Abstract
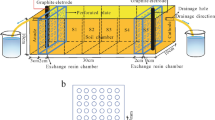
A laboratory study has been carried out to determine the feasibility of in situ remediation of chromium (VI)-contaminated soil using electrodialysis in relation to its speciation in soil. This technique is best suited for low-permeability soils or sediments, which may be difficult to remediate by other means and implies the application of a low-intensity direct current to the soil, which is separated from the electrode compartments by ion-exchange membranes. A clayey soil was prepared for use in the experiments and was characterized before being mixed with a solution of potassium dichromate for several days to produce a final Cr content of 4,056 mg/kg of soil dry wt. Remediation tests were carried out under constant-voltage conditions for periods of 7–14 days and the evolution of applied current to the cell, pH, and conductivity of the electrolytes were recorded periodically. Fractionation of chromium was determined for soil samples before and after remediation using a standardized four-step sequential extraction procedure (SEP) with acetic acid, hydroxylamine, hydrogen peroxide, and aqua regia solutions. Results show that chromium is mobilized from the most labile phases (soluble/exchangeable/carbonate). In a 15 V test, SEP results show that the amount of chromium extracted in the first step drops from 80% to 9%, but also that changes in the total chromium distribution occur during the treatment with some transferred to other soil phases that are more difficult to mobilize.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Probstein, R. F., & Hicks, R. E. (1993). Removal of contaminants from soils by electric fields. Science, 260, 498–503.
Rauret, G., Lopez-Sanchez, J. F., Sahuquillo, A., Rubio, R., Davidson, C., Ure, A., & Quevauviller, P. H. (1999). Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 57–61.
Reddy, K. R., Parupudi U. S., Devulapalli S. N., & Xu, C. Y., (1997). Effects of soil composition on the removal of chromium by electrokinetics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 55(1), 135–158.
Reddy, K., & Chinthamreddy, S., (1999). Electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils under reducing environments. Waste Management, 55, 203–503.
Ross, D. S., Sjogren, R. E., & Barlett, R. J., (1981). Behavior of chromium in soils: IV. Toxicity to microorganisms. Journal of Environmental Quality, 10(2), 145–147.
Sanjay, K., Arora, A., Shekhar, R., & Das, R. P., (2003). Electroremediation of Cr (VI) contaminated soils: Kinetics and energy efficiency. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 222, 253–259.
Turpeinena, R., Pantsar-Kallio, M., Haggblom, M., & Kairesaloa, T. (1999). Influence of microbes on the mobilization, toxicity and biomethylation of arsenic in soil R. The Science of the Total Environment, 236, 173–180.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851.
Acknowledgement
This work is part of R+D project # 256/2006/1-1.2 co-financed by “Secretaria General para la Prevencion de la Contaminacion y el Cambio Climatico” of Spain’s Ministry of Environment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nieto Castillo, A.M., Soriano, J.J. & García-Delgado, R.A. Changes in chromium distribution during the electrodialytic remediation of a Cr (VI)-contaminated soil. Environ Geochem Health 30, 153–157 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9137-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9137-1