Abstract
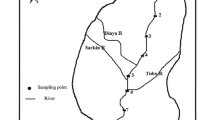
The application of different multivariate statistical approaches for the interpretation of a complex data matrix obtained during the period 2004–2005 from Uluabat Lake surface water is presented in this study. The dataset consists of the analytical results of a 1 year-survey conducted in 12 sampling stations in the Lake. Twelve parameters (T, pH, DO, \({\text{PO}}^{{ - 3}}_{4} - {\text{P}}\), NH4–N, NO2–N, NO3–N, \({\text{SO}}^{{3 - }}_{4} \), BOD, COD, TC, FC) were monitored in the sampling sites on a monthly basis (except December 2004, January and February 2005, a total of 1,296 observations). The dataset was treated using cluster analysis, principle component analysis and factor analysis on principle components. Cluster analysis revealed two different groups of similarities between the sampling sites, reflecting different physicochemical properties and pollution levels in the studied water system. Three latent factors were identified as responsible for the data structure, explaining 77.35% of total variance in the dataset. The first factor called the microbiological factor explained 32.34% of the total variance. The second factor named the organic-nutrient factors explained 25.46% and the third factor called physicochemical factors explained 19.54% of the variances, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 18th Ed. Washington DC. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Pollution Controll Federation, 10–137 pp.
Boyacioglu, H. (2006). Surface water quality assessment using factor analysis. Water S.A., 32(3), 389–393.
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1995). Multivariate data analysis with readings (4th ed.). London: Prentice-Hall.
Hammer, J. M. (1986). Water and wastewater technology, (3rd ed.). New Delhi, India: Prentice Hall. (pp. 63– 69, 473– 477)
Kuppusamy, M. R., & Giridhar, V. V. (2006). Factor analysis of water quality characteristics including trace metal speciation in the coastal environmental system of Chennai Ennore. Environmental International, 32, 174–179.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313, 77–89.
Magnin, G., & Yarar, M. (1997). Important bird breeding areas in Turkey. DHKD (The Society for the Protection Nature) Anabasım AŞ., Istanbul, Turkey, pp 50–52.
Ntengwe, F. W. (2006). Pollutant loads and water quality in streams of heavily populated and industrialised towns. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 31, 832–839.
Ouyang, Y., Nkedi-Kizza, P., Wu, Q. T., Shinde, D., & Huang, C. H. (2006). Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Research, 40, 3800–3810.
Sadar, M. H. (1996). Environmental impact assessment, (2nd ed.). Carleton University Press: Ottawa, Canada.
Salihoğlu, G., & Karaer, G. (2004). Ecological risk assessment and problem formulation for Lake Uluabat, a Ramsar State in Turkey. Environmental Management, 33(6), 899–910.
Sharma, S. (1996). Applied multivariate techniques. New York: Wiley.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin; Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22, 464–475.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., & Anthemidis, A., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (1996). Using multivariate statistics (3rd ed.). New York: Harper Collins College Publishers.
Turkish Standards (2004). Su Kirliliği Yöntmeliği, 25687 sayılı resmi gazete.
Vega, M., Pardo, R., Barrato, E., & Deban, L. (1998). Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32, 3581–3592.
World Health Organization (WHO) (1993). Guidelines for drinking water quality, (2nd ed.), vol. 1, Recommendations, Geneva. 13 pp.
Wunderlin, D. A., Diaz, M. P., Ame, M. V., Pesce, S. F., Hued, A. C., & Bistoni, M. A. (2001). Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquira river basin (Cordoba—Argentina). Water Research, 35, 1894–2881.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filik Iscen, C., Emiroglu, Ö., Ilhan, S. et al. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the assessment of surface water quality in Uluabat Lake, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 144, 269–276 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9989-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9989-3