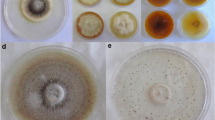
Abstract
Since 2004, a new leaf blight disease on garlic of high severity has been observed in Dangyang County, Hubei province, China. Initial symptoms consisted of multiple, small, irregular to oval, white leaf spots, which enlarge to produce sunken purple lesions, sometimes surrounded by a bright yellow margin. As the disease progressed, lesions expanded and merged, resulting in withering of leaf tips. After isolation and pathogenicity testing, the causal agent of leaf blight of garlic was identified as Stemphylium solani from cultural and morphological characteristics, and subsequent analysis of the internal transcribed spacer region of ribosomal DNA. When fungal plugs of two S. solani isolates were inoculated onto 11 garlic cultivars and 20 other crop species, leaf spots appeared on all inoculated plants, but two garlic cultivars (Qingganruanye and Ruanruanye) and three crop species (Capsicum annuum, Brassica napus and Amaranthus mangostanus) showed the smallest leaf spots. In cross-inoculation experiments, no indications of host specificity were observed, but S. solani isolated from garlic was generally the most virulent on five plant species, while the isolate from leek (Allium odorum) was generally the least virulent. Toxicity testing of the crude culture filtrates indicated that garlic isolates produced toxin(s) that were not heat-labile and induced different levels of phytotoxicity toward various garlic cultivars and crops.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aveling, T. A. S., & Naude, S. P. (1992). First report of Stemphylium vesicarium on garlic in South Africa. Plant Disease, 76, 426.
Basallote, M. J., Prados, A. M., Perez de Algaba, A., & Melero, J. M. (1993). First report in Spain of two leaf spots of garlic caused by Stemphylium vesicarium. Plant Disease, 77, 952.
Boiteux, L. S., Henz, G. P., & Giordano, L. B. (1993). Solanum lycocarpum, a natural host of Stemphylium solani. Plant Disease, 77, 846.
Boiteux, L. S., Lima, M. F., Menezes, J. A., & Lopes, C. A. (1994). A garlic (Allium sativum) leaf blight caused by Stemphylium vesicarium in Brazil. Plant Pathology, 43, 412–414. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.1994.tb02704.x.
Ellis, M. B. (1971). Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Kew: Commonwealth Mycological Institute.
Haegi, A., & Porta-Puglia, A. (1995). Purification and partial characterization of a toxic compound produced by Pyrenophora graminea. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 46, 429–444. doi:10.1006/pmpp.1995.1033.
Hassan, M. H. A., Allam, A. D. A., Abo-Elyousr, K. A. M., & Hussein, M. A. M. (2007). First report of Stemphylium leaf blight of onion caused by Stemphylium vesicarium in Egypt. Plant Pathology, 56, 724. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.2007.01581.x.
Kim, B. S., Yu, S. H., Cho, H. J., & Hwang, H. S. (2004). Grey leaf spot in peppers caused by Stemphylium solani and S. lycopersici. The Plant Pathology Journal, 20, 85–91.
Lalitha, B., Snow, J. P., & Berggren, G. T. (1989). Phytotoxin production by Diaporthe phaseolorum var. caulivora, the causal organism of stem canker of soybean. Phytopathology, 79, 499–504. doi:10.1094/Phyto-79-499.
Lv, P. K., Li, M. Y., & Wu, J. W. (1998). Atlas of insect pests and diseases of vegetable crops in China. Beijing: Agricultural Publishing House.
Mehta, Y. R. (1998). Severe outbreak of Stemphylium leaf blight, a new disease of cotton in Brazil. Plant Disease, 82, 333–336. doi:10.1094/PDIS.1998.82.3.333.
Mehta, Y. R. (2001). Genetic diversity among isolates of Stemphylium solani from cotton. Fitopatologia Brasileira, 26, 703–709.
Mehta, Y. R., & Brogin, R. L. (2000). Phytotoxicity of a culture filtrate produced by Stemphylium solani of cotton. Plant Disease, 84, 838–842. doi:10.1094/PDIS.2000.84.8.838.
Miller, M. E., Taber, R. A., & Amador, J. M. (1978). Stemphylium blight of onion in South Texas. Plant Disease Reporter, 62, 851–853.
Perrone, G., Susca, A., Stea, G., & Mulè, G. (2004). PCR assay for identification of Aspergillus carbonarius and Aspergillus japonicus. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 110, 641–649. doi:10.1023/B:EJPP.0000032403.08921.49.
Pal, A. K., & Basuchaudhary, K. C. (1976). A new leaf blight of garlic caused by Cladosporium echlnulatum (Berk) de Vries, from Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh. Current Science, 45, 739.
Rao, N. N., & Pavgi, M. S. (1975). Stemphylium leaf blight of onion. Mycopathologica, 56, 113–118. doi:10.1007/BF00472582.
Segall, R. H., & Newhall, A. G. (1960). Onion blast or leaf spotting caused by species of Botrytis. Phytopathology, 50, 76–82.
Shang, H. S., Wang, S. Q., Zuo, J. Z., & Zhao, J. Y. (1997). The causal agent of white spot and rot of garlic bolt. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 6, 73–76.
Simmons, E. G. (1969). Perfect states of Stemphylium. Mycology, 61, 1–26. doi:10.2307/3757341.
Simmons, E. G. (1985). Perfect states of Stemphylium. II. Sydowia, 38, 284–293.
Singh, P., Bugiani, R., Cavanni, P., Nakajima, H., Kodama, M., Otani, H., et al. (1999). Purification and biological characterization of host-specific SV-toxins from Stemphylium vesicarium causing brown spot of European pear. Phytopathology, 89, 947–953. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.1999.89.10.947.
Smedegard-Petersen, V. (1977). Isolation of two toxins produced by Pyrenophora teres and their significance in disease development of netspot blotch of barley. Physiological Plant Pathology, 10, 203–211. doi:10.1016/0048-4059(77)90024-8.
Song, H. S., Lim, S. M., & Clark, J. M. (1993). Purification and partial characterization of a host-specific pathotoxin from culture filtrates of Septoria glycines. Phytopathology, 83, 659–661. doi:10.1094/Phyto-83-659.
Suheri, H., & Price, T. V. (2000a). Stemphylium leaf blight of garlic (Allium sativum) in Australia. Australasian Plant Pathology, 29, 192–199. doi:10.1071/AP00034.
Suheri, H., & Price, T. V. (2000b). Infection of onion leaves by Alternaria porri and Stemphylium vesicarium and disease development in controlled environments. Plant Pathology, 49, 377–384. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3059.2000.00458.x.
Taylor, B. H., Manhart, J. R., & Amsoino, R. M. (1993). Isolation and characterization of plant DNA. In B. R. Glick, & J. E. Thompson (Eds.), Methods in plant molecular biology and biotechnology (pp. 37–47). Boca Raton, FL: CRC.
Vidhyasekaran, P., Ponmalar, T. R., Samiyappan, R., Velazhahan, R., Vimala, R., Ramanathan, A., et al. (1997). Host-specific toxin production by Rhizoctonia solani, the rice sheath blight pathogen. Phytopathology, 87, 1258–1263. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.1997.87.12.1258.
Weber, F. G. (1930). Gray leaf spot of tomato caused by Stemphylium solani sp. nov. Phytopathology, 20, 513–518.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In M. A. Innis, D. H. Gelfand, J. J. Sninsky, & T. J. White (Eds.), PCR Protocols: a guide to methods and applications (pp. 315–322). San Diego: Academic.
Zheng, L., Huang, J. B., & Hsiang, T. (2008). First report of leaf blight of garlic (Allium sativum) caused by Stemphylium solani in China. Plant Pathology, 57, 380. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.2007.01724.x.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Key Research Project (2006AA201B06) of Hubei province, China, and by the Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Ontario, Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Lv, R., Hsiang, T. et al. Host range and phytotoxicity of Stemphylium solani, causing leaf blight of garlic (Allium sativum) in China. Eur J Plant Pathol 124, 21–30 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9387-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9387-x