Abstract
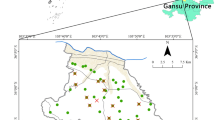
As a major agricultural province in China, it is necessary to study the content of heavy metals in farmland soil and crop in Jilin Province and to evaluate the risks to ecology and human health. This study presented the work completed on 79 soil samples, 10 rice samples, 66 maize samples and 15 soybean samples collected from Jilin Province farmland and evaluated six heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd, Hg and As) concentrations. The results showed that the concentrations of the six heavy metals in farmland soil and crop samples from Jilin Province basically met the soil standards and food health standards of China. The agricultural soil pollution spatial distribution was the most serious in the south of Jilin Province and the lightest in the west. The non-carcinogenic risks faced by children eating crops were higher than those of adults, but the carcinogenic risks were lower than those of adults. Both of the two health risks to adults and children from eating crops were very limited. The results would help determine the heavy metals pollution in farmland soil in Jilin Province efficiently and accurately and helped decision makers to achieve a balance between production and environmental regulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhady, A. A., et al. (2019). Potential biodiversity threats associated with the metal pollution in the Nile—Delta ecosystem (Manzala lagoon, Egypt). Ecological Indicators, 98, 844–853.
Abollino, O., Aceto, M., Malandrino, M., Mentasti, E., Sarzanini, C., & Petrella, F. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils from Piedmont, Italy. Distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment. Chemosphere, 49, 545–557.
Bao, S. (2000). Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Vol. Beijing: China Agriculture Press.
Birch, G. F., Melwani, A., Lee, J. H., & Apostolatos, C. (2014). The discrepancy in concentration of metals (Cu, Pb and Zn) in oyster tissue (Saccostrea glomerata) and ambient bottom sediment (Sydney estuary, Australia). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 80, 263–274.
Burges, A., Epelde, L., & Garbisu, C. (2015). Impact of repeated single-metal and multi-metal pollution events on soil quality. Chemosphere, 120, 8–15.
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC). (1995). General standard for contaminants and toxins in food and feed: CXS 193–1995.
Cai, L., Wang, Q., Luo, J., Chen, L., Zhu, R., Wang, S., et al. (2019). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for children near a large Cu-smelter in central China. Science of the Total Environment, 650, 725–733.
Chai, Y., Guo, J., Chai, S., Cai, J., Xue, L., & Zhang, Q. (2015). Source identification of eight heavy metals in grassland soils by multivariate analysis from the Baicheng-Songyuan area, Jilin Province, Northeast China. Chemosphere, 134, 67–75.
Chandrasekaran, A., & Ravisankar, R. (2019). Potential ecological risk assessment in soils of Yelagiri hill, Tamil Nadu using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) technique. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 147, 76–82.
Chen, G., Sun, G., Liu, A., & Zhou, W. (2008). Lead enrichment in different genotypes of rice grains. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 46, 1152–1156.
Chen, H., Teng, Y., Lu, S., Wang, Y., & Wang, J. (2015). Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Science of the Total Environment, 512–513, 143–153.
Chen, T., Chang, Q., Liu, J., Clevers, J. G. P. W., & Kooistra, L. (2016). Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Science of the Total Environment, 565, 155–164.
Chen, Y., Zhang, F., Zhang, J., Zhou, M., Li, F., & Liu, X. (2018). Accumulation characteristics and potential risk of PAHs in vegetable system grow in home garden under straw burning condition in Jilin, Northeast China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 162, 647–654.
China Ministry of Ecological Environment (China MOEE). (2018). Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land. GB 15618–2018.
China National Health Committee (CNH). (2017). National food safety standards limit of pollutants in foods. GB 2762–2017.
Dauvalter, V., & Rognerud, S. (2001). Heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pasvik River drainage. Chemosphere, 42, 9–18.
Devi, N. L., & Yadav, I. C. (2018). Chemometric evaluation of heavy metal pollutions in Patna region of the Ganges alluvial plain, India: Implication for source apportionment and health risk assessment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40, 2343–2358.
Doumett, S., et al. (2008). Heavy metal distribution between contaminated soil and Paulownia tomentosa, in a pilot-scale assisted phytoremediation study: Influence of different complexing agents. Chemosphere, 72, 1481–1490.
European Union (EU). (2006). Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. EC 1881/2006.
Facchinelli, A., Sacchi, E., & Mallen, L. (2001). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environmental Pollution, 114, 313–324.
Fangmin, C., Ningchun, Z., Haiming, X., Yi, L., Wenfang, Z., Zhiwei, Z., et al. (2006). Cadmium and lead contamination in japonica rice grains and its variation among the different locations in southeast China. Science of the Total Environment, 359, 156–166.
Fayiga, A. O. (2017). Metal (Loid)s in farmland soils and strategies to reduce bioavailability. Journal of Environmental Biology, 1, 9–24.
Goher, M. E., Farhat, H. I., Abdo, M. H., & Salem, S. G. (2014). Metal pollution assessment in the surface sediment of Lake Nasser, Egypt. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 40, 213–224.
Guo, E., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Wang, C., Wang, R., et al. (2017). Assessing spatiotemporal variation of drought and its impact on maize yield in Northeast China. Journal of Hydrology, 553, 231–247.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. An sediment ecological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additive (JECFA). (2010a). Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. WHO Technical Report Series, 959.
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additive (JECFA). (2010b). Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. WHO Technical Report Series, 960.
Kaur, M., Kumar, A., Mehra, R., & Kaur, I. (2019). Quantitative assessment of exposure of heavy metals in groundwater and soil on human health in Reasi district, Jammu and Kashmir. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00294-7.
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Zheng, Y. M., Huang, Y. Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2008). Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 152, 686–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.056.
Li, F., et al. (2018). Human health risk assessment of toxic elements in farmland topsoil with source identification in Jilin Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 1040.
Li, G., Sun, G., Williams, P. N., Nunes, L., & Zhu, Y. (2011a). Inorganic arsenic in Chinese food and its cancer risk. Environment International, 37, 1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.05.007.
Li, R., He, L., Wei, W., Hao, L., Ji, X., Zhou, Y., et al. (2015). Chlorpyrifos residue levels on field crops (rice, maize and soybean) in China and their dietary risks to consumers. Food Control, 51, 212–217.
Li, Z., et al. (2011b). Mercury and other metal and metalloid soil contamination near a Pb/Zn smelter in east Hunan province, China. Applied Geochemistry, 26, 160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.11.014.
Liu, J., et al. (2003). Lead toxicity, uptake, and translocation in different rice cultivars. Plant Science, 165, 793–802.
Ljung, K. (2006). Natural and anthropogenic metal inputs to soils in urban Uppsala, Sweden. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-9031-6.
Long, E. R., Macdonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Yusoff, F. M., Isa, N. M., & Haris, H. (2019). Application of enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, and ecological risk index in assessing the elemental pollution status of surface sediments. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41, 27–42.
Lu, X., Wu, X., Wang, Y., Chen, H., Gao, P., & Fu, Y. (2014). Risk assessment of toxic metals in street dust from a medium-sized industrial city of China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 106, 154–163.
McLaughlin, M. J., Parker, D. R., & Clarke, J. M. (1999). Metals and micronutrients—Food safety issues. Field Crops Research, 60, 143–163.
Möller, A., Müller, H. W., Abdullah, A., Abdelgawad, G., & Utermann, J. (2005). Urban soil pollution in Damascus, Syria: Concentrations and patterns of heavy metals in the soils of the Damascus Ghouta. Geoderma, 124, 63–71.
Pejman, A., Nabi Bidhendi, G., Ardestani, M., Saeedi, M., & Baghvand, A. (2015). A new index for assessing heavy metals contamination in sediments: A case study. Ecological Indicators, 58, 365–373.
Qing, X., Yutong, Z., & Shenggao, L. (2015). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 120, 377–385.
Rashed, M. N. (2010). Monitoring of contaminated toxic and heavy metals, from mine tailings through age accumulation, in soil and some wild plants at Southeast Egypt. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178, 739–746.
RDA RDA. (1989). Subcommittee on the tenth edition of the RDAs. Washington, DC: 10th National Academic Press.
Rodríguez Martín, J. A., Ramos-Miras, J. J., Boluda, R., & Gil, C. (2013). Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a Mediterranean environment region (Spain). Geoderma, 200–201, 180–188.
Saljnikov, E., Mrvić, V., Čakmak, D., Jaramaz, D., Perović, V., Antić-Mladenović, S., & Pavlović, P. (2019). Pollution indices and sources appointment of heavy metal pollution of agricultural soils near the thermal power plant. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00281-y.
Satarug, S., Baker, J. R., Urbenjapol, S., Haswell-Elkins, M., Reilly, P. E., Williams, D. J., et al. (2003). A global perspective on cadmium pollution and toxicity in non-occupationally exposed population. Toxicology Letters, 137, 65–83.
Statistical Yearbook of Jilin Province. (2018). Statistical yearbook of Jilin Province. http://tjj.jl.gov.cn/tjsj/tjnj/2018/2018/B12_11.htm. 2019/4/1.
Sun, C., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Sun, L., & Yu, H. (2013). Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere, 92, 517–523.
Tahri, M., Benya, Ch F, Bounakhla, M., Bilal, E., Gruffat, J. J., Moutte, J., et al. (2005). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contents in soils, sediments and water in the region of Meknes (central Morocco). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 102, 405–417.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566–575.
Tong, J., Guo, H., & Wei, C. (2014). Arsenic contamination of the soil–wheat system irrigated with high arsenic groundwater in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Science of the Total Environment, 496, 479–487.
Ullah, A., Heng, S., Munis, M. F. H., Fahad, S., & Yang, X. (2015). Phytoremediation of heavy metals assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: A review. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 117, 28–40.
USEPA USEP. (1986). Guidelines for the health risk assessment of chemical mixtures. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (1989). Risk assessment guidance for superfund. Volume I: Human health evaluation manual (Part A). Office of Emergency and Remedial Response.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2002). Aupplyment guidance for developing soil screening levels for superfund sites. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response.
Wang, S., Cai, L., Wen, H., Luo, J., Wang, Q., & Liu, X. (2019). Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Science of the Total Environment, 655, 92–101.
Wang, S., Wu, W., Liu, F., Liao, R., & Hu, Y. (2017). Accumulation of heavy metals in soil-crop systems: A review for wheat and corn. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 15209–15225.
Wu, Q., Qi, J., & Xia, X. (2017). Long-term variations in sediment heavy metals of a reservoir with changing trophic states: Implications for the impact of climate change. Science of the Total Environment, 609, 242–250.
Yang, Q. W., Shu, W. S., Qiu, J. W., Wang, H. B., & Lan, C. Y. (2004). Lead in paddy soils and rice plants and its potential health risk around Lechang Lead/Zinc Mine, Guangdong, China. Environment International, 30, 883–889.
Ye, C., Li, S., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2011). Assessing soil heavy metal pollution in the water-level-fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 191, 366–372.
Zahra, A., Hashmi, M. Z., Malik, R. N., & Ahmed, Z. (2014). Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Science of the Total Environment, 470–471, 925–933.
Zhang, H., Liu, G., Shi, W., & Li, J. (2014). Soil heavy metal contamination and risk assessment around the Fenhe Reservoir, China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 93, 182–186.
Zhang, H., & Shan, B. (2008). Historical records of heavy metal accumulation in sediments and the relationship with agricultural intensification in the Yangtze-Huaihe region, China. Science of the Total Environment, 399, 113–120.
Zhang, Z., et al. (2018). Tillage and crop succession effects on soil microbial metabolic activity and carbon utilization in a clay loam soil. European Journal of Soil Biology, 88, 97–104.
Zhao, S., Feng, C., Wang, D., Tian, C., & Shen, Z. (2014). Relationship of metal enrichment with adverse biological effect in the Yangtze Estuary sediments: Role of metal background values. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 464–472.
Zhou, X., Liao, P., & Wang, K. (2018). Is the “One Province One Rate” premium policy reasonable for Chinese crop insurance? The case in Jilin Province. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 17, 1900–1911.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Scientific and Technology Research and Development Program of Jilin Province (20190303081SF) and the National Science Foundation of China (41571491 and 41877520). Thanks to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, J., Li, F., Zhang, J. et al. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals pollution of farmland soil and crops in Jilin Province. Environ Geochem Health 42, 4369–4383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00416-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00416-1