Abstract
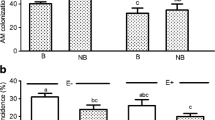
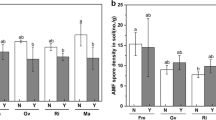
Both arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) Claroideoglomus etunicatum and grass endophytes (Epichloë) could improve disease tolerance. Research is limited on the dual infection by AMF and Epichloë on plant diseases. Bipolaris sorokiniana is a fungal species that causes leaf spot in cereals, and also in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne), impacting its growth and production. This experiment tested the dual infection of AMF and Epichloë on perennial ryegrass growth and the physiological and biochemical indexes under limited soil conditions occurs in nature ecosystem. The results showed that infection with B. sorokiniana significantly decreased plant growth and shoot N concentration (P < 0.05), and this negative effect was exaggerated by AMF × Epichloë. The pathogen alone decreased AMF colonization (P < 0.05); however, the interactions of the pathogen and grass endophyte showed the highest value of perennial ryegrass AM colonization. Infection with AMF or Epichloë alone, or the combination of the two, suppressed the occurrence of leaf spot. Epichloë×AMF × B. sorokiniana had the highest amount of β-1,3-glucanase activity and jasmonic acid activity, whereas AMF and Epichloë alone or combined significantly increased the lignin content in diseased plants (P < 0.05). Limited soil nutrients did not affect the inhibition function of AMF and Epichloë for PRG leaf spot disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. F., Smith, W. K., Moore, T. S., & Christensen, M. (1981). Comparative water relations and photosynthesis of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal Bouteloua gracilis H.B.K. Lag Ex Steud. New Phytologist, 88, 683–693.
Arnold, A. E., Maynard, Z., Gilbert, G. S., Coley, P. D., & Kursar, T. A. (2002). Are tropical fungal endophytes hyperdiverse? Ecology Letters, 3, 267–274.
Boller, T., Gehri, A., Mauch, F., & Vgeli, U. (1983). Chitinase in bean leaves induction by ethylene, purification, properties, and possible function. Planta, 157, 22–31.
Chen, K., Sun, J. Q., Liu, R. J., & Li, M. (2013). Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on the seedling growth of grafted watermelon and the defensive enzyme activities in the seedling roots. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 135–141 (in Chinese).
Cheng, G. W., & Breen, P. J. (1991). Activity of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and concentrations of anthocyanins and phenolics in developing strawberry fruit. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 116, 865–869.
Clarke, B. B., White, J. F. J., Hurley, R. H., Torres, M. S., Sun, S., & Huff, D. R. (2006). Endophyte-mediated suppression of dollar spot disease in fine fescues. Plant Disease, 90, 994–998.
Clay, K., & Schardl, C. (2002). Evolutionary origins and ecological consequences of endophyte symbiosis with grasses. American Naturalist, 160, 99–127.
Duan, T. Y., Facelli, E., Smith, S. E., Smith, F. A., & Nan, Z. B. (2011). Differential effects of soil disturbance and plant residue retention on function of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbiosis are not reflected in colonization of roots or hyphal development in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43, 571–578.
Feldmann, F., & Boyle, C. (1998). Concurrent development of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization and powdery mildew infection on three Begonia Hiemalis Cultivars. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, 2, 121–129.
Fitter, A. H. (1991). Costs and benefits of mycorrhizas: Implications for functioning under natural conditions. Experientia, 47, 350–355.
Gao, P., Li, Y. D., Guo, Y. E., & Duan, T. Y. (2018). Co-inoculation of an AM fungus and a rhizobium reduce alfalfa spring black stem and leaf spot occurrence caused by Phoma medicaginis. In Crop and Pasture Science (Vol. 69, p. 933). https://doi.org/10.1071/CP18135.
Giovannetti, M., & Mosse, B. (1980). An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytologist, 84, 489–500.
Gu, Y. X., Wang, D. J., & Hu, Y. G. (2007). The effect of endophytic fungus on Curvularia lunate in Festuca Arundinacea. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 29, 112–115 (In Chinese).
Harper, J. K., Arif, A. M., Ford, E. J., Strobel, G. A., Porco, J. A., Tomer, D. P., Oneill, K. L., Heider, E. M., & Grant, D. M. (2003). Pestacin: A 1,3-dihydro isobenzofuran from Pestalotiopsis microspora possessing antioxidant and antimycotic activities. Tetrahedron, 59, 2471–2476.
Hilou, A., Zhang, H., Franken, P., & Hause, B. (2014). Do jasmonates play a role in arbuscular mycorrhiza-induced local bioprotection of Medicago truncatula against root rot disease caused by Aphanomyces euteiches. Mycorrhiza, 24, 45–54.
Huang, J. H., Zeng, R. S., & Luo, S. M. (2006). Studies on disease resistance of maize toward sheath blight induced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 14, 167–169.
Jiang, S. P., & Wang, Z. Y. (2006). Study on the resistance of tall fescue infected by endophyte fungus to brown patch. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 34, 4345–4346 (In Chinese).
Kauffmann, S., Legrand, M., & Geoffroy, P. (1987). Biological function of pathogenesis-related′proteins: Four PR proteins of tobacco have β-1, 3-glucanase activity. EMBO Journal, 6, 3209–3212.
Kelemu, S., Jr., J, W., Muñoz, F., & Takayama, Y. (2001). An endophyte of the tropical forage grass Brachiaria brizantha: Isolating, identifying, and characterizing the fungus, and determining its antimycotic properties. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 47, 55–62.
Klironomos, J. N. (2003). Variation in plant response to native and exotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecology, 84, 2292–2301.
Koch, K. E., & Johnson, C. R. (1984). Photosynthate partitioning in split-root citrus seedlings with mycorrhizal and nonmycorrhizal root systems. Plant Physiology, 75, 26–30.
Li, F. (2016). Influence of grass endophyte and two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on leaf spot disease of perennial ryegrass. Master Degree Thesis of Lanzhou University. (In Chinese).
Li, M. S., & Yan, X. F. (2014). Jasmonic acid signaling in plants and its biological functions in relation to environment. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34.
Li, F., Guo, Y. E., Christensen, M. J., Gao, P., Li, Y. Z., & Duan, T. Y. (2018). An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and Epichloë festucae var. lolii reduce Bipolaris sorokiniana disease incidence and improve perennial ryegrass growth. Mycorrhiza, 28, 159–169.
Liu, Q., Parsons, A. J., Xue, H., Fraser, k., Ryan, G. D., & Newman, A. N. (2011). Competition between foliar Neotyphodium lolii, endophytes and mycorrhizal Glomus, spp. fungi in Lolium perenne, depends on resource supply and host carbohydrate content. Functional Ecology, 25, 910–920.
Ma, M. Z., & Nan, Z. B. (2011). Effects of fungal endophytes from perennial ryegrass on the growth of plant pathogens. Pratacultural Science, 28, 962–968 (In Chinese).
Ma, M. Z., Christensen, M. J., & Nan, Z. B. (2015). Effects of the endophyte Epichloë festucae, var. lolii, of perennial ryegrass ( Lolium perenne ) on indicators of oxidative stress from pathogenic fungi during seed germination and seedling growth. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 141, 571–583.
Mack, K. M. L., & Rudgers, J. A. (2008). Balancing multiple mutualists: Asymmetric interactions among plants, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and fungal endophytes. Oikos, 117, 310–320.
Müller, J. (2003). Artificial infection by endophytes affects growth and mycorrhizal colonisation of Lolium perenne. Functional Plant Biology, 30, 419–424.
Müse, G., Schindler, T., Bergfeld, R., Ruel, K., Jacquet, G., Lapierre, C., Speth, V., & Schopfer, P. (1997). Structure and distribution of lignin in primary and secondary cell walls of maize coleoptiles analyzed by chemical and immunological probes. Planta, 201, 146–159.
Mustafa, G. B., Randoux, B., Tisserant, J., Fontaine, J., Magnin-Robert, M., Lounès-Hadj, S. A., & Reignault, P. (2016). Phosphorus supply, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal species, and plant genotype impact on the protective efficacy of mycorrhizal inoculation against wheat powdery mildew. Mycorrhiza, 26, 685–697.
Nan, Z. B. (1995). Fungicide seed treatments of sainfoil control seed-borne and root-invading fungi. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 38, 413–420.
Nan, Z. B., & Li, C. J. (2004). Roles of the grass-Neotyphodium association in pastoral agriculture systems. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 605–616 (In Chinese).
Novas, M. V., Cabral, D., & Godeas, A. M. (2005). Interaction between grass endophytes and mycorrhizas in Bromus setifolius from Patagonia, Argentina. Symbiosis, 40, 23–30.
Omacini, M., Eggers, T., Bonkowski, M., Gange, A. C., & Jones, T. H. (2006). Leaf endophytes affect mycorrhizal status and growth of co-infected and neighbouring plants. Functional Ecology, 20, 226–232.
Phillips, J. M., & Hayman, D. S. (1970). Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 55, 158–163.
Pirttila, A. M., Laukkanen, H., & Hohtola, A. (2002). Chitinase production in pine callus (Pinus sylvestris): A defense reaction against endophytes? Planta, 214, 848–852.
Pozo, M. J., Cordier, C., Dumas-Gaudot, E., Gianinazzi, S., Barea, J. M., & Azcónaguilar, C. (2002). Localized versus systemic effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on defence responses to Phytophthora infection in tomato plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53, 525–534.
Prestidge, R. A., & Ball, O. J. P. (1993). The role of endophytes in alleviating plant biotic stress in New Zealand. Palmerston North: Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Acremonium/Grass Interactions, 141–151.
Qin, J. H., Lu, Y., Li, X., Zhou, Y., Ren, A. Z., & Gao, Y. B. (2015). Effects of methyl jasmonate treatments and endophyte infection on growth of Achnatherum sibiricum. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26, 1145–1152 (In Chinese).
Ruiz-Lozano, J. M., Gianinazzi, S., & Gianinazzi-Pearson, V. (1999). Genes involved in resistance to powdery mildew in barley differentially modulate root colonization by the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae. Mycorrhiza, 4, 237–240.
Singh, D. P., Srivastava, J. S., Bahadur, A., & Singh, S. (2004). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi induced biochemical changes in pea (Pisum sativum) and their effect on powdery mildew (Erysiphe pisi). Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, 111, 266–272.
Smith, S. E., & Read, D. J. (2008). Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Longdon: Academic press.
Snellgrove, R. C., Splittstoesser, W. E., Stribley, D. P., & Tinker, P. B. (2010). The distribution of carbon and the demand of the fungal symbiont in leek plants with vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas. New Phytologist, 92, 75–87.
Spatafora, J. W., Chang, Y., Benny, G. L., Lazarus, K., Smith, M. E., & Berbee, M. L. (2016). A phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia, 108, 1028–1046.
Strobel, G., & Daisy, B. (2003). Bioprospecting for microbial endophytes and their natural products. Microbiology & Molecular Biology Reviews MMBR, 67, 491–502.
Sutherland, B. L., & Hogland, J. H. (1989). Effect of ryegrass containing the endophyte Acremonium lolii, on the performance of associated white clover and subsequent crops. Proceedings of the New Zealand Grassland Association, 50, 265–269.
Tian, P., Nan, Z. B., & Li, C. J. (2008). Effect of the endophyte Neotyphodium lolii on susceptibility and host physiological response of perennial ryegrass to fungal pathogens. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 122, 593–602.
Van Wees, S. C., Van, D. E. S., & Pieterse, C. M. (2008). Plant immune responses triggered by beneficial microbes. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 11, 443–448.
Vigo, C., Norman, J. R., & Hooker, J. E. (2000). Biocontrol of the pathogen Phytophthora parasitica by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is a consequence of effects on infection loci. Plant Pathology, 49, 509–514.
Wang, J. B., Wang, H. F., Wang, H. Y., Ren, J., & Zhang, S. Y. (2009). Study on determination of jasmonic acid in plants by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 24, 226–230.
Wang, C. X., Li, X. L., Song, F. Q., Wang, G. Q., & Li, B. Q. (2012). Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on fusarium wilt and disease resistance-related enzyme activity in cucumber seedling root. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 20, 53–57.
Wen, Z. H., Duan, T. Y., Christensen, M. J., & Nan, Z. B. (2015). Microdochium tabacinum, confirmed as a pathogen of alfalfa in Gansu Province, China. Plant Disease, 99, 87–92.
Wright, D. P., Scholes, J. D., & Read, D. J. (1998). Effects of VA mycorrhizal colonization on photosynthesis and biomass production of Trifolium repens L. Plant, Cell and Environment, 21, 209–216.
Zhang, X. X., Li, C. J., & Nan, Z. B. (2010). Effects of cadmium stress on growth and anti-oxidative systems in Achnatherum inebrians symbiotic with Neotyphodium gansuense. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 175, 703–709.
Zhang, X. X., Li, C. J., & Nan, Z. B. (2011). Effects of salt and drought stress on alkaloid production in endophyte-infected drunken horse grass (Achnatherum inebrians). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 39, 471–476.
Zhang, X. X., Nan, Z. B., Li, C. J., & Gao, K. (2014). Cytotoxic effect of ergot alkaloids in Achnatherum inebrians infected by the Neotyphodium gansuense endophyte. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62, 7419–7422.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by The National Natural Science Foundation (31100368), The China Agriculture Research System-Green manure (CARS-22), and The China Agriculture Research System-Forage Grass Research System (CARS-34).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig S1
Shoot dry weight (a) and root dry weight (b) of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) with grass endophyte (E+) and without grass endophyte (E-), infected by Bipolaris sorokiniana, colonized by AMF Glomus etunicatum, NM = not inoculated with AMF. Bars topped by the same lower case letter do not differ significantly between treatments at P ≤ 0.05 by Tukey’s HSD. See Table 1 for ANOVA results. (DOCX 55 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Gao, P., Li, F. et al. Effects of AM fungi and grass endophytes on perennial ryegrass Bipolaris sorokiniana leaf spot disease under limited soil nutrients. Eur J Plant Pathol 154, 659–671 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01689-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01689-z