Abstract
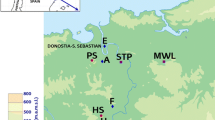
In order to explore the environmental behavior of reduced sulfur compounds (RSC) as malodorous components emitted from diverse source processes, the distribution characteristics of four sulfur (S) compounds - hydrogen sulfide (H2S), methyl mercaptan (CH3SH), dimethyl sulfide (DMS: (CH3)2S), and dimethyl disulfide (DMDS: (CH3)2S2) – were investigated in a municipal landfill area. In the course of this study, their ambient concentration levels were measured during two time periods from 13 individual spots selected as a function of distance from the center of the landfill site. The results generally indicated the absolute dominance of H2S over the other S compounds investigated (up to 5 km radius) such that their mean values were found as 1415 (H2S), 148 (DMS), 20.6 (CH3SH), and 14.4 ppt (DMDS). When our data were compared in terms of either varying distance from the source or relationship with meteorological conditions, the H2S data sets were most evident to reflect the potential effects of strong source processes in the landfill environment, relative to other S gases (or to volatile organic compounds measured concurrently). The results of this study further indicated the relatively good correspondence between the measured H2S concentration level and humans' intuitive sensory of odor and nuisance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae, M. O., Andreae, T.W., Meyerdierks, D. and Thiel, C.: 2003, ‘Marine sulfur cycling and the atmospheric aerosol over the springtime North Atlantic’, Chemosphere 52, 1321-1343.
Black, M. S., Herbst, R. P. and Hitchcock, D. R.: 1978, ‘Solid adsorbent preconcentration and gas chromatographic analysis of sulfur gases’, Analyt. Chem. 50(7), 848-851.
Cecil County Government: 2002, Odor investigation: Cecil County central landfill, Department of Public Works, Cecil County Government, Elkton, Maryland, USA.
Charlson, R. J., Lovelock, J. E., Andreae, M. O. and Warren, S. G.: 1987, ‘Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulfur, cloud albedo, and climate’, Nature 326, 655-661.
Chin, M. and Jacob, D. J.: 1996, ‘Anthropogenic and natural contributions to tropospheric sulfate: A global model analysis’, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 18,691-18,699.
Choi, Y.-J., Kim, K.-H., Oh, S.-I. and Shon, Z. H.: 2004, ‘Continuous measurements of reduced sulfur gases in urban air’, J. Korean Society of Atmos. Environ. 20(2), 195-204.
Delmas, R., Baudet, J., Servant, J. and Baziard, Y.: 1980, ‘Emissions and concentrations of hydrogen sulfide in the air of the tropical forest of the Ivory Coast and of temperate regions in France’, J.Geophys. Res. 85, 4468-4474.
Kim, K.-H.: 2005a, ‘Performance characterization of the GC/PFPD for H2S, CH3SH, DMS, and DMDS in air’, Atmos. Environ. 39(12), 2251-2258.
Kim, K.-H.: 2005b, ‘Some insights into the gas chromatographic determination of reduced sulfur compounds (RSC) in air’, Environ. Sci. and Technol. 39(17), 6765-6769.
Kim, K.-H., Lee, G. and Kim, Y. P.: 2000,‘ Dimethylsulfide and its oxidation products in coastal atmospheres of Cheju Island’, Environ. Pollut. 110(1), 147-155.
Kim, K.-H., Swan, H., Shon, Z.-H., Lee, G., Kim, J. and Kang, C.-H.: 2004, ‘Monitoring of reduced sulfur compounds in the atmosphere of Gosan, Jeju during the Spring of 2001’, Chemosphere 54(4), 515-526.
Kim, K.-H., Choi, Y.-J., Jeon, E.-C. and Sunwoo, Y.: 2005a, ‘Characterization of malodorous sulfur compounds in landfill gas’, Atmos. Environ. 39(6), 1103-1112.
Kim, K.-H., Ju, D.W. and Joo, S.W.: 2005b, The evaluation of recovery rate associated with the use of thermal desorption system for the analysis of atmospheric reduced sulfur compounds (RSC) using the GC/PFPD method, TALANTA. 67(5), 955–959.
NDEQ: 1997, Technical Basis for a Total Reduced Sulfur Ambient Air Quality Standard, Nebraska Dept. of Environmental Quality (NDEQ), May 1997, Nebraska, USA.
NEPI: 1982, A Study on Quantitative Analysis of Odors by Gas Chromatograph, Dept. of Air Pollution Research, National Environmental Protection Institute (NEPI), Seoul, Korea. 298
NEPI: 1983, A Study on Quantitative Analysis of Odors by Gas Chromatograph 2, Dept. of Air Pollution Research, National Environmental Protection Institute (NEPI), Seoul, Korea.
USEPA: 2000, Method 16 of Sulfur (Semicontinuous Determination) in the list of Specific Promulgated Test Methods.
Yujing, M., Hai, W., Zhang, X. and Jiang, G.: 2002, ‘Impact of anthropogenic sources on carbonyl sulfide in Bejing city’, J. Geophys. Res. 107(D24), 4769. .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, KH., Choi, YJ., Oh, SI. et al. Short-term Distributions of Reduced Sulfur Compounds in the Ambient Air Surrounding a Large Landfill Facility. Environ Monit Assess 121, 343–354 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9128-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9128-y