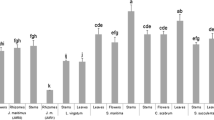
Abstract
Berberine showed in vitro remarkable antifungal activity against rice pathogens including Bipolaris oryzae, Curvularia lunata, Pyricularia oryzae and Rhizoctonia solani with MIC values of 125 μg/mL. It showed potent preventative and curative activities in suppression of brown leaf spot disease of a susceptible Oryza sativa var. KDML 105 under greenhouse conditions. Berberine at 5 mg/mL showed effective brown leaf spot disease suppression in rice when applied before pathogen inoculation. It also showed higher fungicidal activity in suppression of brown leaf spot disease in plants aged 30 and 60 days than did difenoconazole and mancozeb when applied after pathogen inoculation. Moreover, berberine at 10 mg/mL significantly (P < 0.05) reduced the percentage of rice blast disease severity by 49.81%, which was similar to the action of difenoconazole and mancozeb when applied twice under field conditions. However, it showed low fungicidal activity against dirty particle disease, a complex disease of rice, under field conditions when compared with synthetic fungicides. These results indicated that berberine is a promising bioactive compound which may be developed as a lead compound in a new fungicide to control brown leaf spot and blast diseases of rice.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awla, H. K., Kadir, J., Othman, R., Rashid, T. S., Hamid, S., & Wong, M.-Y. (2017). Plant growth-promoting abilities and biocontrol efficacy of Streptomyces sp. UPMRS4 against Pyricularia oryzae. Biological Control, 112, 55–63.
Basha, S. A., Mishra, R. K., Jha, R. N., Pandey, V. B., & Singh, U. P. (2002). Effect of berberine and (±)-bicuculline isolated from Corydalis chaerophylla on spore germination of some fungi. Folia Microbiologica, 47, 161–165.
Chen, L., Bu, Q., Xu, H., Liu, Y., She, P., Tan, R., & Wu, Y. (2016). The effect of berberine hydrochloride on Entercoccus faecalis biofilm formation and dispersion in vitro. Microbiological Research, 186–187, 44–51.
Cong, L., Liao, Y., Yang, S., & Yang, R. (2017). In vitro activity of berberine alone and in combination with antifungal drugs against planktonic forms and biofilms of Trichosporon asahii. Mycopathologia, 182, 829–837.
Cortes, M. V. C. B., Silva-Lobo, V. L., Filippi, M. C. C., Lima, D. C. S., & Prabhu, A. S. (2014). Potential for using crude extract of Sarocladium oryzae for suppression of rice blast. Tropical Plant Pathology, 39, 28–34.
da Silva, A. R., de Andrade Neto, J. B., da Silva, C. R., de Sousa Campos, R., Silva, R. A. C., Freitas, D. D., do Nascimento, F. B. S. A., de Andrade, L. N. D., Sampaio, L. S., Grangeiro, T. B., Magalhães, H. I. F., Cavalcanti, B. C., de Moraes, M. O., & Jũnior, H. V. N. (2016). Berberine antifungal activity in fluconazole-resistant pathogenic yeasts: Action mechanism evaluated by flow cytometry and biofilm growth inhibition in Candida spp. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 60, 3551–3557.
de Frana, S. K. S., Cardoso, A. F., Lustosa, D. C., Ramos, E. M. L. S., de Filippi, M. C. C., & da Silva, G. B. (2015). Biocontrol of sheath blight by Trichoderma asperellum in tropical lowland rice. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 35, 317–324.
Dethoup, T., Songkumorn, P., Rueangrit, S., Suesa-ard, S., & Kaewkarjay, C. (2018). Fungicidal activity of Thai medicinal plant extracts against Alternaria brassicicola causing black spot of Chinese kale. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 152, 157–167.
Dhamgaye, S., Devaux, F., Vandeputte, P., Khandelwal, N. K., Sanglard, D., Mukhopadhyay, G., & Prasad, R. (2014). Molecular mechanisms of action of herbal antifungal alkaloid berberine, in Candida albicans. PLoS One, 9, e104554.
Dong, F., Li, J., Chankvetadze, B., Cheng, Y., Xu, J., Liu, X., Li, Y., Chen, X., Bertucci, C., Tedesco, D., Zanasi, R., & Zheng, Y. (2013). Chiral triazole fungicide difenoconazole: Absolute stereochemistry, stereoselective bioactivity, aquatic toxicity, and environmental behavior in vegetables and soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 3386–3394.
Eksteen, D., Pretorius, J. C., Nieuwoudt, T. D., & Zietsman, P. C. (2001). Mycelial growth inhibition of plant pathogenic fungi by extracts of south African plant species. Annals of Applied Biology, 139, 243–249.
Fu, W., Tian, G., Pei, Q., Ge, X., & Tian, P. (2017). Evaluation of berberine as a natural compound to inhibit peach brown rot pathogen Monolinia fracticola. Crop Protection, 91, 20–26.
Gullino, G. L., Tinivella, F., Garibaldi, A., Kemmitt, G. M., Bacci, L., & Sheppard, B. (2010). Mancozeb: Past, present, and future. Plant Disease, 94, 1076–1087.
Harish, S., Saravanakumar, D., Radjacommare, R., Ebenezar, E. G., & Seetharaman, K. (2008). Use of plant extracts and biocontrol agents for the management of brown spot disease in rice. BioControl, 53, 555–567.
Hobbeelen, P. H. F., Pavaley, N. D., & van den Bosch, F. (2014). The emergence of resistance to fungicides. PLoS One, 9, e91910.
International Rice Research Institute. (1996). Standard evaluation system for rice: 4th Edition. Los Banos, The Philippines.
International Rice Research Institute. (2013). Standard evaluation system for rice: 5th Edition. Los Banos, The Philippines.
International Seed Testing Association. (1996). International rules for seed testing. Zurich: The International Seed Testing Association.
Kumar, A., Chopra, K., Mukherjee, M., Pottabathini, R., & Dhull, D. K. (2015). Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update. European Journal of Pharmacology, 761, 288–297.
Leng, P., Zhang, Z., Li, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhao, M., & Pan, G. (2012). Development of a difenoconazole/ propiconazole microemulsion and its antifungal activities against Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA. Pharmazie, 67, 534–541.
Liu, Q., Niu, H., Zhang, W., Mu, H., Sun, C., & Duan, J. (2015). Synergy among thymol, eugenol, berberine, cinnamaldehyde and streptomycin against planktonic and biofilm-associated food-borne pathogens. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 60, 421–430.
Madden, L. V., Hughes, G., & Van den Bosch, F. (2007). Temporal analysis III: Advanced topics. In L. V. Madden, G. Hughes, & F. Van den Bosch (Eds.), The study of plant disease epidemics (pp. 145–171). St Paul: American Phytopathological Society.
Naveenkumar, R., Muthukumar, A., Sangeetha, G., & Mohanapriya, R. (2017). Developing eco-friendly biofungicide for the management of major seed borne diseases of rice and assessing their physical stability and storage life. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 340, 214–225.
Neag, M. A., Mocan, A., Echeverria, J., Pop, R. M., Bocsan, C. I., Crisan, G., & Buzoianu, A. D. (2018). Berberine: Botanical occurrence, traditional uses, extraction methods, and relevance in cardiovascular, metabolic, hepatic, and renal disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 557. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00557.
Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P., Maipas, S., Kotampasi, C., Stamatis, P., & Hens, L. (2016). Chemical pesticides and human health: The urgent need for a new concept in agriculture. Frontiers in Public Health, 4, 148. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2016.00148.
Raveloson, H., Ramonta, I. R., Tharrean, D., & Sester, M. (2018). Long-term survival of blast pathogen in infected rice residues as major source of primary inoculum in high altitude upland ecology. Plant Pathology, 67, 610–618.
Shao, Z., Li, Z., Fu, Y., H., Wen, Y., & Wei, S. (2018). Induction of defense responses against Magnaporthe oryzae in rice seedling by a new potential biological agent Streptomyces JD211. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 58, 686–697.
Singburaudom, N. (2015). The alkaloid berberine isolated from Coscinium fenestratum is an inhibitor of phytopathogenic fungi. Journal of Biopesticides, 8, 28–36.
Spence, C., Alff, E., Johnson, C., Ramos, C., Donofrio, N., Sundaresan, V., & Bais, H. (2014). Natural rice rhizospheric microbes suppress rice blast infections. BMC Plant Biology, 14, 130. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-130.
Thi, Q. N., Ueda, K., Kihara, J., & Ueno, M. (2015). Inhibition of Magnaporthe oryzae by culture filtures of fungi isolated from wild mushrooms. Advances in Microbiology, 5, 686–692.
Torres, E. J. P., Cabrera, A. B., Virelles, P. M., Mora, M. L., Reyes, Y. S., & Santana, R. C. (2017). Antagonistic activity Trichoderma harzianum Rifai on the causal agent of rice blast (Pyricularia grisea Sacc.). Centre Agricola, 44, 13–19.
Van de Wouw, A. P., Elliott, V. L., Chang, S., Lόpez-Ruiz, F. J., Marcroft, S. J., & Idnurm, A. (2017). Identification of isolates of plant pathogen Leptospheria maculans with resistance to the triazole fungicide fluquinconazole using a novel in planta assay. PLoS One, 15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188106.
Wang, X., Yao, X., Zhu, Z., Tang, T., Dai, K., Sadavskaya, I., Fiahaut, S., & Jabbouri, S. (2009). Effect of berberine on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 34, 60–66.
Yuan, G., Chen, Y., Li, F., Zhou, R., Li, Q., Lin, W., & Huang, L. (2017). Isolation of an antibacterial substance from Mahonia fortunei and its biological activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Journal of Phytopathology, 165, 289–296.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Graduate School, Kasetsart University and the Kasetsart University Research Development Institute (KURDI) for financial support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by all authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokkrua, S., Ismail, S.I., Mazlan, N. et al. Efficacy of berberine in controlling foliar rice diseases. Eur J Plant Pathol 156, 147–158 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01871-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01871-3