Abstract
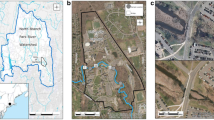
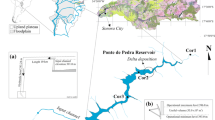
Phase I of the Kissimmee River restoration project included backfilling of 12 km of canal and restoring flow through 24 km of continuous river channel. We quantified the effects of construction activities on four water quality parameters (turbidity, total phosphorus flow-weighted concentration, total phosphorus load and dissolved oxygen concentration). Data were collected at stations upstream and downstream of the construction and at four stations within the construction zone to determine if canal backfilling and construction of 2.4 km of new river channel would negatively impact local and downstream water quality. Turbidity levels at the downstream station were elevated for approximately 2 weeks during the one and a half year construction period, but never exceeded the Florida Department of Environmental Protection construction permit criteria. Turbidity levels at stations within the construction zone were high at certain times. Flow-weighted concentration of total phosphorus at the downstream station was slightly higher than the upstream station during construction, but low discharge limited downstream transport of phosphorus. Total phosphorus loads at the upstream and downstream stations were similar and loading to Lake Okeechobee was not significantly affected by construction. Mean water column dissolved oxygen concentrations at all sampling stations were similar during construction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association: 1985, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, Washington, DC.
Brookes, A. and Shields Jr. D.F.: 1996, River Channel Restoration: Guiding Principles for Sustainable Projects, Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, pp. 2–3.
Cairns, J.: 1991, ‘The status of the theoretical and applied science of restoration ecology’, Environ. Prof. 13, 186–194.
Colangelo, D.J. and Jones, B.L.: 2001, Dissolved Oxygen in the Kissimmee River: Baseline Report, South Florida Water Management District, West Palm Beach, FL.
FDEP: 2001, ‘Total Maximum Daily Load for Total Phosphorus in Lake Okeechobee, Florida’, Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Tallahassee, FL.
Federico, A.C., Dickson, K.G., Kratzer, C.R. and Davis, F.E.: 1981, Lake Okeechobee Water Quality Studies and Eutrophication Assessment, South Florida Water Management District, West Palm Beach, FL.
Florida Game and Fresh Water Fish Commission: 1991, Lake Okeechobee-Kissimmee River-Everglades Resource Evaluation Project, Federal Wallop-Breaux Completion Report, (F-52-5), 328 pp.
Furse, J.B., Davis, L.J. and Bull, L.A.: 1996, ‘Habitat use and movements of largemouth bass associated with changes in dissolved oxygen and hydrology in Kissimmee River, Florida’, Proc. Annu. Conf. Southeast Assoc. Fish Wildl. Agencies 50, 12–25.
Gammon, J.R.: 1970, The Effect of Inorganic Sediment on Stream Biota, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Water Quality Office, Grant Number 18050DWC, Washington, DC.
Havens, K.E., Aumen, N.G., James, R.T. and Smith, V.H.: 1996, ‘Rapid ecological changes in a large subtropical lake undergoing cultural eutrophication’, Ambio 25, 150–155.
Jones, B.L.: 2002, Water Quality in the Channelized Kissimmee River System, South Florida Water Management District, West Palm Beach, FL.
Jungwirth, M., Muhar, S. and Schmutz, S.: 2002, ‘Re-establishing and assessing ecological integrity in riverine landscapes’, Freshw. Biol. 47, 867–887.
Koebel, J.W., Jr., Jones, B.L. and Arrington, D.A.: 1999, ‘Restoration of the Kissimmee River, Florida: Water quality impacts from canal backfilling’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 57, 85–107.
Koebel, J.W., Jr.: 1995, ‘An historical perspective on the Kissimmee River restoration project’, Restoration Ecol. 3(3), 149–159.
LaPerriere, J.D., Bjerklie, D.M., Simmons, R.C., Van Nieuwenhuyse, E., Wagener, S.M. and Reynolds, J.B.: 1983, Effect of Gold Placer Mining on Interior Alaska Stream Ecosystems, Managing Water Resources for Alaska’s Development, University of Alaska, Institute of Water Resources Report IWR-105, Fairbanks.
Lloyd, D.S.: 1987, ‘Turbidity as a water quality standard for salmonid habitats in Alaska’, N Am. J. Fish. Manage. 7, 18–33.
Mortimer, C.H.: 1941–1942, ‘The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes’, J. Ecol. 29, 280–329 and 30, 147–201.
Muncy, R.J., Atchison, G.J., Bulkley, R.V., Menzel, B.W., Perry, L.G. and Summerfelt, R.C.: 1979, Effects of Suspended Solids and Sediment on Reproduction and Early Life of Warmwater Fishes: A Review, U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, EPA Report 600/3-79-042, Washington, DC.
National Research Council: 1992, ‘Restoration of Aquatic Ecosystems, Science, Technology, and Public Policy’, National Academy Press, Washington, DC, p. 6.
Rosenberg, D.M. and Snow, N.B.: 1975a, Ecological Studies of Aquatic Organisms in the Mackenzie and Porcupine River Drainages in Relation to Sedimentation, Department of the Environment, Fisheries and Marine Service, Freshwater Institute, Technical Report 547,Winnipeg, Manitoba.
Rosenberg, D.M. and Snow, N.B.: 1975b, A Design for Environmental Impact Studies with Special Reference to Sedimentation in the Mackenzie and Porcupine River Drainages’, in Proceedings of the Circumpolar Conference on Northern Ecology, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, pp. 65–78.
SAS Institute Inc. 1999. SAS ver. 8.0. Cary, North Carolina
Shields, F.D., Jr. and Sanders, T.G.: 1986, ‘Water quality effects of excavation and diversion’, J. Environ. Eng. 112(2), 211–228.
Simmons, C.E. and Watkins, S.A.: 1982, ‘The Effects of Channel Excavation on Water Quality Characteristics of the Black River and on Ground-Water Levels Near Dunn, NC’, Water-Resources Investigations of the U.S. Geological Survey, Book 5, Ch. A1, U.S. Geological Survey, Washington, DC.
Society for Ecological Restoration Science and Policy Working Group: 2002, ‘The SER Primer on Ecological Restoration’, www.ser.org/.
Toth, L.A.: 1993, ‘The ecological basis of the Kissimmee River restoration plan’, Florida Scientist 56, 25–51.
Toth, L.A., Arrington, D.A., Brady, M.A. and Muszik, D.A.: 1995, ‘Conceptual evaluation of factors potentially affecting restoration of habitat structure within the channelized Kissimmee River’, Restoration Ecol. 3(3), 160–180.
Toth, L.A., Miller, S.J. and Loftin, M.K.: 1990, ‘September 1988 Kissimmee River Fish Kill’, in M.K. Loftin, L. A. Toth and J. Obeysekera (eds.), Proceedings of the Kissimmee River Restoration Symposium, October 1988, Orlando, Florida, South Florida Water Management District, West Palm Beach. pp. 241–248.
Waters, T.F.: 1995, ‘Sediment in streams: sources, biological effects and control’, Am. Fish. Soc. Monogr. 7.
Wullschleger, J.G., Miller, S.J. and Davis, L.J.: 1990, ‘An Evaluation of the Effects of the Restoration Demonstration Project on the Kissimmee River Fishes’, in M. K., Loftin, L. A. Toth and J. Obeysekera, (eds.), Proceedings of the Kissimmee River Restoration Symposium, October 1988, Orlando, Florida, South Florida Water Management District, West Palm Beach,, pp. 67–81.
Zar, J.H.: 1996, ‘Biostatistical Analysis, 3rd ed.’ Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colangelo, D.J., Jones, B.L. Phase I of the Kissimmee River restoration project, Florida, USA: Impacts of construction on water quality. Environ Monit Assess 102, 139–158 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-6017-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-6017-3