journal—American Water Works Association, 38, 169.
Majumdar, D., & Gupta, N. (2000). Nitrate pollution of groundwater and associated human health disorders. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 42, 28–39.
Niranjan Babu, P., Subba Rao, N., Chandra Rao, P., & Prakasa Rao, J. (1997). Groundwater quality and its importance in the land development programmes. Indian Journal of Geology, 69, 305–312.
Sawyer, C. N., & McCarty, P. l. (1967). Chemistry for sanitary engineers (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Shitumbanuma, V., Tembo, F., Tembo, J. M., Chilala, S., & Van Ranst, E. (2007). Dental fluorosis associated with drinking water from hot springs in Choma District in Southern province, Zambia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29, 51–58. doi:10.1007/s10653-006-9062-0.
Statistical Hand Book (2006). Ramanathapuram District, Salient features of 2001 Census.
Subba Rao, N. (2006). Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 49, 413–429. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0089-9.
Subba Rao, C., Vachaspathi Sarma, A., & Somu Naidu, Y. (2006). The Chemistry of three ‘holy’ waters: A hydrologist’s pilgrimage. Current Science, 91, 262.
Tiwari, T. N., & Mishra, M. (1985). A preliminary assessment of water quality index of major Indian rivers. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 5, 276–279.
World Health Organisation (2004). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality. Health Criteria and other supporting information (Vol. 2, 2nd ed.). Geneva.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramachandramoorthy, T., Sivasankar, V. & Subramanian, V. The seasonal status of chemical parameters in shallow coastal aquifers of Rameswaram Island, India. Environ Monit Assess 160, 127–139 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0663-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0663-1