Abstract
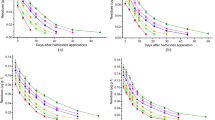
Long term stability of sulfosulfuron was investigated in subsoil under the natural wheat cropping conditions. Experiments were conducted by applying a commercial formulation of sulfosulfuron on soil at 50 g/ha and 100 g/ha. To understand the factors influencing the persistence of residues two different experiments were conducted. In one experiment wheat crop was cultivated once at the beginning of the two years study period and subsequently the plots were kept undisturbed for the remaining period. In another experiment cultivation of subsequent crops were continued during the study period. In both the cases sulfosulfuron was applied only once at the beginning of the study. Representative soil samples were collected from the depths viz., 0–5, 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90 cm on different pre determined sampling occasions 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 and 600 days after the application of the herbicide. The collected soil samples were analyzed for the residues of sulfosulfuron. Under the influence of continuous cropping conditions residues of sulfosulfuron were found to be relatively low when compared with the soil samples collected from the agriculture plots maintained without any cultivation. The residues detected are in the range 0.001 to 0.017 μg/g. Samples collected from the depth, at 30 to 45 cm showed higher residual concentrations. Soil samples were also showed the presence of break down products. The data has been confirmed by LC–MS/MS. The relation between residue content of sulfosulfuron and the factors contributing the stability of herbicide concentration were also studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brar, L. S., Walia, U. S., & Dhaliwal, B. K. (1999). Bioefficacy of new herbicides for the control of Resistant Phalaris minor in wheat. Pesticide Research Journal, 11(2), 177–180.
Brown, C. D., Dubus, I. G., Fogg, P., Spirlet, M., & Gustin, C. (2004). Exposure to sulfosulfuron in agricultural drainage ditches: Field monitoring and scenario-based modeling. Pest Management Science, 60(8), 765–776, August.
Charnay, M. P., Tuis, S., Coquet, Y., & Barriuso, E. (2005). Spatial variability in 14C-herbicide degradation in surface and subsurface soils. Pest Management Science, 61(9), 845–855, Sept.
Davies, J., Honegger, J. L., Tencalla, F. G., Meregalli, G., Brain, P., Newman, J. R., et al. (2003). Herbicide risk assessment for non-target aquatic plants: Sulfosulfuron – A case study. Pest Management Science, 59(2), 231–237, Feb.
Duffy, M. J., Carski, T. H., & Hanafy, M. K. (1993). Conceptually and experimentally coupling herbicide sorption and degradation in soil. Proceedings 9th symposium on pesticide chemistry (295–308). Piacenza, Italy.
Eleftherohorinos, I., Dhima1, K., & Vasilakoglou I. (2004). Activity, adsorption, mobility and field persistence of sulfosulfuron in soil. Phytoparasitica, 32(3), 274–285.
European Commission Directive (2002). Working document 91/414/EEC. Sulfosulfuron.
Foster, S. S. D., Chilton, P. J., & Stuart, M. E. (1991). Mechanisms of ground water pollution by pesticides. Journal of the Institution of Water and Environmental Management, 5(92), 186–193.
Gottesburen, B., Pestemer, W., & Beulke (1994). Characteristics and effects of the time course of the sorption behaviour of herbicides in soil. Book of abstracts, Vol, 1. 8th IUPAC congress of pesticide chemistry (p. 261). Washington D.C.
Healy, C. E., Heydens, W. F., & Naylor, M. W. (2004). Mammalian toxicology overview and human risk assessment for sulfosulfuron. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 39(3), 310–324, Jun.
Martin, J. P. (1950). Use of acid, rose Bengal and streptomycin in the plate method for estimating soil fungi. Soil Science, 69, 215.
Mishael, Y. G., Undabeytia, T., Rabinovitz, O., Rubin, B., & Nir, S. (2003). Sulfosulfuron incorporated in micelles adsorbed on montmorillonite for slow release formulations. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 51(8), 2253–2259, Apr 9.
Proposed Regulatory Decision Document (PRDD98–01) for Sulfosulfuron by Pest Management Regulatory Agency (1998) December.
Ramesh, A., & Maheswari, S. T. (2003). Dissipation of sulfosulfuron in soil and wheat plant under predominant cropping conditions and in a simulated model ecosystem. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51(11), 3396–3400, May 21.
Saha, S., & Kulshrestha, G. (2002). Degradation of sulfosulfuron, a sulfonylurea herbicide, as influenced by abiotic factors. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(16), 4572–4575, Jul 31.
Saha, S., Singh, S. B., & Kulshrestha, G. (2003). High performance liquid chromatographic method for the residue determination of sulfosulfuron. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part B, 38(3), 337–347, May.
Singh, S., Singh, T., & Singh, V. P. (2002). Effect of doses and stages of application of sulfosulfuron on weeds and wheat yield. Indian Journal of Weed Science, 34(3–4), 172–174.
Undabeytia, T., Mishael, Y. G., Nir, S., Papahadjopoulos Sternberg, B., Rubin, B., Morillo, E., et al. (2003). A novel system for reducing leaching from formulations of anionic herbicides: Clay-liposomes. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(19), 4475–4480, Oct 1.
Waksman, S. A, & Fred, E. B. (1922). A tentative outline of the plate method for determining number of micro organisms in soil. Soil Science, 14, 27–28.
Walker, A., Allen, R., Bailey, S. W., Blair, A. M., Brown, C. D., Gunther P., et al. (1995). Monograph No.62, Pesticide movement to Water. Proceedings of British Crop Protection Council. Farnham, UK, April.
Walker, A., Cotterill, S. J., & Welch, S. J. (1989). Adsorption and degradation of chlorsulfuron and metsulfuron methyl in soils from different depths. Weed Research, 29, 281–287.
Walker, A, & Welch, S. J. (1989). The relative movement and persistence in soil of chlorsulfuron, metsulfuron-methyl and triasulfuron. Weed Research, 29, 375–383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atmakuru, R., Perumal Elumalai, T. & Sivanandam, S. Identification of Residues of Sulfosulfuron and its Metabolites in Subsoil-dissipation Kinetics and Factors Influencing the Stability and Degradation of Residues from Topsoil to Subsoil Under Predominant Cropping Conditions. Environ Monit Assess 130, 519–528 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9441-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9441-0