Abstract
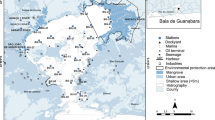
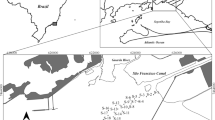
The Odiel salt marshes (Marismas del Odiel) are an important nature area declared a Biosphere Reserve, but they are greatly affected by pollution from the Odiel River. Surface sediments from this area were analysed using the latest version of the BCR sequential extraction procedure to determine the fractionation of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn among four geochemical phases (acid-soluble, reducible, oxidisable and residual). The total content of each of the metals and As was also determined. The results showed high concentrations of As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn, with maximums of 791 mg kg−1 of As, 8.5 mg kg−1 of Cd, 2,740 mg kg−1 of Cu, 1,580 mg kg−1 of Pb and 3,920 mg kg−1 of Zn. The concentrations of Cr, Mn and Ni were low since there are no sources of pollution by them in the area. A comparison of the metal and As levels with the sediment quality guidelines showed that the pollution is sufficient to produce noxious effects in aquatic organisms in most of the Odiel salt marshes. Based on the chemical distribution of the elements, it was found that Cd and Zn were the most mobile (i.e., elements that can pass easily into the water under changing environmental conditions). However, Cr, Fe, Ni and As were present in the greatest percentages in the residual fraction, which implies that these elements are strongly linked to the sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batley, G. (1991). Collection, preparation, and storage of samples for speciation analysis. In G. Batley (Ed.), Trace element speciation: Analytical methods and problems (pp. 1–24). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Bird, G., Brewer, P., Macklin, M., Balteanu, D., Driga, B., Serban, M., et al. (2003). The solid state partitioning of contaminant metals and As in river channel sediments of the mining affected Tisa drainage basin, northwestern Romania and eastern Hungary. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 1583–1595.
Burgos, M., & Rainbow, P. (2001). Availability of cadmium and zinc from sewage sludge to the flounder, Platichthys flesus, via a marine food chain. Marine Environmental Research, 51, 417–439.
Cabrera, F., Clemente, L., Díaz Barrientos, E., López, R., & Murillo, J. (1999). Heavy metal pollution of soil affected by the Guadiamar toxic flood. Science of the Total Environment, 242, 117–129.
Canfield, D. (1989). Reactive iron in marine sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53, 619–632.
Caplat, C., Texier, H., Barillier, D., & Lelievre, C. (2005). Heavy metals mobility in harbour contaminated sediments: The case of Port-en-Bessin. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(5), 504–511.
Cuong, D., & Obbard, J. (2006). Metal speciation in coastal marine sediments from Singapore using a modified BCR-sequential extraction procedure. Applied Geochemistry, 21(8), 1335–1346.
Das, A., Chakraborty, R., Cervera, M., & de la Guardia, M. (1995). Metal speciation in solid matrices. Talanta, 42, 1007–1030.
Dassenakis, M., Andrianos, H., Depiazi, G., Konstantas, A., Karabela, M., Sakellari, A., et al. (2003). The use of various methods for the study of metal pollution in marine sediments, the case of Euvoikos Gulf, Greece. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 781–794.
Förstner, U., & Salomons, W. (1988). Environmental management of solid waste. Heidelberg: Springer.
França, S., Vinagre, C., Caçador, I., & Cabral, H. (2005). Heavy metal concentrations in sediment, benthic invertebrates and fish in three salt marsh areas subjected to different pollution loads in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(9), 998–1003.
Gleyzes, C., Tellier, S., & Astruc, M. (2002). Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: A review of sequential extraction procedures. TrAC. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 21(6–7), 451–467.
Guhathakurta, H., & Kaviraj, A. (2000). Heavy metal concentration in water, sediment, shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and mullet (Liza parnia) in some brackish water ponds of Sunderban, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(11), 914–920.
Horsfall, M., & Spiff, A. (2002). Distribution and Partitioning of trace metals in sediments of the lower reaches of the New Calabar River, Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 78, 309–326.
ISO 11466 (1995). Soil quality: Extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
ISO/IEC 17025 (1999). General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
Izquierdo, C., Usero, J., & Gracia, I. (1997). Speciation of heavy metals in sediments from salt marshes on the southern Atlantic coast of Spain. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34(2), 123–128.
Jemiola-Rzeminska, M., Rivera, C., Suwalsky, M., & Strzalka, K. (2007). Interaction of arsenic compounds with model phospholipid membranes. Thermochimica Acta, 458, 132–137.
Jones, B., & Turki, A. (1997). Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in superficial sediments from the Tees estuary, North-east England. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34(10), 768–779.
Kuang-Chung, Y., Li-Jyur, T., Shih-Hsiuns, C., & Shien-Tsong, H. (2001). Correlation analyses binding behavior of heavy metals with sediment matrices. Water Research, 35(10), 2417–2428.
Li, X., Shen, Z., Wai, O., & Li, Y. (2001). Chemical forms of Pb, Zn and Cu in the sediment profiles of the Pearl River estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(3), 215–223.
Long, E., Macdonald, D., Smith, S., & Calder, F. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19(1), 81–97.
López-Sánchez, J., Rubio, R., & Rauret, G. (1993). Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for trace metal partitioning in sediments. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 51, 113–121.
Luque, C., Castellanos, E., Castillo, J., Gonzalez, M., Gonzalez-Vilches, M., & Figueroa, M. (1999). Metals in halophytes of a contaminated estuary (Odiel Salt Marshes, SW Spain). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 38, 49–51.
Marin, B., & Giresse, P. (2001). Particulate manganese and iron in recent sediments if the Gulf of Lions continental margin (north-western Mediterranean Sea): Deposition and diagenetic process. Marine Geology, 172(1), 147–165.
Morillo, J., Usero, J., & Gracia, I. (2002). Partitioning of metals in sediments from the Odiel River (Spain). Environment International, 28, 263–271.
Morillo, J., Usero, J. & Gracia, I. (2004). Heavy metal distribution in marine sediments from the southwest coast of Spain. Chemosphere, 55, 431–442.
Neff, J. (2002). Bioacumulation in marine organism. Oxford: Elservier.
Nikolaidis, N., Dobbs, G., Chen, J., & Lackovic, J. (2004). Arsenic mobility in contaminated lake sediments. Environmental Pollution, 129(3), 479–487.
Pandey, P., Nair, S., Bhui, A., & Pandey, M. (2004). Sediment contamination by arsenic in parts of central–east India and analytical studies on its mobilization. Current Science, 86(1), 190–197.
Patra, M., Bhowmik, N., Bandopadhyay, B., & Sharma, A. (2004). Comparison of mercury, lead and arsenic with respect to genotoxic effects on plant systems and the development of genetic tolerance. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 52, 199–223.
Petersen, W., Wallman, K., Li, P., Schroeder, F., & Knauth, H. (1995). Exchange of trace elements at the sediment-water interface during early diagenesis processes. Marine and Freshwater Research, 46, 19–26.
Ramirez, M., Massolo, S., Frache, R., & Correa, J. (2005). Metal speciation and environmental impact on sandy beaches due to El Salvador copper mine, Chile. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(1), 62–72.
Ramos, L., González, M., & Hernández, L. (1999). Sequential extraction of copper, lead, cadmium, and zinc in sediments from Ebro River (Spain): Relationship with levels detected in earthworms. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 62, 301–308.
Rauret, G., López-Sánchez, J., Sauquillo, A., Barahona, E., Lachica, M., Ure, A., et al. (2000). Application of a modified BCR sequential extraction (three-step) procedure for the determination of extractable trace metal contents in a sewage sludge amended soil reference material (CRM 483), complemented by a three-year stability study of acetic acid and EDTA extractable metal content. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2, 228–233.
Rauret, G., López-Sánchez, J., Sauquillo, A., Rubio, R., Davidson, C., Ore, A., et al. (1999). Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 57–61.
Ridgway, J., & Shimmield, G. (2002). Estuaries as repositories of historical contamination and their impact on shelf seas. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 55, 903–928.
Roychoudhury, A., & Starke, M. (2006). Partitioning and mobility of trace metals in the Blesbokspruit: Impact assessment of dewatering of mine waters in the East Rand, South Africa. Applied Geochemistry, 21, 1044–1063.
Sahuquillo, A., López-Sánchez, J., Rubio, R., Rauret, G., Thomas, R., Davidson, C., et al. (1999). Use of a certified reference material for extractable trace metals to assess sources of uncertainty in the BCR three-stage sequential extraction procedure. Analytica Chimica Acta, 382, 317–327.
Sahuquillo, A., Rigol, A. & Rauret, G. (2003). Overview of the use of leaching/extraction test for risk assessment of trace metals in contaminated soils and sediments. TrAC. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2(3), 152–159.
Sing, S., Tack, F., & Verloo, M. (1998). Heavy metals fractionations and extractability in dredged sediment derived surface soils. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 102, 313–328.
Summers, R. (1980). The diet and feeding behaviour of the flounder Platichthys flesus (L.) in the Ythan Estuary, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2, 217–232.
Turekian, K., & Wedepohl, K. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of Earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192.
Usero, J., Morillo, J., & Gracia, I. (2005). Heavy metal concentrations in molluscs from the Atlantic coast of southern Spain. Chemosphere, 59, 1175–1181.
Weisz, M., Polyák, K., & Hlavay, J. (2000). Fractionation of elements in sediment samples collected in rivers and harbors at Lake Balaton and its catchment area. Microchemical Journal, 67, 207–217.
Xiangdong, L., Zhenguo, S., Onyx, W., & Yok-Sheung, L. (2001). Chemical forms of Pb, Zn and Cu in the sediments profiles of the Pearl River Estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(3), 215–223.
Yuang, C., Shi, J., He, B., Liu, J., Liang, L., & Jiang, G. (2004). Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments from the East China Sea by ICP-MS with sequential extraction. Environment International, 30(6), 769–783.
Zoumis, T., Schmidt, A., Grigorova, L., & Calmano, W. (2001). Contaminants in sediments: Remobilisation and demobilisation. The Science of the Total Environment, 266, 195–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morillo, J., Usero, J. & Rojas, R. Fractionation of metals and As in sediments from a biosphere reserve (Odiel salt marshes) affected by acidic mine drainage. Environ Monit Assess 139, 329–337 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9839-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9839-3