Abstract
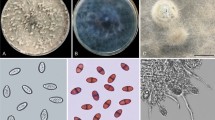
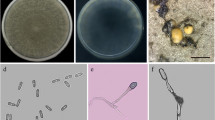
Adonis palaestina Boiss. is one of the top three natural sources of red pigment astaxanthin, which has been used as a valuable antioxidant nutraceutical and a feed additive for salmonid fish raising. Since 2004, a blight disease causing significant damage to plants of A. palaestina in Inner Mongolia, China has occurred. The disease caused small, brown lesions on petioles and stems of the host plants. The disease initially appeared in the field as a brown necrosis on lower parts of the plant, and eventually expanded to the whole plant resulting in complete defoliation. The fungus consistently isolated from symptomatic tissues was identified as Phoma adonidicola based on morphological characteristics. Phylogenetic analysis based on LSU (Large Subunit - 28S), ITS (ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 region), and TUB (β-tubulin) showed that the P. adonidicola isolates fall in the same well-supported clade, which is closely related to Stagonosporopsis ajacis. All isolates of P. adonidicola also caused typical spots on inoculated plants, and were successfully reisolated from the symptomatic tissues. The disease of A. palaestina was proposed as spot blight.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aveskamp, M. M., Verkley, G. J. M., De Gruyter, J., Murace, M. A., Perello, A., Woudenberg, J. H. C., et al. (2009). DNA phylogeny reveals polyphyly of Phoma section Peyronellaea and multiple taxonomic novelties. Mycologia, 101(3), 363–382.
Aveskamp, M., De Gruyter, J., Woudenberg, J., Verkley, G., & Crous, P. W. (2010). Highlights of the Didymellaceae: a polyphasic approach to characterise Phoma and related pleosporalean genera. Studies in Mycology, 65(1), 1–60.
Boerema, G. H., de Gruyter, J., Noordeloos, M. E., & Hamers, M. E. C. (2004). Phoma identification manual, differentiation of specific and infra-specific taxa in culture. Wallingford: CABI Publishing.
Cober, E. R., Donaldson, P. A., Simmonds, D. H., Rioux, S., & Rajcan, I. (2003). Partial resistance to white mold in a transgenic soybean line. Crop Science, 43(1), 92–95.
Den Breeÿen, A., Groenewald, J. Z., Verkley, G. J. M., & Crous, P. W. (2006). Morphological and molecular characterisation of Mycosphaerellaceae associated with the invasive weed, Chromolaena odorata. Fungal Diversity, 23, 89–110.
Fassett, R. G., & Coombes, J. S. (2009). Astaxanthin, oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Future Cardiology, 5(4), 333–342.
Gardes, M., & Bruns, T. D. (1993). ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Molecular Ecology, 2(2), 113–118.
Higuera-Ciapara, I., Felix-Valenzuela, L., & Goycoolea, F. M. (2006). Astaxanthin: a review of its chemistry and applications. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 46(2), 185–196.
Johnson, E. A., Villa, T. G., & Lewis, M. J. (1980). Phaffia rhodozyma as an astaxanthin source in salmonid diets. Aquaculture, 20(2), 123–134.
Kobayashi, M., Kakizono, T., & Nagai, S. (1991). Astaxanthin production by a green alga, Haematococcus pluvialis accompanied with morphological changes in acetate media. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 71(5), 335–339.
Koike, S. T., Subbarao, K. V., Verkley, G. J. M., Fogle, D., & O’Neill, T. M. (2006). Phoma basal rot of Romaine lettuce in California caused by Phoma exigua: occurrence, characterization, and control. Plant Disease, 90(10), 1268–1275.
Li, Y., Wang, Q., Mei, R. H., & Lu, G. Z. (2006). Phoma adonidicola sp. nov. on Adonis palaestina. Mycotaxon, 98, 237–240.
López, M., Arce, L., Garrido, J., Rı́os, A., & Valcárcel, M. (2004). Selective extraction of astaxanthin from crustaceans by use of supercritical carbon dioxide. Talanta, 64(3), 726–731.
Montel, E., Bridge, P., & Sutton, B. (1991). An integrated approach to Phoma systematics. Mycopathologia, 115(2), 89–103.
Olaizola, M. (2000). Commercial production of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis using 25,000-liter outdoor photobioreactors. Journal of Applied Phycology, 12(3–5), 499–506.
Pashkow, F. J., Watumull, D. G., & Campbell, C. L. (2008). Astaxanthin: a novel potential treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. The American Journal of Cardiology, 101(10), S58–S68.
Rayton, S., Rayton, J., Foley, L., & Jones, P. W. (2006). Ketocarotenoids from Adonis palaestina. In U. S. P. A. Publication (Ed.).
Rehner, S. A., & Samuels, G. J. (1994). Taxonomy and phylogeny of Gliocladium analysed from nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycological Research, 98(6), 625–634.
Sedmak, J. J., Weerasinghe, D. K., & Jolly, S. O. (1990). Extraction and quantitation of astaxanthin from Phaffia rhodozyma. Biotechnology Techniques, 4(2), 107–112.
Seybold, A., & Goodwin, T. W. (1959). Occurrence of astaxanthin in the flower petals of Adonis annua L. Nature, 184(Suppl 22), 1714–1715.
Sharma, S., & Kolte, S. (1994). Effect of soil-applied NPK fertilizers on severity of black spot disease (Alternaria brassicae) and yield of oilseed rape. Plant and Soil, 167(2), 313–320.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2007). MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24(8), 1596–1599.
Vaghefi, N., Pethybridge, S. J., Ford, R., Nicolas, M. E., Crous, P. W., & Taylor, P. W. J. (2012). Stagonosporopsis spp. associated with ray blight disease of Asteraceae. Australasian Plant Pathology, 41(6), 675–686.
Vilgalys, R., & Hester, M. (1990). Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. Journal of Bacteriology, 172(8), 4238–4246.
Wang, W.-T. (1994). Revision of Adonis (Ranunculaceae) (II). Bulletin of Botanical Research, 14(2), 24.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications, 18, 315–322.
Zhang, J., Wu, X., Bai, D., Zhang, C., Bai, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2004). Pigment crops: Adonis palaestina and Marigold. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 5, 43–44.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by grants from Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant number: IRT1042) and the program from Tongliao Academy of Agricultural Science in Inner Mongolia. We are grateful to Dr. Xingzhong Liu of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Dr. Ching-Hong Yang of University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, USA for critical discussions and reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zheng, C., Zhao, Z. et al. Characterization of Phoma adonidicola causing a spot blight on Adonis palaestina . Eur J Plant Pathol 137, 127–136 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0224-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0224-5