Abstract
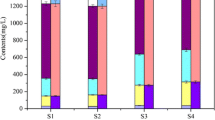
Phosphorus (P) fractions and the effect of phytoremediation on nitrogen and phosphorus removal from eutrophicated water and release from sediment were investigated in the eco-remediation experiment enclosures installed in the Hua-jia-chi pond (Hangzhou city, Zhejiang province, China). The main P fraction in the sediment was inorganic phosphorus (IP). For the mesotrophic sediments, IP mainly consisted of HCl-extractable P (Ca-P). The annual-average concentration of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP) in water and the content of TN, TP in different vertical depth of sediment in the experiment enclosures with hydrophyte were always much lower than those in the control enclosure without hydrophyte and those outside of experiment enclosures. It is suggested that phytoremediation was an effective technology for N and P removal from eutrophicated water and release from sediment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams, M. M., & Jarrell, W. M. (1995). Soil-phosphorus as a potential non-point source for elevated stream phosphorus levels. Journal of Environmental Quality, 24, 132–138.
APHA, AWWA, & WPCE (Ed.) (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (p. 456). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Bostrom, B. (1988). Relations between chemistry, microbial biomass and activity in sediments of a polluted vs. a non-polluted eutrophic lake. Verhandlungen International Verein, 23, 451–459.
Fan, C. X., Yang, L. Y., & Zhang, L. (2000). Vertical distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediment and its interstitial water in Taihu Lake and their correlation. Journal of Lake Science, 12(4), 359–366 (in Chinese).
Gonsiorczyk, T., Casper, P., & Koschel, R. (1998). Phosphorus binding forms in the sediment of an oligotrophic and an eutrophic hardwater lake of the Baltic district (Germany). Water Science and Technology, 37(3), 51–58. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00055-9.
Institute of Soil Science & Chinese Academy of Sciences. (1978). Physico-chemistry analysis of soil (pp. 35–45). Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing Company (in Chinese).
Kaiserli, A., Voutsa, D., & Samara, C. (2002). Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments—Lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Chemosphere, 46, 1147–1155. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00242-9.
Li, X. M., Yang, Z. Y., Jian, S. G., Huang, Z. X., & Liang, J. G. (2000). Effects of effective microorganisms (simplified as EM) on control of algae bloom in eutrophic water. Journal of Transaction of Zhongshan University, 39(3), 81–85 (Nature Science Edition).
Lijklema, L., Koelmans, A. A., & Portielje, R. (1993). Water quality impacts of sediment pollution and the role of early diagenesis. Water Science and Technology, 28, 1–12.
Liu, C. G., Qiu, J. Q., Wang, W., & Zhuang, Y. Y. (2004). Advances of biomanipulation theory for control of eutrophicated lakes. Journal of Transaction of Agriculture Environmental Science, 23(1), 198–201 (in Chinese).
National Bureau of Environment Protection Editorial Committee of Water and Waste Water Monitoring Analytical Methods (Eds.) (2002). Water and wastewater monitoring analysis method (4th ed.). Beijing, China: Chinese Environment Science Press.
Penn, M. R., Auer, M. T., Van Orman, E. L., & Korienek, J. J. (1995). Phosphorus diagenesis in lake sediments: Investigation using fractionation techniques. Marine & Freshwater Research, 46, 89–99.
Ruban, V., Brigault, S., Demare, D., & Philippe, A. M. (1999). An investigation of the origin and mobility of phosphorus in freshwater sediments from Bort-Les-Orgues Reservoir, France. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 403–407. doi:10.1039/a902269d.
Ruban, V., López-Sánchez, J. F., Pardo, P., Rauret, G., Muntau, H., & Quevauviller, P. (2001). Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments—a synthesis of recent works. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 370, 224–228. doi:10.1007/s002160100753.
Wang, G. X., Pu, P. M., Zhang, S. Z., Li, W. C., Hu, W. P., & Hu, C. H. (1998). Purification of artificial complex ecosystem for local water in Taihu Lake. Journal of China Environmental Science, 18(5), 410–414 (in Chinese).
Wu, F. C., Qing, H. R., & Wan, G. J. (2001). Regeneration of N, P, and Si near the sediment/water interface of lakes from southwestern China plateau. Water Research, 35(5), 1334–1337. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00380-8.
Wu, F. C., Qing, H. R., Wan, G. J., Huang, R. G., & Cai, Y. R. (1997). Geochemistry of \(\text{HCO}_{3}^{-}\) in the sediment–water interface of lakes from China Southwestern Plateau. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 99, 381–390.
Xu, H., Chen, H. Z., Xiong, Q. Q., & Wang, B. Z. (1999). Research on the purification efficiency and mechanism of macrohydrophyte pools. Journal of Transaction of Herbin Architecture University, 32(4), 69–73 (in Chinese).
Xu, Y. Q., Xiong, H. X., & Zhao, X. L. (2003). Advanced research on phosphorus absorption and release in sediment. Journal of Chongqing Environmental Science, 25(11), 141–149 (in Chinese).
Xie, L. Q., Xie, P., & Tang, H. J. (2003). Enhancement of dissolved phosphorus release from sediment to lake water by Microcystis blooms—an enclosure experiment in a hyper-eutrophic, subtropical Chinese lake. Environmental Pollution, 122, 391–399. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00305-6.
Zanini, L., Robertson, W. D., Ptacek, C. J., Schiff, S. L., & Mayer, T. (1998). Phosphorus characterization in sediments impacted by septic effluent at four sites in central Canada. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 33, 405–429. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(98)00082-5.
Zou, H. X., Sheng, G. Y., Sun, C., & Xu, O. Y. (1996). Distribution of organic contaminants on Lake Taihu. Water Recourse, 30(9), 2003–2008 (in Chinese). doi:10.1016/0043-1354(96)00025-5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Key Project from the Education Ministry of China (No. 200406-MOE-K), the Key Project from Zhejiang Science and Tech. Bureau (No. 2005C22020), and the program for Changjiang Scholars from Ministry of Education of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, W., Xiao-E, Y. & Rengel, Z. Phytoremediation facilitates removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from eutrophicated water and release from sediment. Environ Monit Assess 157, 277–285 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0534-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0534-9