Abstract
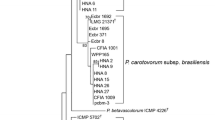
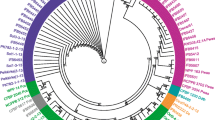
Using a DNA-based typing method, 48 bacterial strains isolated from infected potato (Solanum tuberosum) tubers originating from Kenya were characterized. The pel gene specific primers showed that all the 48 bacterial strains were pectolytic. Subspecies-specific primers EXPCCF/EXPCCR and Br1f/L1r identified 66 % of the strains as Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum while 34 % were identified as Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense based on their characteristic band sizes of 550 and 322 bp, respectively. Amplification of the 16S-23S rDNA (ITS) region did not yield observable differences in banding patterns between the Kenyan strains. However, PCR-RFLP analysis together with partial nucleotide sequences of the housekeeping mdh and gapA genes confirmed the results obtained by the specific primers. Phylogenetic analysis of the concatenated partial gene sequences grouped Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense Kenyan strains together with those identified in other parts of the world with 90 % and 99 % bootstrap support values, respectively. Pathogenicity assays using representative Kenyan strains demonstrated varied levels of tuber maceration ability. The Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense Kenyan strains were shown to be less aggressive in causing soft rot when compared to type strains. This study describes for the first time the genetic diversity of pectolytic bacteria causing soft rot disease of potatoes in Kenya.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baghaee-Ravari, S., Rahimian, H., Shams-Bakhsh, M., Lopez-Solanilla, E., Antunes-Lamas, M., & Rodriguez-Palenzuela, P. (2011). Characterization of Pectobacterium species from Iran using biochemical and molecular methods. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 129, 413–425.
Choi, O., & Kim, J. (2013). Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense causing soft rot on paprika in Korea. Journal of Phytopathology, 161, 125–127.
Costa, A. B., Eloy, M., Cruz, L., Janse, J. D., & Oliveira, H. (2006). Studies on pectolytic Erwinia spp. in Portugal reveal unusual strains of E. carotovora subsp. atroseptica. Journal of Plant Pathology, 88, 161–169.
Czajkowski, R., Pérombelon, M. C. M., van Veen, J. A., & van der Wolf, J. M. (2011). Control of blackleg and tuber soft rot of potato caused by Pectobacterium and Dickeya species: a review. Plant Pathology, 60, 999–1013.
Darrasse, A., Priou, S., Kotoujansky, A., & Bertheau, Y. (1994). PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism of a pel gene as a tool to identify Erwinia carotovora in relation to potato diseases. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 1437–1443.
De Boer, S. H., & Ward, L. J. (1995). PCR detection of Erwinia carotovorum subsp. atrosepticum associated with potato tissue. Phytopathology, 85, 854–858.
de Haan, E. G., Dekker-Nooren, T. C. E. M., van den Bovenkamp, G. W., Speksnijder, A. G. C. L., van der Zouwen, P. S., & van der Wolf, J. M. (2008). Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum can cause potato blackleg in temperate climates. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 122, 561–569.
Duarte, V., Boer, S. H. D., Ward, L. J., & Oliveira, A. M. R. D. (2004). Characterization of atypical Erwinia carotovora strains causing blackleg of potato in Brazil. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 96, 535–545.
Gardan, L., Gouy, C., Christen, R., & Samson, R. (2003). Elevation of three subspecies of Pectobacterium carotovorum to species level: Pectobacterium atrosepticum sp. nov., Pectobacterium betavasculorum sp. nov. and Pectobacterium wasabiae sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53, 381–391.
Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95–98.
Hauben, L., Moore, E. R. B., Vauterin, L., Steenackers, M., Mergaert, J., Verdonck, L., et al. (1998). Phylogenetic position of phytopathogens within the Enterobacteriaceae. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 21, 384–397.
Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat, N., Condemine, G., Nasser, W., & Reverchon, S. (1996). Regulation of pectinolysis in Erwinia chrysanthemi. Annual Review of Microbiology, 50, 213–257.
Hyman, L. J., Sullivan, L., Toth, I. K., & Perombelon, M. C. M. (2001). Modified crystal violet pectate medium (CVP) based on a new polypectate source (Slendid) for the detection and isolation of soft rot erwinias. Potato Research, 44, 265–270.
Kang, H. W., Kwon, S. W., & Go, S. J. (2003). PCR-based specific and sensitive detection of Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. carotovorum by primers generated from a URP-PCR fingerprinting-derived polymorphic band. Plant Pathology, 52, 127–133.
Katoh, K., Kuma, K., Toh, H., & Miyata, T. (2005). MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, 511–518.
Kim, H.-S., Ma, B., Perna, N. T., & Charkowski, A. O. (2009). Phylogeny and virulence of naturally occurring type III secretion-deficient Pectobacterium strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 4539–4549.
Lee, J.-H., Shin, H., Ji, S., Malhotra, S., Kumar, M., Ryu, S., et al. (2012). Complete genome sequence of phytopathogenic Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum bacteriophage PP1. Journal of Virology, 86, 8899–8901.
Ma, B., Hibbing, M. E., Kim, H.-S., Reedy, R. M., Yedidia, I., Breuer, J., et al. (2007). Host range and molecular phylogenies of the soft rot Enterobacterial genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya. Phytopathology, 97, 1150–1163.
McCarter-Zorner, N. J., Franc, G. D., Harrison, M. D., Michaud, J. E., Quinn, C. E., Sells, A. I., et al. (1984). Soft rot Erwinia bacteria in surface and underground waters in southern Scotland and in Colorado, United States. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 57, 95–105.
McCarter-Zorner, N. J., Harrison, M. D., Franc, G. D., Quinn, C. E., Sells, A. I., & Graham, D. C. (1985). Soft rot Erwinia bacteria in the rhizosphere of weeds and crop plants in Colorado, United States and Scotland. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 59, 357–368.
Moleleki, L. N., Onkendi, E. M., Mongae, A., & Kubheka, G. C. (2013). Characterisation of Pectobacterium wasabiae causing blackleg and soft rot diseases in South Africa. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 135, 279–288.
Molina, J. J., Harrison, M. D., & Brewer, J. W. (1974). Transmission of Erwinia carotovora var atroseptica by Drosophila melanogaster MEIG1. Acquisition and transmission of the bacterium. American Potato Journal, 51, 245–250.
Muthoni, J., Shimelis, H., & Melis, R. (2013). Potato production in Kenya: farming systems and production constraints. Journal of Agricultural Science, 5, 182–197.
Nabhan, S., De Boer, S. H., Maiss, E., & Wydra, K. (2012a). Taxonomic relatedness between Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum, Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense subsp. nov. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 113, 904–913.
Nabhan, S., Wydra, K., Linde, M., & Debener, T. (2012b). The use of two complementary DNA assays, AFLP and MLSA, for epidemic and phylogenetic studies of pectolytic enterobacterial strains with focus on the heterogeneous species Pectobacterium carotovorum. Plant Pathology, 61, 498–508.
Naum, M., Brown, E. W., & Mason-Gamer, R. J. (2011). Is a robust phylogeny of the enterobacterial plant pathogens attainable? Cladistics, 27, 80–93.
Ngadze, E., Brady, C. L., Coutinho, T. A., & van der Waals, J. E. (2012). Pectinolytic bacteria associated with potato soft rot and blackleg in South Africa and Zimbabwe. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 134, 533–549.
Onkendi, E., Maluleke, N., & Moleleki, L. N. (2013). First report of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense causing soft rot and blackleg diseases of potatoes in Kenya. Plant Disease. doi:10.1094/PDIS-09-13-0988-PDN.
Pérombelon, M. C. M. (2002). Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: an overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathology, 51, 1–12.
Perombelon, M. C. M., & van der Wolf, J. M. (1998). Methods for the detection and quantification of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica (Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. atrosepticum) on potatoes: a laboratory manual. Scottish Crop Research Institute, publication No. 10.
Pirhonen, M., Flego, D., Heikinheimo, R., & Palva, E. T. (1993). A small diffusible signal molecule is responsible for the global control of virulence and exoenzyme production in the plant pathogen Erwinia carotovora. The EMBO Journal, 12, 2467–2476.
Pitman, A. R., Wright, P. J., Galbraith, M. D., & Harrow, S. A. (2008). Biochemical and genetic diversity of pectolytic enterobacteria causing soft rot disease of potatoes in New Zealand. Australasian Plant Pathology, 37, 559–568.
Pitman, A. R., Harrow, S. A., & Visnovsky, S. B. (2010). Genetic characterisation of Pectobacterium wasabiae causing soft rot disease of potato in New Zealand. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 126, 423–435.
Posada, D., & Crandall, K. A. (1998). MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics Application Note, 14, 817–818.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2011). MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology, 28, 2731–2739.
Togashi, J., Uedal, K., & Namai, T. (2001). Diseased tissues in soil and its role as inoculum for soft rot of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris, Pekinensis group). Journal of General Plant Pathology, 67, 45–50.
Toth, I. K., Bertheau, Y., Hyman, L. J., Laplaze, L., López, M. M., McNicol, J., et al. (1999). Evaluation of phenotypic and molecular typing techniques for determining diversity in Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 87, 770–781.
Toth, I. K., Avrova, A. O., & Hyman, L. J. (2001). Rapid identification and differentiation of the soft rot Erwinias by 16S-23S intergenic transcribed spacer-PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism analyses. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 4070–4076.
Toth, I. K., Bell, K. S., Holeva, M. C., & Birch, P. R. J. (2003). Soft rot erwiniae: from genes to genomes. Molecular Plant Pathology, 4, 17–30.
van der Merwe, J. J., Coutinho, T. A., Korsten, L., & van der Waals, J. (2010). Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis causing blackleg on potatoes in South Africa. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 126, 175–185.
Yap, M.-N., Barak, J. D., & Charkowski, A. O. (2004). Genomic diversity of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora and its correlation with virulence. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 3013–3023.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by National Research Foundation-NRF (Grant number 69362) and the University of Pretoria. Any opinion, finding and conclusion or recommendation expressed in this material is that of the authors and the NRF does not accept any liability in this regard.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onkendi, E.M., Moleleki, L.N. Characterization of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and brasiliense from diseased potatoes in Kenya. Eur J Plant Pathol 139, 557–566 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0411-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0411-z