Abstract
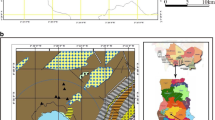
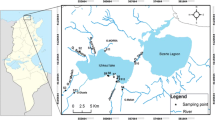
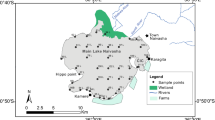
The aim of this study was to estimate the geochemical baseline concentrations of various heavy metals in the surface sediments of two large freshwater lakes in Taihu and Dianchi, China, and to assess the character and history of heavy metal contamination around the two lakes. Heavy metal concentrations in the sediments were obtained by field surveys and were supplemented with published data. The statistical methods of cumulative frequency and normalization were employed to obtain the baselines. The respective baseline concentrations for As, Sb, Hg, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn were 9.92, 1.67, 0.14, 22.62, 100.56, 31.63, 31.97, 33.05 and 97.01 mg/kg, respectively, in Taihu, and 24.60, 4.29, 0.25, 36.78, 135.68, 90.05, 50.76, 73.56 and 208.76 mg/kg, respectively, in Dianchi. The baseline concentrations of these heavy metals in Lake Taihu were equivalent to the pre-industrial concentrations determined from lakes in Sweden and Europe. Conversely, those in Lake Dianchi were much higher than the pre-industrial values. Li, Fe, Sc, Ti, V and Al were found to be the suitable reference elements for normalization, and one of these elements could be used to predict the baseline concentrations of heavy metals except Hg. Most of the heavy metals had one inflexion, and only Cu and Pb in Taihu, Sb, Pb and Zn in Dianchi, were found to have two inflexions in the cumulative curves, suggesting remarkable anthropogenic inputs of Cu and Pb in Taihu, Sb, Pb and Zn in Dianchi, which are generally consistent with the respective industrial structure around Taihu and Dianchi.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballesta, R. J., Bueno, P. C., Rubi, J. A. M., & Gimenez, R. G. (2010). Geochemical background levels and influence of the geological setting on pedogeochemical baseline concentrations of trace elements in selected soils of Castilla-La Mancha (Spain). Estudios Geologicos-Madrid, 66(1), 123–130.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1966). Trace elements in biochemistry. London: Academic Press.
Cheng, H. X., Zhao, C. D., Zhuang, G. M., Xia, W. L., Liu, Y. H., Yang, K., et al. (2008). Reconstruction of the regional soil pollution history by heavy metal in Taihu lake drainage area: taking Pb and Cd as examples. Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese with English abstract), 15, 167–178.
Colizza, E., Fontolan, G., & Brambati, A. (1996). Impact of a coastal disposal site for inert wastes on the physical marine environment, Barcola-Bovedo, Trieste, Italy. Environmental Geology, 27(4), 270–285.
Dai, Q. Y. (1983). Heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of Lake Dianchi. Environmental Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract), 8(2), 57–60.
Darnley, A. G. (1997). A global geochemical reference network: The foundation for geochemical baselines. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 60(1), 1–5.
EuroGeoSurveys (1998) Geochemical Atlas of Europe.
Fan, C. X., & Zhang, L. (2009). Lake Taihu: Principles of sediment pollution and remediation (in Chinese). Bejing: Science Press.
Fan, C. X., Zhu, G. W., & Sun, C. C. (2004). The historic and present status of the sediments in lake Taihu. In B. Q. Qin, W. P. Hu, & W. M. Chen (Eds.), The evolutions and mechanisms of the aquatic environment in lake Taihu. Beijing: Science Press.
Feng, J. B. (1991). A remote sensing study of Dianchi draninage area. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk Index for aquatic pollution-control—a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
He, M. C., Wang, X. Q., Wu, F. C., Fu, Z. Y. (2011). Antimony pollution in China. Science of the total environment, 421–422, 41–45
Li, B. M., Wan, G. J., Jiang, C. Z., & Zeng, S. G. (1995). Concentration levels, change records and enrichment patterns of heavy metals in waters and sediments in both lake Dianchi and lake Erhai, Yunnan Province. Environmental Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract), 16(2), 50–52.
Loring, D. H., Dahle, S., Naes, K., dos Santos, J., Skei, J. M., & Matishov, G. G. (1998). Arsenic and other trace metals in sediments from the Kara sea and the Ob and Yenisey estuaries, Russia. Aquatic Geochemistry, 4(2), 233–252.
Matschullat, J., Maenhaut, W., Zimmermann, F., & Fiebig, J. (2000). Aerosol and bulk deposition trends in the 1990′s, Eastern Erzgebirge, Central Europe. Atmospheric Environment, 34(19), 3213–3221.
McCarthy, L. H., Williams, T. G., Stephens, G. R., Peddle, J., Robertson, K., & Gregor, D. J. (1997). Baseline studies in the Slave river, NWT, 1990–1994.1. Evaluation of the chemical quality of water and suspended sediment from the Slave river (NWT). Science of the Total Environment, 197(1–3), 21–53.
Newman, B. K., & Watling, R. J. (2007). Definition of baseline metal concentrations for assessing metal enrichment of sediment from the south-eastern Cape coastline of South Africa. Water Sa, 33(5), 675–691.
Orr, K. K., Burgess, J. E., & Froneman, P. W. (2008). The effects of increased freshwater inflow on metal enrichment in selected Eastern Cape estuaries, South Africa. Water Sa, 34(1), 39–52.
Qin, B. Q., Xu, P. Z., Wu, Q. L., Luo, L. C., & Zhang, Y. L. (2007). Environmental issues of lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia, 581, 3–14.
Reeder, S., Plant, J. A., & Smith, D. B. (2002). IUGS/IAGC working group on global geochemical baselines. Episodes, 25(4), 286–287.
Rose, N. L., Boyle, J. F., Du, Y., Yi, C., Dai, X., Appleby, P. G., et al. (2004). Sedimentary evidence for changes in the pollution status of Taihu in the Jiangsu region of eastern China. Journal of Paleolimnology, 32(1), 41–51.
Schiff, K. C., & Weisberg, S. B. (1999). Iron as a reference element for determining trace metal enrichment in southern California coastal shelf sediments. Marine Environmental Research, 48(2), 161–176.
Schneider, P. M., & Davey, S. B. (1995). Sediment contaminants off the coast of Sydney, Australia: A model for their distribution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4–12), 262–272.
Schropp, S. J., Lewis, F. G., Windom, H. L., Ryan, J. D., Calder, F. D., & Burney, L. C. (1990). Interpretation of metal concentrations in estuarine sediments of Florida using aluminum as a reference element. Estuaries, 13(3), 227–235.
Siegel, F. R. (1995). Environmental geochemistry in development planning: An example from the Nile delta, Egypt. Geochemical Exploration, 55(2), 265–273.
Sun, S. C., & Huang, Y. P. (1993). Taihu lake. Beijng: China Ocean Press.
Teng, Y. G., Ni, S. J., Wang, J. S., & Niu, L. G. (2009). Geochemical baseline of trace elements in the sediment in Dexing area, South China. Environmental Geology, 57(7), 1649–1660.
Trimble, C. A., Hoenstine, R. W., Highley, A. B., Donoghue, J. F., & Ragland, P. C. (1999). Baseline sediment trace metals investigation: Steinhatchee river estuary, Florida, northeast Gulf of Mexico. Marine Georesources and Geotechnology, 17(2–3), 187–197.
Weisberg, S. B., Wilson, H. T., Heimbuch, D. G., Windom, H. L., & Summers, J. K. (2000). Comparison of sediment metal: Aluminum relationships between the eastern and gulf coasts of the United States. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 61(3), 373–385.
Wu, F. C., Meng, W., Zhao, X. L., Li, H. X., Zhang, R. Q., Cao, Y. J., et al. (2010). China embarking on development of its own national water quality criteria system. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(21), 7992–7993.
Xie, X. J., & Chen, H. X. (2001). Global geochemical mapping and its implementation in the Asia-Pacific region. Applied Geochemistry, 16(11–12), 1309–1321.
Xue, C. D., Liu, X., Qin, C. Y., Wei, H. X., Song, X. L., Liu, Y. Q., et al. (2007a). Element geochemical characteristics of modern sediments in the Dianchi Lake, Kunming, and their environmental significance. Aata Petrologica et Mineralogica, 26, 582–590.
Xue, B., Yao, S. C., & Xia, W. L. (2007b). Environmental changes in lake Taihu during the past century as recorded in sediment cores. Hydrobiologia, 581, 117–123.
Yang, H. D., & Rose, N. (2005). Trace element pollution records in some UK lake sediments, their history, influence factors and regional differences. Environment International, 31(1), 63–75.
Yang, Y. H., Zhou, F., Guo, H. C., Sheng, H., Liu, H., Dao, X., et al. (2010). Analysis of spatial and temporal water pollution patterns in lake Dianchi using multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 170(1–4), 407–416.
Yuan, H. Z., Shen, J., Liu, E. F., Wang, J. J., & Meng, X. H. (2011). Assessment of nutrients and heavy metals enrichment in surface sediments from Taihu Lake, a eutrophic shallow lake in China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(1), 67–81.
Zhu, G. W., Qin, B. Q., & Gao, G. (2005). Accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in the sediments of lake Taihu, China. Journal of Lake Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract), 17, 143–150.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China on “Water Environmental Quality Evolution and Water Quality Criteria in Lakes” (No. 2008CB418201). We thank Mr. Nan Zhang, Dr. Jianyang Guo, Dr. Shaofeng Wang, Dr. Renwei Feng, Ms. Yanming Zhu, Mr. Shuai Fu and Ms. Zhaofeng Ge for their assistance in the field surveys.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, C., Wen, H. Geochemical baselines of heavy metals in the sediments of two large freshwater lakes in China: implications for contamination character and history. Environ Geochem Health 34, 737–748 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9492-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9492-9