Abstract
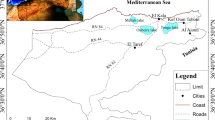
Mobility of metals in water, mine wastes, and stream sediments around the abandoned Alaşehir mercury mine was investigated to evaluate the environmental effects around the area. Mine waters are dominantly acidic with pH values of 2.55 in arid season and 2.70 in wet season and are sulfate rich. Acidity is caused mainly by the oxidation of sulfide minerals. Pyrite is the main acid-producing mineral in the Alaşehir area. Of the major ions, SO4 shows a notable increase reaching 3981 mg/l, which exceeds the WHO (WHO guidelines for drinking water quality, vol. 2. Health criteria and other supporting information, 1993) and TS (Sular-İçme ve kullanma suları. Ankara: Türk Standartları Enstitüsü, 1997) drinking water standard of 250 mg/L. Mine waters have As, Fe, Mn, Ni, and Al with concentrations higher than drinking water standards. Hg concentrations of adit water samples and surface waters draining the mine area are between 0.25 and 0.274 µg/L and are below the WHO (WHO guidelines for drinking water quality, vol. 2. Health criteria and other supporting information, 1993) drinking water standard of 1.0 µg/L. However, the concentrations are above the 0.012 µg/L standard (EPA, Water quality standards. Establishment of numeric criteria for priority toxic pollutants, states’ compliance, final rule. Fed. Reg., 40 CFR, Part 131, 57/246, 60847–60916, 1992) used to protect aquatic life. Stream sediment samples have abnormally high values of especially Hg, As, Ni, and Cr metals. Geoaccumulation (Igeo) and pollution index (PI) values are significantly high and denote heavy contamination in stream sediments. The stream sediments derived from the mining area with the surface waters are potentially hazardous to the environment adjacent to the abandoned Hg mine and are in need of remediation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks, D., Younger, P. L., Arnesen, R. T., Iversen, E. R., & Banks, S. B. (1997). Mine-water chemistry: The good, the bad and the ugly. Environmental Geology, 32/3, 157–174.
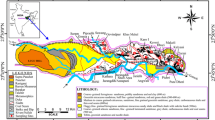
Baykal, F. (1954). Alaşehir-Uşak mıntıkasının jeolojisi hakkında rapor. MTA Rap. No. 2296, Ankara.
Bircan, A., Aydoğanlı, E. (1969). Türkiye Civa Envanteri. Maden Tetkik ve Arama yayınları, No.143. Ankara.
Calmbach, L. (1997). Aquachem Computer Code – Version 3.7.42. Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, N2L 3L3: Waterloo Hydrogeologic.
Chon, H. T., Cho, C. H., Kim, K. W., & Moon, H. S. (1996). The occurrence and dispersion of potentially toxic elements in areas covered with black shales and slates in Korea. Applied Geochemistry, 11, 69–76.
Cidu, R., Caboi, R., Fanani, L., & Frau, F. (1997). Acid drainage from sulfides hosting gold mineralization (Furtei, Sardinia). Environmental Geology, 30, 231–237.
Çolak, M., Gemici, Ü., & Tarcan, G. (2003). The effects of colemanite deposits on the arsenic concentrations of soil, and groundwater in İğdeköy-Emet, Kütahya, Turkey. Water, Soil and Air Pollution, 149, 127–143.
Deutsch, W. J. (1997). Groundwater geochemistry, fundamentals and applications to contamination.. Boca Raton: Lewis 219 pp.
Dove, P. M., & Rimstidt, J. D. (1996). The solubility of scorodite, FeAsO4 H2O. American Mineralogist, 70, 838–844.
EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (1992). Water quality standards, Establishment of numeric criteria for priority toxic pollutants, states’ compliance, final rule, Fed. Reg., 40 CFR, Part 131, 57/246, 60, 847–60, 916.
Gal, N. E. (2000). The impact of acid-mine drainage on groundwater quality. Davis Pyrite Mine, Massachusetts. PhD, University of Massachusetts, USA.
Gemici, Ü. (2004). Impact of acid mine drainage from the abandoned Halıköy mercury mine (Western Turkey) on surface and groundwaters. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72/3, 482–489.
Gemici, Ü., & Oyman, T. (2003). The influence of the abandoned Kalecik Hg mine on waters and stream sediments, (Karaburun, İzmir, Turkey). The Science of the Total Environment, 312, 155–166.
Gemici, Ü., & Tarcan, G. (2004). Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical features of the Heybeli Spa, Afyon, Turkey: Arsenic and the other contaminants in the thermal waters. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72/6, 1104–1114.
Gemici, Ü., & Tarcan, G. (2007). Assessment of the pollutants in farming soils and waters around untreated abandoned Türkönü mercury mine (Turkey). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 79, 20–24.
Gemici, Ü., Tarcan, G., Çolak, M., & Helvacı, C. (2004). Hydrogeochemical and hydrogeological investigations for thermal waters in Emet area (Kütahya-Turkey). Applied Geochemistry, 19, 105–117.
Gray, J. E., Theodorakos, P. M., Bailey, E. A., & Turner, R. A. (2000). Distribution, speciation and transport of mercury in stream-sediment, stream-water and fish collected near abandoned mercury mines in southwestern Alaska, USA. The Science of the Total Environ, 260, 21–33.
Herr, C., Gray, N. F. (1995). Environmental impact of acid mine drainage on the Avoca River: Metal fluxes in water and sediment. Part II. Metal contamination of riverine sediments. Technical report 14. Water Technology Research, Dublin, 36 pp.
Holzer, H. (1953). 88/3, 89/3 ve 105/41 ile 89/1 paftalarının jeolojik haritası hakkında rapor. MTA Rap. No. 2365, Ankara.
IAH (International Association of Hydrogeologists). (1979). Map of mineral and thermal water of Europe, scale 1:500,000. London: International Association of Hydrogeologists.
Kim, K. K., Kim, K. W., Kim, J. Y., Kim, I. S., Cheong, Y. W., & Min, J. S. (2001). Characteristics of tailings from the closed metal mines as potential contamination sources in South Korea. Environmental Geology, 41, 358–364.
Lee, C. H., Lee, H. K., & Lee, J. C. (2001). Hydrogeochemistry of mine, surface and groundwaters from the Sanggok mine creek in the upper Chungju Lake, Republic of Korea. Environmental Geology, 40(4–5), 482–494.
Loska, K., Wiechula, D., & Korus, I. (2004). Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environmental International, 30, 159–165.
Milu, V., Leroy, J., & Peiffert, C. (2002). Water contamination downstream from a copper mine in the Apuseni Mountains, Romania. Environmental Geology, 42, 773–782.
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal, 2, 108–18.
Nimick, D. A., Moore, J. M. (1991). Prediction of water soluble metal concentrations in fluvially deposited tailings sediments, upper Clark Fork Valley, Montana, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 6, 635–646.
Nishida, H., Miyai, M., Tada, F., & Suzuki, S. (1982). Computation of the index of pollution caused by heavy metals in river sediment. Environment Pollution (series B), 4, 241–248.
Ongley, L. K., Armienta, M. A., Heggeman, K., Lathrop, A. S., Mango, H., Miller, W., & Pickelner, S. (2001). Arsenic removal from contaminated water by the Soyatal Formation, Zimapan mining district, Mexico – A potential low-cost low-tech remediation system. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 1, 23–31.
Parkhurst, D. L., Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2) – A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport and inverse geochemical calculations. Denver: US Geological Survey.
Pierce, M. L., & Moore, C. B. (1980). Adsorption of arsenite on amorphpus iron hydroxide from dilute aqueous solution. Environmental Science & Technology, 14, 214–216.
Salomons, W., & Förstner, U. (1984). Metals in hydrocycle. Berlin: Springer.
Schuiling, R. D. (1962). Türkiey’nin güneybatısındaki migmatit kompleksinin petrolojisi, yaşı ve yapısı hakkında. MTA Dergisi No 58, Ankara.
Shacklette, H. T., Boerngen, J. G. (1984). Element concentrations in soils and other surficial materials of the conterminous United States. USGS Professional paper 1270.
Sponza, D., & Karaoglu, N. (2002). Environmental geochemistry and pollution studies of Aliağa metal industry district. Environmental International, 27, 541–553.
Tarcan, G., & Gemici, Ü. (2003). Water chemistry of the Seferihisar geothermal area, Izmir, Turkey. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 126, 225–242.
Tarcan, G., & Gemici, U. (2005). Effects of the contaminants from Turgutlu-Urganli thermomineral waters on cold ground and surface waters. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 74(3), 485–492.
Tarcan, G., Gemici, U., & Aksoy, N. (2005). Hydrogeological and geochemical assessments of the Gediz Graben geothermal areas, western Anatolia, Turkey. Environmental Geology, 47(4), 523–534.
TS (Turkish drinking water standards). (1997). Sular-İçme ve kullanma suları. Ankara: Türk Standartları Enstitüsü.
Vink, B. W. (1996). Stability relations of antimony and arsenic compounds in the light of revised and extended Eh–pH diagrams. Chemical Geology, 130, 21–30.
Wang, X. J., & Chen, J. S. (1998). Trace element contents and correlation in surface soil in China’s eastern alluvial plains. Environmental Geology, 36(3–4), 277–284.
WHO (World Health Organization). (1993). WHO guidelines for drinking water quality, vol 2. Health criteria and other supporting information.. Geneva: WHO.
Yıldız, M. (1978). Türkiye’de bazı civa yataklarının oluşum ve mukayesesi. Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitüsü Yayınlarından, No. 173, Ankara.
Yıldız, M., Bailey, E. H. (1978). Mercury deposits in Turkey. United States Geological Survey Bulletin, 1456, 28–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gemici, Ü. Evaluation of the water quality related to the acid mine drainage of an abandoned mercury mine (Alaşehir, Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 147, 93–106 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0101-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0101-9