Abstract
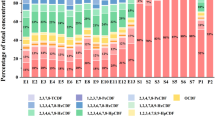
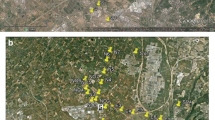
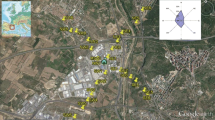
Municipal solid waste incinerators (MSWIs) are usually considered to be important sources of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs). To examine the influence of PCDD/Fs emissions from a MSWI on the surrounding environment, 21 soil samples were collected from various sampling sites distributed at distances of 300–1,700 m away from the stack of a MSWI. International Toxic Equivalent (I-TEQ) concentrations ranged from 0.47 to 2.07 pg I-TEQ g−1, with average and median concentrations of 1.08 and 1.05 pg I-TEQ g−1, respectively. Comparison of the results presented herein with other worldwide studies suggested that the concentrations of PCDD/Fs in the ambient soil were relatively low, indicating a limited impact on the surrounding environment. The emission concentrations from the incinerator were the critical factor in generating an environmental impact on the surrounding environment. An exponential function was developed, indicating a slight decline in TEQs of PCDD/Fs with increasing distance from the MSWI stack. The ordinary kriging interpolation technique was selected to create a contour map, which intuitively showed that a limited surrounding area (≤1,000 m from the stack) was obviously influenced by the MSWI.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brzuzy, L. P., & Hites, R. A. (1995). Estimating the atmospheric deposition of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 29(8), 2090–2098.
Carr, R., Zhang, C., Moles, N., & Harder, M. (2008). Identification and mapping of heavy metal pollution in soils of a sports ground in Galway City, Ireland, using a portable XRF analyser and GIS. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 30(1), 45–52.
Caserini, S., Cernuschi, S., Giugliano, M., Grosso, M., Lonati, G., & Mattaini, P. (2004). Air and soil dioxin levels at three sites in Italy in proximity to MSW incineration plants. Chemosphere, 54(9), 1279–1287.
Cheng, P. S., Hsu, M. S., Ma, E., Chou, U., & Ling, Y. C. (2003). Levels of PCDD/Fs in ambient air and soil in the vicinity of a municipal solid waste incinerator in Hsinchu. Chemosphere, 52(9), 1389–1396.
Dao, L., Morrison, L., Kiely, G., & Zhang, C. (2012). Spatial distribution of potentially bioavailable metals in surface soils of a contaminated sports ground in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 1–12.
Domingo, J., Schuhmacher, M., Müller, L., Rivera, J., Granero, S., & Llobet, J. (2000). Evaluating the environmental impact of an old municipal waste incinerator: PCDD/F levels in soil and vegetation samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 76(1), 1–12.
Fiedler, H. (1996). Sources of PCDD/PCDF and impact on the environment. Chemosphere, 32(1), 55–64.
Fries, G. F. (1995). A review of the significance of animal food products as potential pathways of human exposures to dioxins. Journal of Animal Science, 73(6), 1639–1650.
Gaus, C., Päpke, O., Dennison, N., Haynes, D., Shaw, G. R., Connell, D. W., et al. (2001). Evidence for the presence of a widespread PCDD source in coastal sediments and soils from Queensland, Australia. Chemosphere, 43(4), 549–558.
Kulkarni, P. S., Crespo, J. G., & Afonso, C. A. M. (2008). Dioxins sources and current remediation technologies—A review. Environment International, 34(1), 139–153.
Kutz, F. W., Barnes, D. G., Bottimore, D. P., Greim, H., & Bretthauer, E. W. (1990). The international toxicity equivalency factor (I-TEF) method of risk assessment for complex mixtures of dioxins and related compounds. Chemosphere, 20(7), 751–757.
Lee, S. J., Choi, S. D., Jin, G. Z., Oh, J. E., Chang, Y. S., & Shin, S. K. (2007). Assessment of PCDD/F risk after implementation of emission reduction at a MSWI. Chemosphere, 68(5), 856–863.
Li, Y., Jiang, G., Wang, Y., Cai, Z., & Zhang, Q. (2008). Concentrations, profiles and gas-particle partitioning of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the ambient air of Beijing, China. Atmospheric Environment, 42(9), 2037–2047.
Li, X., Yan, M., Chen, T., Lu, S., Yan, J., & Cen, K. (2010). Levels of PCDD/Fs in soil in the vicinity of a medical waste incinerator in China: The temporal variation during 2007–2009. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1), 783–789.
Liu, H., Lu, S., Buekens, A. G., Chen, T., Li, X., Yan, J., et al. (2012a). Baseline soil levels of PCDD/Fs established prior to the construction of municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere, 86, 300–307.
Liu, W., Zhang, W., Li, S., Meng, C., Tao, F., Li, H., et al. (2012b). Concentrations and profiles of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in air and soil samples in the proximity of a municipal solid waste incinerator plant. Environmental Engineering Science, 29(7), 693–699.
Lorber, M., Pinsky, P., Gehring, P., Braverman, C., Winters, D., & Sovocool, W. (1998). Relationships between dioxins in soil, air, ash, and emissions from a municipal solid waste incinerator emitting large amounts of dioxins. Chemosphere, 37(9–12), 2173–2197.
Meneses, M., Schuhmacher, M., & Domingo, J. (2002). A design of two simple models to predict PCDD/F concentrations in vegetation and soils. Chemosphere, 46(9–10), 1393–1402.
Ogura, I., Masunaga, S., & Nakanishi, J. (2001). Congener-specific characterization of PCDDs/PCDFs in atmospheric deposition: comparison of profiles among deposition, source, and environmental sink. Chemosphere, 45(2), 173–183.
Oh, J. E., Choi, S. D., Lee, S. J., & Chang, Y. S. (2006). Influence of a municipal solid waste incinerator on ambient air and soil PCDD/Fs levels. Chemosphere, 64(4), 579–587.
Pirard, C., Focant, J. F., Massart, A. C., & De Pauw, E. (2004). Assessment of the impact of an old MSWI. Part1: Level of PCDD/Fs and PCBs in surrounding soils and eggs. Organohalogen Compounds, 66, 2059–2063.
Polder, A., Gabrielsen, G., Odland, J. Ø., Savinova, T., Tkachev, A., Løken, K., et al. (2008). Spatial and temporal changes of chlorinated pesticides, PCBs, dioxins (PCDDs/PCDFs) and brominated flame retardants in human breast milk from Northern Russia. Science of the Total Environment, 391(1), 41–54.
Rovira, J., Mari, M., Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M., & Domingo, J. (2010). Environmental monitoring of metals, PCDD/Fs and PCBs as a complementary tool of biological surveillance to assess human health risks. Chemosphere, 80(10), 1183–1189.
Schuhmacher, M., Granero, S., Llobet, J., De Kok, H., & Domingo, J. (1997). Assessment of baseline levels of PCDD/F in soils in the neighbourhood of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere, 35(9), 1947–1958.
Si, Z., Li, S., Huang, L., & Chen, Y. (2010). Visualization programming for batch processing of contour maps based on VB and Surfer software. Advances in Engineering Software, 41(7), 962–965.
Wu, J., Dong, S., Liu, G., Zhang, B., & Zheng, M. (2011). Cooking process: A new source of unintentionally produced dioxins? Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(10), 5444–5449.
Xu, M., Yan, J., Lu, S., Li, X., Chen, T., Ni, M., et al. (2009). Concentrations, profiles, and sources of atmospheric PCDD/Fs near a municipal solid waste incinerator in Eastern China. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(4), 1023–1029.
Yan, J., Xu, M., Lu, S., Li, X., Chen, T., Ni, M., et al. (2008). PCDD/F concentrations of agricultural soil in the vicinity of fluidized bed incinerators of co-firing MSW with coal in Hangzhou, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 151(2), 522–530.
You, H., Ding, J., Zhao, X. S., Li, Y. F., Liu, L. Y., Ma, W. L., et al. (2011). Spatial and seasonal variation of polychlorinated biphenyls in Songhua River, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(3), 291–299.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National 973 Program (2011CB201500), the Environmental Public Welfare Projects (201209019, 201109001), the National 863 Program (2012AA062803) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20977099, 21077121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Li, H., Tian, Z. et al. Spatial distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in soil around a municipal solid waste incinerator. Environ Geochem Health 35, 605–611 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9543-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9543-x