Abstract
Objective
To compare vascular and glucose related mechanisms of type 2 diabetes on cognitive performance.
Research design and methods:
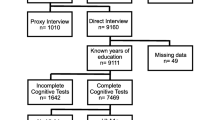
A cross-sectional observational study of type 2 diabetes defined by non insulin dependant self-report diabetes or fasting blood glucose ≤ 7.0 mmol/l of 2205 men eligible for the third phase of the Caerphilly Collaborative Heart Disease Study. Men were aged 55–69 years at time of testing. Tests of cognitive function included NART (crystallised IQ), AH4 (fluid IQ), verbal fluency (executive function) Cambridge Cognitive Examination (CAMCOG) and Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) (global function), four choice serial reaction time (psychomotor function) and memory. Men with prior stroke were omitted from the analysis.
Results:
Men with diabetes showed cognitive deficits for verbal fluency, National Adult Reacting Test (NART) and AH4. Adjusting for vascular risk factors had minimal effect. Including blood glucose removed the deficit for verbal fluency and NART but the effect on AH4 score (−2.58; 95% CI: −5.0, −0.1, p = 0.039) was retained. More detailed analyses of AH4 score on men with diabetes showed a curvilinear relationship indicating that men with both low and high glucose levels had worse performance (AH4 = −66 + 80 loge glucose – 18 loge glucose2; 95% CI: −29, −6; p=0.002).
Conclusions:
These data identify a direct effect of glucose regulation on cognitive performance associated with diabetes in a population sample. These data suggest that an effect of glucose regulation on cognitive performance in diabetes is distinct from any effect of macro-vascular disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
PA Scherr MS Albert HH Funkenstein et al. (1988) ArticleTitleCorrelates of cognitive function in an elderly community population Am J Epidemiol 128 1084–1101 Occurrence Handle3189282
J Woo SC Ho S Lau J Lau YK Yuen (1994) ArticleTitlePrevalence of cognitive impairment and associated factors among elderly Hong Kong Chinese aged 70 years and over Neuroepidemiol 13 50–58
I Bourdel-Marchasson B Dubroca G Manciet A Decamps JP Emeriau JF Dartigues (1997) ArticleTitlePrevalence of diabetes and effect on quality of life in older French living in the community: The PAQUID epidemiological survey J Am Geriatr Soc 45 295–301 Occurrence Handle9063274
S Kalmijn EJ Feskens LJ Launer T Stijnen D Kromhout (1995) ArticleTitleGlucose intolerance, hyperinsulinaemia and cognitive function in a general population of elderly men Diabetologia 38 1096–1102 Occurrence Handle8591825
MP Boxtel Particlevan F Buntinx PJ Houx JF Metsemakers A Knottnerus J Jolles (1998) ArticleTitleThe relation between morbidity and cognitive performance in a normal aging population J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 53 M147–M154 Occurrence Handle9520922
L Kilander H Nyman M Boberg H Lithell (1997) ArticleTitleCognitive function, vascular risk factors and education. A cross-sectional study based on a cohort of 70-year-old men J Intern Med 242 313–321 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2796.1997.00196.x Occurrence Handle9366810
DW Desmond TK Tatemichi M Paik Y Stern (1993) ArticleTitleRisk factors for cerebrovascular disease as correlates of cognitive function in a stroke-free cohort Arch Neurol 50 162–166 Occurrence Handle8431135
MW Strachan BM Frier IJ Deary (2003) ArticleTitleType 2 diabetes and cognitive impairment Diabet Med 20 1–2 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00855.x
JH Wu MN Haan J Liang D Ghosh HM Gonzalez WH Herman (2003) ArticleTitleImpact of diabetes on cognitive function among older Latinos: A population-based cohort study J Clin Epidemiol 56 686–693 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0895-4356(03)00077-5 Occurrence Handle12921938
EA Robertson-Tchabo D Arenberg JD Tobin JB Plotz (1986) ArticleTitleA longitudinal study of cognitive performance in noninsulin dependent (type II) diabetic men Exp Gerontol 21 459–467 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0531-5565(86)90051-3 Occurrence Handle3493169
D Knopman LL Boland T Mosley et al. (2001) ArticleTitleCardiovascular risk factors and cognitive decline in middle-aged adults Neurology 56 42–48 Occurrence Handle11148234
R Peila BL Rodriguez LJ Launer (2002) ArticleTitleType 2 diabetes, APOE gene, and the risk for dementia and related pathologies: The Honolulu-Asia Aging Study Diabetes 51 1256–1262 Occurrence Handle11916953
JA Luchsinger MX Tang Y Stern S Shea R Mayeux (2001) ArticleTitleDiabetes mellitus and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with stroke in a multiethnic cohort Am J Epidemiol 154 635–641 Occurrence Handle10.1093/aje/154.7.635 Occurrence Handle11581097
A Ott RP Stolk F Harskamp Particlevan HA Pols A Hofman MM Breteler (1999) ArticleTitleDiabetes mellitus and the risk of dementia: The Rotterdam Study Neurology 53 1937–1942 Occurrence Handle10599761
A Fontbonne C Berr P Ducimetiere A Alperovitch (2001) ArticleTitleChanges in cognitive abilities over a 4-year period are unfavorably affected in elderly diabetic subjects: Results of the epidemiology of vascular aging study Diabetes Care 24 366–370 Occurrence Handle11213894
MN Haan L Shemanski WJ Jagust TA Manolio L Kuller (1999) ArticleTitleThe role of APOE epsilon4 in modulating effects of other risk factors for cognitive decline in elderly persons JAMA 282 40–46 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.282.1.40 Occurrence Handle10404910
G Logroscino JH Kang F Grodstein (2004) ArticleTitleProspective study of type 2 diabetes and cognitive decline in women aged 70–81 years BMJ 328 548 Occurrence Handle10.1136/bmj.37977.495729.EE Occurrence Handle14980984
Z Arvanitakis RS Wilson JL Bienias DA Evans DA Bennett (2004) ArticleTitleDiabetes mellitus and risk of Alzheimer disease and decline in cognitive function Arch Neurol 61 661–666 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archneur.61.5.661 Occurrence Handle15148141
AM Kanaya E Barrett-Connor G Gildengorin K Yaffe (2004) ArticleTitleChange in cognitive function by glucose tolerance status in older adults: A 4-year prospective study of the Rancho Bernardo study cohort Arch Intern Med 164 1327–1333 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archinte.164.12.1327 Occurrence Handle15226167
EW Gregg K Yaffe JA Cauley et al. (2000) ArticleTitleIs diabetes associated with cognitive impairment and cognitive decline among older women? Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group Arch Intern Med 160 174–180 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archinte.160.2.174 Occurrence Handle10647755
T Yoshitake Y Kiyohara I Kato et al. (1995) ArticleTitleIncidence and risk factors of vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in a defined elderly Japanese population: The Hisayama Study Neurology 45 1161–1168 Occurrence Handle7783883
CM Ryan MO Geckle TJ Orchard (2003) ArticleTitleCognitive efficiency declines over time in adults with Type 1 diabetes: Effects of micro- and macro-vascular complications Diabetologia 46 940–948 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00125-003-1128-2 Occurrence Handle12819900
R Stewart D Liolitsa (1999) ArticleTitleType 2 diabetes mellitus, cognitive impairment and dementia Diabet Med 16 93–112 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00027.x Occurrence Handle10229302
MW Strachan FM Ewing BM Frier RJ McCrimmon IJ Deary (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of acute hypoglycaemia on auditory information processing in adults with Type I diabetes Diabetologia 46 97–105 Occurrence Handle12637988
IJ Deary AJ Sommerfield V McAulay BM Frier (2003) ArticleTitleModerate hypoglycaemia obliterates working memory in humans with and without insulin treated diabetes J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74 278–279 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.74.2.278-a
JN Henderson KV Allen IJ Deary BM Frier (2003) ArticleTitleHypoglycaemia in insulin-treated Type 2 diabetes: Frequency, symptoms and impaired awareness Diabet Med 20 1016–1021 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.01072.x Occurrence Handle14632703
MW Strachan IJ Deary FM Ewing SS Ferguson MJ Young BM Frier (2001) ArticleTitleAcute hypoglycemia impairs the functioning of the central but not peripheral nervous system Physiol Behav 72 83–92 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0031-9384(00)00380-2 Occurrence Handle11239984
AJ Sommerfield IJ Deary BM Frier (2004) ArticleTitleAcute hyperglycemia alters mood state and impairs cognitive performance in people with type 2 diabetes Diabetes Care 27 2335–2340 Occurrence Handle15451897
S Craft SE Dagogo-Jack BV Wiethop et al. (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of hyperglycemia on memory and hormone levels in dementia of the Alzheimer type: a longitudinal study Behav Neurosci 107 926–940 Occurrence Handle10.1037//0735-7044.107.6.926 Occurrence Handle8136068
MT Draelos AM Jacobson K Weinger et al. (1995) ArticleTitleCognitive function in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus during hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia Am J Med 98 135–144 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9343(99)80397-0 Occurrence Handle7847430
C MacKnight K Rockwood E Awalt I McDowell (2002) ArticleTitleDiabetes mellitus and the risk of dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive impairment in the Canadian Study of Health and Aging Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 14 77–83 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000064928 Occurrence Handle12145454
A Fontbonne C Berr P Ducimetiere A Alperovitch (2001) ArticleTitleChanges in cognitive abilities over a 4-year period are unfavorably affected in elderly diabetic subjects: Results of the Epidemiology of Vascular Aging Study Diabetes Care 24 366–370 Occurrence Handle11213894
VC Crooks JG Buckwalter DB Petitti (2003) ArticleTitleDiabetes mellitus and cognitive performance in older women Ann Epidemiol 13 613–619 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1047-2797(03)00059-0 Occurrence Handle14732300
The Caerphilly, Speedwell Collaborative Group, Caerphilly and Speedwell collaborative heart disease studies. J Epidemiol Commun Health 1984; 38: 259–262.
JW Yarnell JE Pickering PC Elwood et al. (1994) ArticleTitleDoes non-diabetic hyperglycemia predict future IHD? Evidence from the Caerphilly and Speedwell studies J Clin Epidemiol 47 383–388 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0895-4356(94)90159-7 Occurrence Handle7730863
PD Goldberg (1972) The Detection of Psychiatric Illness by Questionnaire Oxford University Press London
M Roth FA Huppert E Tym CQ Mountjoy (1988) CAMDEX: The Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly Cambridge University press Cambridge
MF Folstein SE Folstein PR McHugh (1975) ArticleTitleMini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician J Psychiatr Res 12 189–198 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6 Occurrence Handle1202204
HE Nelson (1982) National Adult Reading Test (NART) Manual NFER-Nelson Windsor
AW Heim (1970) AH4 Group Test of Intelligence NFER-Nelson Windsor
BT Stollery (1996) ArticleTitleThe Automated Cognitive Test (ACT) system Neurotoxicol Teratol 18 493–497 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0892-0362(96)00032-3 Occurrence Handle8866543
PC Elwood A Beswick J Pickering et al. (2001) ArticleTitlePlatelet tests in the prediction of myocardial infarction and ischaemic stroke: evidence from the Caerphilly prospective study Br J Haematol 113 514–520 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02728.x Occurrence Handle11380425
JE Gallacher PC Elwood C Hopkinson et al. (1999) ArticleTitleCognitive function in the Caerphilly study: Associations with age social class, education and mood Eur J Epidemiol 15 161–169 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007576324313 Occurrence Handle10204646
PC Elwood JE Gallacher CA Hopkinson et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSmoking, drinking, and other life style factors and cognitive function in men in the Caerphilly cohort J Epidemiol Commun Health 53 9–14
BT Stollery (1996) ArticleTitleThe Automated Cognitive Test (ACT) system Neurotoxicol Teratol 18 493–497 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0892-0362(96)00032-3 Occurrence Handle8866543
R Cosway MW Strachan A Dougall BM Frier IJ Deary (2001) ArticleTitleCognitive function and information processing in type 2 diabetes Diabet Med 18 803–810 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1464-5491.2001.00577.x Occurrence Handle11678970
TJ Gradman A Laws LW Thompson GM Reaven (1993) ArticleTitleVerbal learning and/or memory improves with glycemic control in older subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus J Am Geriatr Soc 41 1305–1312 Occurrence Handle8227912
W Jagusch DY Voncramon R Renner KD Hepp (1992) ArticleTitleCognitive function and metabolic state in elderly diabetic-patients Diabetes Nutr Metab 5 265–274
W Hewer M Mussell F Rist B Kulzer K Bergis (2003) ArticleTitleShort-term effects of improved glycemic control on cognitive function in patients with type 2 diabetes Gerontology 49 86–92 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000067947 Occurrence Handle12574669
AM Maclullich IJ Deary JM Starr BR Walker JR Secki (2004) ArticleTitleGlycosylated hemoglobin levels in healthy elderly nondiabetic men are negatively associated with verbal memory J Am Geriatr Soc 52 848–849 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52230_7.x Occurrence Handle15086680
MW Strachan IJ Deary FM Ewing BM Frier (1997) ArticleTitleIs type II diabetes associated with an increased risk of cognitive dysfunction? A critical review of published studies Diabetes Care 20 438–445 Occurrence Handle9051402
JA Atiea JL Moses AJ Sinclair (1995) ArticleTitleNeuropsychological function in older subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Diabet Med 12 679–685 Occurrence Handle7587006
GM Reaven LW Thompson D Nahum E Haskins (1990) ArticleTitleRelationship between hyperglycemia and cognitive function in older NIDDM patients Diabetes Care 13 16–21 Occurrence Handle2298111
A Assisi M Alimenti F Maceli S Di Pietro G Lalloni P Montera (1996) ArticleTitleDiabetes and cognitive function: Preliminary studies Arch Gerontol Geriatr 5 229–232 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0167-4943(96)86942-1
RE Warren KV Allen AJ Sommerfield IJ Deary BM Frier (2004) ArticleTitleAcute hypoglycemia impairs nonverbal intelligence: Importance of avoiding ceiling effects in cognitive function testing Diabetes Care 27 1447–1448 Occurrence Handle15161802
C Messier M Tsiakas M Gagnon A Desrochers N Awad (2003) ArticleTitleEffect of age and glucoregulation on cognitive performance Neurobiol Aging 24 985–1003 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0197-4580(03)00004-6 Occurrence Handle12928059
I Deary (1999) Symptoms of hypoglycaemia and effects on mental performance and emotions BM Frier BM Fisher (Eds) Hypoglycaemia in Clinical Diabetes John Wiley & Sons Chichester 29–54
C Kong L Nimmo T Elatrozy et al. (2001) ArticleTitleSmoking is associated with increased hepatic lipase activity, insulin resistance, dyslipidaemia and early atherosclerosis in Type 2 diabetes Atherosclerosis 156 373–378 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00664-X Occurrence Handle11395034
PG Persson S Carlsson L Svanstrom CG Ostenson S Efendic V Grill (2000) ArticleTitleCigarette smoking, oral moist snuff use and glucose intolerance J Intern Med 248 103–110 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2796.2000.00708.x Occurrence Handle10947888
AJ Sinclair AJ Girling AJ Bayer (2000) ArticleTitleCognitive dysfunction in older subjects with diabetes mellitus: Impact on diabetes self-management and use of care services. All Wales Research into Elderly (AWARE) Study Diabetes Res Clin Pract 50 203–212 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-8227(00)00195-9 Occurrence Handle11106835
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallacher, J.E., Pickering, J., Elwood, P.C. et al. Glucoregulation has Greater Impact on Cognitive Performance than Macro-vascular Disease in Men with type 2 Diabetes: Data from the Caerphilly Study. Eur J Epidemiol 20, 761–768 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-005-2146-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-005-2146-9