Abstract
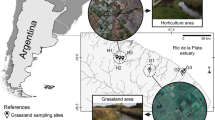
For less-developed regions like the Blue Ridge Mountains, data are limited that link basin-scale land use with stream quality. Two pairs of lightly-impacted (90–100% forested) and moderately-impacted (70–80% forested) sub-basins of the upper Little Tennessee River basin in the southern Blue Ridge were identified for comparison. The pairs contain physically similar stream reaches, chosen for the purpose of isolating forest conversion as a potential driver of any detected differences in water quality. Streams were sampled during baseflow conditions twice monthly over a six-month period from September 2003 through February 2004. Parametric t-tests were run for each parameter measured between the lightly-and moderately-impacted streams within each pair. Statistically significantly higher mean values of suspended and dissolved solids, nitrate, specific conductivity, turbidity, and temperature were observed in the moderately impacted streams versus the lightly impacted streams in both pairs, while dissolved oxygen levels were lower in the moderately-impacted streams. No significant differences were demonstrated in orthophosphate or ammonium concentration. A near-bankfull runoff event on February 6, 2004, was sampled for stormflow values, and the results support baseflow findings. The water quality of these streams is very good when compared with lower relief areas like the Piedmont, and none of the parameters measured in this study exceeds levels of known threat to stream biota. However, the demonstration that moderate reductions in forest cover are associated with stream water quality degradation carries important implications for stream management in this rapidly developing mountainous region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers, H. B. and Ashe, W. W.: 1904, The Southern Appalachian Forests, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 37
Clark, J. J. and Wilcock, P. R.: 2000, ‘Effects of land-use change on channel morphology in northeastern Puerto Rico’, GSA Bulletin 112, 1763–1777.
Delcourt, P. A. and Delcourt, H. R.: 2004, Prehistoric Native Americans and Ecological Change: Human ecosystems in eastern North America since the Pleistocene. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 203.
Delcourt, P. A., Delcourt, H. R., Cridlebaugh, P. A. and Chapman, J.: 1986, ‘Holocene ethnobotanical and paleoecological record of human impact on vegetation in the Little Tennessee River Valley, Tennessee’, Quaternary Research 25, 330–349.
Diamond, J. M., Dressier, D. W. and Serveiss, V. B.: 2002, ‘Assessing relationships between human land uses and the decline of native mussels, fish, and macroinvertebrates in the Clinch and Powell river watershed, USA’, Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 21, 1147–1155.
Dunne, T. and Leopold, L. B.: 1978, Water in Environmental Planning. W.H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco, 818 pp.
Eaton, L. S., Morgan, B. A., Kochel, R. C. and Howard, A. D.: 2003, ‘Role of debris flows in long-term landscape denudation in the central Appalachians of Virginia’, Geology 31, 339–342.
Everest, F. L., Beschta, R. L., Scrivener, J. C., Koski, K. V., Sedell, J. R. and Cederholm, C. J.: 1987, ‘Fine sediment and salmonid production – a paradox’, in: E. O. Salo, and T. W. Cundy (eds.), Stream Management: Forestry and Fishery Interactions, University of Washington, College of Forest Resources, Seattle, WA, pp. 98–142.
Flum, T. and Nodvin, S. C.: 1995, ‘Factors affecting streamwater chemistry in the Great Smoky Mountains, USA’, Water Air and Soil Pollution 85, 1707–1712.
Frick, E. A., Hippe, D. J., Buell, G. R., Couch, C. A., Hopkins, E. H., Wangsness, D. J. and Garrett, J. W.: 1998, Water Quality in the Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint River Basin, Georgia, Alabama, and Florida, 1992–1995, U.S. Geological Survey Circular, 1164.
The H. John Heinz Center for Science, and the Environment: 2002, The State of the Nation's Ecosystems: Measuring the Lands, Waters, and Living Resources of the United States. Cambridge University Press, New York City, 276 pp.
Hibbert, A. R.: 1966, ‘Forest treatment effects on water yield’, National Science Foundation Advanced Science Seminar: International Symposium on Forest Hydrology, pp. 527–543.
Hirsch, R. M., Walker, J. F., Day, J. C. and Kallio, R.: 1990, ‘The influence of man on hydrologic systems’, in: M. G. Wolman, and H. C. Riggs, (eds.), Surface Water Hydrology, Geological Society of America, Boulder, CO, pp. 329–359.
Jackson, C. R., Sturm, C. A. and Ward, J. M.: 2001, ‘Timber harvest impacts on small headwater stream channels in the coast ranges of Washington’, Journal of the American Water Resources Association 37, 1533–1549.
Jones, E. B. D., III., Helfman, G. S., Harper, J. O. and Bolstad, P. V.: 1999, ‘Effects of riparian forest removal on fish assemblages in southern Appalachian streams’, Conservation Biology 13, 1454–1465.
Kennan, J. G.: 1999, ‘Relation of macroinvertebrate community impairment to catchment characteristics in New Jersey streams’, Journal of the American Water Resources Association 35, 939–954.
Kennan, J. G. and Ayers, M. A.: 2002, ‘Relation of Environmental Characteristics to the Composition of Aquatic Assemblages Along a Gradient of Urban Land Use in New Jersey, 1996–1998’, U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report, 02-4069, West Trenton, NJ.
Knighton, D.: 1998, Fluvial Forms and Processes: A New Perspective, Edward Arnold, London, pp. 383.
Knox, J. C.: 1987, ‘Historical valley floor sedimentation in the Upper Mississippi Valley’, Annals of the Association of American Geographers 77, 224–244.
Kondolf, G. M.: 2000, ‘Assessing salmonid spawning gravel quality’, Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 129, 262–281.
Kondolf, G. M., Lisle, T. E. and Wolman, M. G.: 2003, ‘Bed sediment measurement’, in: G. M. Kondolf, and H. Piegay (eds.), Tools in Fluvial Geomorphology, Wiley, West Sussex, pp. 347–396.
Krumblein, W. C.: 1934, ‘Size frequency distribution of sediments’, Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 4, 65–77.
Leigh, D. S., Walters, D. M., Roy, A. H., Freeman, B. J., Freeman, M. C., Kramer, E. A., Paul, M. J., Pringle, C. M., and Rosemond, A. D.: 2002, ‘Landscape Indicators of Biotic Integrity in Piedmont Streams of the Etowah Basin, North Georgia, U.S.A. Final Technical Report Submitted to the United States Environmental Protection Agency to Fulfill Requirements of a Science to Achieve Results (STAR) Grant (#R826597-01-0)’, The University of Georgia Geomorphology Laboratory Research Report, 2, Athens, GA.
Martin, L. A., Mullholland, P. J., Webster, J. R. and Valett, H. M.: 2001, ‘Denitrification potential in sediments of headwater streams in the southern Appalachian Mountains, USA, Journal of the North American Benthological Society 20, 505–519.
Meade, R. H., Yuzyk, T. R. and Day, T. J.: 1990, ‘Movement and storage of sediment in the rivers of the United States and Canada’, in: M. G. Wolman, and H. C. Riggs, (eds.), Surface Water Hydrology, Geological Society of America, Boulder, CO, pp. 255–280.
Meehan, W. R.: 1991, ‘Influences of forest and rangeland management on salmonid fishes and their habitats’, American Fisheries Society Special Publication, 19.
Meybeck, M.: 1998, ‘Man and river interface: Multiple impacts on water and particulates chemistry illustrated in the Seine River basin’, Hydrobiologia 373, 1–20.
Montgomery, D. R. and Buffington, J. M.: 1997, ‘Channel-reach morphology in mountain drainage basins’, GSA Bulletin 109, 596–611.
National Climate Data Center (NCDC): 2003, Climatography of the United States no. 84, 1971–2000.
Paul, M. J., Leigh, D. S. and Lo, C. P.: 2001, ‘Urbanization in the Etowah River basin: Effects on stream temperature and chemistry’, Georgia Water Resources Conference, Athens, Georgia, pp. 241– 245.
Peck, M. F. and Garrett, J. W.: 1994, ‘Quality of surface and ground water in the White Creek and Mossy Creek watersheds, White County, Georgia, 1992–1993’, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report, 94-450, Atlanta, GA.
Pope, B. F., Tasker, G. D. and Robbins, J. C.: 2001, ‘Estimating the Magnitude and Frequency of Floods in Rural Basins of North Carolina – Revised’, U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report, 01-4207, Raleigh, NC.
Price, K. and Leigh, D. S.: ‘Stream morphological and sedimentological response to human impact in the southern Blue Ridge Mountains, USA’, submitted to Geomorphology.
Richards, C., and Bacon, K. L.: 1994, ‘Influence of fine sediment on macroinvertebrate colonization of surface and hyporheic stream substrates’, Great Basin Naturalist 54, 106–113.
Richards, C., Johnson, L. B. and Host, G. E.: 1996, ‘Landscape-scale influences on stream habitats and biota’, Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 53, 295–311.
Robinson, G. R., Jr., Lesure, F. G., Marlowe, J. I., II, Foley, N. K. and Clark, S. H.: 1992, ‘Bedrock geology and mineral resources of the Knoxville 1 degrees by 2 degrees quadrangle, Tennessee, North Carolina, and South Carolina’, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin, 1979, Reston, VA.
Roth, N. E., Allan, J. D. and Erickson, D. L.: 1996, ‘Landscape influences on stream habitats and biotic integrity assessed at multiple spatial scales’, Landscape Ecology 11, 141–156.
Roy, A. H., Rosemond, A. D., Leigh, D. S., Paul, M. J. and Wallace, J. B.: 2003a, ‘Habitat-specific responses of macroinvertebrates to land cover disturbance: biological consequences and monitoring implications’, Journal of the North American Benthological Society 22, 293–307.
Roy, A. H., Rosemond, A. D., Paul, M. J., Leigh, D. S. and Wallace, J. B.: 2003b, ‘Stream macroinvertebrate response to catchment urbanization (Georgia, U.S.A.)’, Freshwater Biology 48, 329–346.
Schoeneberger, P. J., Wysocki, D. A., Benham, E. G. and Broderson, W. D., eds. (2002). Field Book for Describing and Sampling Soils, Version 2.0. National Resources Conservation Center, National Soil Survey Center, Lincoln, NE.
Schumm, S. A.: 1977, The Fluvial System, John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 338.
Scott, M. C. and Helfman, G. S.: 2001, ‘Native invasions, homogenization, and the mismeasure of integrity of fish assemblages’, Fisheries 26, 6–15.
Shirmohammadi, A., Yoon, K. S. and Magette, W. L.: 1996, ‘Water quality in a mixed land use watershed – Piedmont region’, Journal of Environmental Science and Health A 31, 429–450.
Sponseller, R. A., Benfield, E. F. and Valett, H. M.: 2001, ‘Relationships between land use, spatial scale, and stream macroinvertebrate communities’, Freshwater Biology 46, 1409–1424.
Sutherland, A. S., Meyer, J. L. and Gardiner, E. P.: 2002, ‘Effects of land cover on sediment regime and fish assemblage structure in four southern Appalachian streams’, Freshwater Biology 47, 1791–1805.
Swank, W. T.: 1988, ‘Stream chemistry responses to disturbance’, in: W. T. Swank, and D. A. Crossley, Jr. (eds.), Forest Hydrology and Ecology at Coweeta, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 339–357.
Trimble, S. W.: 1974, Man-Induced Soil Erosion on the Southern Piedmont 1700–1970. Soil Conservation Society of America, Arkeny, IA, pp. 180.
U.S. DPA: 1983, ‘Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes’, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, EPA-600/4-79-020, Cincinatti, OH.
U.S. EPA: 1990, ‘The Quality of Our Nation's Water: a Summary of the 1988 Water Quality Inventory’, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, EPA-440/4-90-005, Washington, D.C.
U.S. EPA: 1997, ‘Volunteer stream monitoring: A methods manual’, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water, EPA-841-B-97-003, Washington, D.C.
U.S. EPA: 2000, ‘Ambient Water Quality Criteria Recommendations: Information Supporting the Development of State and Tribal Nutrient Criteria, Rivers and Streams in Ecoregion XI’, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water, EPA 822-BOO-020, Washington, D.C.
Walker, L. C.: 1991, The Southern Forest, University of Texas Press, Austin, TX, pp. 322.
Walling, D. E., Collins, A. L. and McMellin, G. K.: 2003, ‘A reconaissance survey of the source of interstitial fine sediment recovered from salmonid spawning gravels in England and Wales’, Hydrobiologia 497, 91–108.
Walling, D. E. and Fang, D.: 2003, ‘Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world's rivers’, Global and Planetary Change 39, 111–126.
Walters, D. M., Freeman, M. C., Leigh, D. S., Freeman, B. J., Paul, M. J. and Pringle, C. M.: 2001, ‘Bed texture and turbidity as indicators of fish biotic integrity in the Etowah River system’. In: K. J. Hatcher, (ed.), Proceedings of the 2001 Georgia Water Resources Conference, Athens, GA, pp. 233–236.
Walters, D. M., Leigh, D. S. and Bearden, A. B.: 2003a, ‘Urbanization, sedimentation, and homogenization of fishes in the Etowah River basin, Georgia Piedmont, USA’, Hydrobiologia 494, pp. 5–10.
Walters, D. M., Leigh, D. S., Freeman, M. C., Freeman, B. J. and Pringle, C. M.: 2003b, ‘Geomorphology and fish assemblages in a Piedmont river basin, U.S.A.’, Freshwater Biology 48, pp. 1950–1970.
Wang, L., Lyons, J., Kanehl, P. and Gatti, R.: 1997, ‘Influences of watershed land use on habitat quality and biotic integrity in Wisconsin streams’, Fisheries 22, pp. 6–12.
Waters, T. F.: 1995, Sediment in Streams: Sources, Biological Effects and Control, American Fisheries Monograph 7, American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, MD.
Wear, D. N. and Bolstad, P.: 1998, ‘Land-use changes in Southern Appalachian landscapes: Spatial analysis and forecast evolution’, Ecosystems 1, 575–594.
Wohl, E.: 2000, Mountain Rivers, Water Resources Monograph 14, American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C.
Wohl, E.: 2001, Virtual Rivers: Lessons from the Mountain Rivers of the Colorado Front Range, Yale University Press, New Haven, CT, pp. 210.
Wolman, M. G.: 1967, ‘A cycle of sedimentation and erosion in urban river channels’, Geografiska Annaler 49A, 385–395.
Yarnell, S. L.: 1998, The Southern Appalachians: A History of the Landscape, U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Southern Research Station General Technical Report, SRS-18, Asheville, N.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Price, K., Leigh, D.S. Comparative Water Quality of Lightly- and Moderately-Impacted Streams in the Southern Blue Ridge Mountains, USA. Environ Monit Assess 120, 269–300 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9060-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9060-1