Abstract
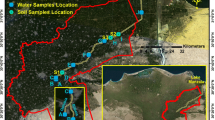
Molasses-based distilleries generate large quantities of effluent, which is used for irrigation in many countries including India. The effluent is rich in organic and inorganic ions, which may leach down and pollute the groundwater. An on-farm experiment was conducted to assess the impact of long-term irrigation with post-methanation distillery effluent (PMDE) on nitrate, sulphate, chloride, sodium, potassium, and magnesium contents in the groundwater of two sites in northwest India. Electrical conductivity (EC), pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) and colour were also determined to assess the chemical load in the groundwater. Nitrate content in the groundwater samples ranged from 16.95 mg L−1 in the unamended fields to 59.81 mg L−1 in the PMDE-amended fields during the 2-year study (2001–2002). Concentrations of TDS in water samples from tubewell of the amended field was higher by 40.4% over the tubewell water of the unamended field. Colour of the water samples of the amended fields was also darker than that of the unamended fields. The study indicated that the organic and inorganic ions added through the effluent could pose a serious threat to the groundwater quality if applied without proper monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BOD:
-
Biochemical oxygen demand
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- CPU:
-
Chloroplatinate colour unit
- EC:
-
Electrical conductivity
- MCL:
-
Maximum concentration limit
- PAR:
-
Potassium adsorption ratio
- PMDE:
-
Post-methanated distillery effluent
- QUEFTS:
-
Quantitative Evaluation of Fertility of Tropical Soils-model
- SAR:
-
Sodium adsorption ratio
- TDS:
-
Total dissolved solids
- USEPA:
-
United State Environment Protection Agency
References
Albus, W. L. and Knighton, R. E.: 1998, ‘Water quality in a sand plain after conversion from dry land to irrigation: Tillage and cropping systems compared’, Soil Tillage Res. 48, 195–205.
American Public Health Association: 1998, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th Edn. American Public Health Association American Water Works Association/Water Pollution Control Federation, Washington, DC.
Brown, S., Schreier, H., Shah, P. B. and Lavkulich, L. M.: 1999, ‘Modeling soil nutrient budgets: An assessment of agricultural sustainability in Nepal’, Soil Use Manage. 15, 101–108.
Chonker, P. K., Datta, S. P., Joshi, H. C. and Pathak, H.: 2000, ‘Impact of industrial effluent on soil health and agriculture – Indian experience: Part 1-Distillery and paper mill effluent’, J. Sci. Indust. Res. 59, 350–361.
Deverajan, L., Rajannan, G., Ramanathan, G. and Oblisami, G.: 1994, ‘Effect of one time application of treated effluent on soil fertility status, yield and quality of sugarcane’, SISSTA Sugar J. 21(1), 133.
Falkiner, R. A. and Smith, C. J.: 1997, ‘Changes in soil chemistry in effluent-irrigated Pinus radiata and Eucalyptus grandis plantations’, Aust. J. Soil Res. 35, 131–147.
Jagdale, H. N. and Sawant, N. K.: 1979, ‘Influence of added spent wash (Distillery waste) on growth and chemical composition of immature sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) cultivar CO-740’, Indian Sugar 29(7), 433–440.
Johnson, B. and Ryder, I.: 1988, The Disposal of Pulp and Paper Mill Effluents by Spray Irrigation onto Farmland, in: R. Bhamidimarri (ed), AlternativeWaste Treatment Systems, Elsevier Applied Science, London, pp. 55–66.
Joshi, H. C.: 1999, ‘Bioenery potential of distillery effluent’, Bioenergy News 3(3), 10–15.
Joshi, H. C., Kalra, N., Chaudhary, R., Pathak, H., Chaudhary, A. and Singh, N. N.: 1996, ‘Agrocycling – A pollution control strategy for distilleries in India’, Botanica 46, 170–176.
Joshi, H. C., Pathak, H., Chaudhary, A., Joshi, T. P., Phogat, V. K. and Kalra, N.: 2000, ‘Changes in soil properties with distillery effluent irrigation’, J. Environ. Res. 6(4), 153–162.
Mishra, B.: 1980, ‘A systems approach for fertilizer management practices in rice-wheat cropping system’, Fert. News 25(8), 14–18.
Pathak, H., Aggarwal, P. K., Roetter, R., Kalra, N., Bandyopadhaya, S. K., Prasad, S. and Van Keulen, H.: 2003, ‘Modelling the quantitative evaluation of soil nutrient supply, nutrient use efficiency, and fertilizer requirements of wheat in India’, Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 65(2), 105–113.
Pathak, H., Joshi, H. C., Chaudhary, A., Chaudhary, R., Kalra, N. and Dwivedi, M. K.: 1999, ‘Soil amendment with distillery effluent for wheat and rice cultivation’, Water, Air Soil Pollut. 113, 133–140.
Regmi, A. P., Ladha, J. K., Pathak, H., Pasuquin, E., Dawe, D., Hobbs, P. R., Joshy, D., Maskey, S. L. and Pandey, S. P.: 2002, ‘Analyses of yield and soil fertility trends in a 20-year rice-rice-wheat experiment in Nepal’, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 66, 857–867.
Roper, M. M. and Ladha, J. K.: 1995, ‘Biological N2 fixation by heterotrophic and phototrophic bacteria in association with straw’, Plant Soil 174, 211–224.
Smaling, E. M. A. and Fresco, L. O.: 1993, ‘A decision support model for monitoring nutrient balances under agricultural land use NUTMON’, Geoderma 60, 235–256.
Tandon, H. L. S.: 1994, Fertilizers, Organic Manures, Recyclable Wastes and Bio Fertilizers, Fertilizer Development and Consultation Organisation (FDCO), New Delhi, India.
Witt, C., Dobermann, A., Abdulrachman, S., Gines, H. C., Guanghuo, W., Nagarajan, R., Satawathananont, S., Tran Thuc Son, Pham Sy Tan, Van Tiem, Le, Simbahan, G. and Olk, D. C.: 1999, ‘Internal nutrient efficiencies in irrigated lowland rice of tropical and subtropical Asia’, Field Crops Res. 63, 113–138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, N., Bhatia, A., Kaushik, R. et al. Impact of Post-Methanation Distillery Effluent Irrigation on Groundwater Quality. Environ Monit Assess 110, 243–255 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-7695-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-7695-6