Abstract
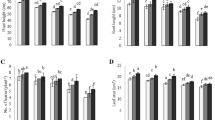
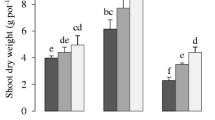
This study evaluates the possibility of using contaminated soil by treated tannery wastewater and the use of tannery sludge in agriculture. The plants of Vigna radiata var. PDM 54 grown on contaminated soil and irrigated with ground water have not shown the translocation of toxic metal (Cr) in the upper part. The biomass of the plant increased when irrigated with treated tannery wastewater compared to ground water, whereas no significant change was observed in chlorophyll and protein contents. In both the varieties (var. PDM 54 and var. NM 1) of V. radiata grown on tannery sludge amendments, the growth parameters exhibited a pronounced positive growth response up to 35% tannery sludge amendments compared with the plants grown on garden soil. Despite the Cr accumulation at lower amendments, no toxicity symptoms were observed in both the varieties of the plants. Higher amendments affected various growth parameters, NR activity, and carbohydrate content of the plants. The results suggest that the plants of V. radiata (var. PDM 54) may be grown on contaminated soil or lower sludge amendments and irrigated with ground water. No translocation of toxic metal Cr was found in the seeds of the plants grown in up to 25% tannery sludge. However, periodical monitoring is required before the consumption of seeds. Overall, the results showed that plant growth patterns were influenced to some extent by the level of soil contamination and the water used for irrigation.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Arnon, I. (1949). Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiology, 24, 1–15.
Barman, S. C., Sahu, R. K., Bhargava, S. K., & Chaterjee, C. (2000). Distribution of heavy metals in wheat, mustard and weed grown on field irrigated with industrial effluents. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64, 489–496.
Campbell, W. H. (1999). Nitrate reductase structure, function and regulation: bridging the gap between biochemistry and physiology. Annual Review of Plant Physiology. Plant Molecular Biolology, 50, 277–303.
Casado-Vela, J., Selleś, S., Dıáz-Crespo, C., Navarro-Pedrenõ, J., Mataix-Beneyto, J., & Gómez, I. (2006). Effect of composted sewage sludge application to soil on sweet pepper crop (Capsicum annuum var. annuum) grown under two exploitation regimes. Waste Management, 27, 1509–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.07.016.
Crawford, N. M., & Glass, D. M. A. (1998). Molecular and physiological aspect of nitrate uptake in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 3, 389–395.
Demirevska-Kepova, K., Simova-Stoilova, L., Stoyanova, Z., Hölzer, R., & Feller, U. (2004). Biochemical changes in barley plants after excessive supply of copper and manganese. Environmental Experimental Botany, 52, 253–266.
Dhir, B., Sharmila, P., & Saradhi, P. P. (2004). Hydrophytes lack potential to exhibit cadmium stress induced enhancement in lipid peroxidation and accumulation of proline. Aquatic Toxicology, 66, 141–147.
Dolgen, D., Alpaslan, M. N., & Delen, N. (2007). Agricultural recycling of treatment-plant sludge: a case study for a vegetable-processing factory. Journal of Environmental Management, 84, 274–281.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugar and related substance. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350–356.
Fytianos, K., Katsianis, G., Triantafyllou, P., & Zachariadis, G. (2001). Accumulation of heavy metals in vegetables grown in an industrial area in relation to soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67, 423–430.
Gomez, K. A., & Gomez, A. A. (1984). Statistical procedure for agricultural research. New York: Wiley.
Guo, T. R., Zhang, G. P., & Zhang, Y. H. (2007). Physiological changes in barley plants under combined toxicity of aluminum, copper and cadmium. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 57, 182–188.
Gupta, A. K., & Sinha, S. (2006a). Chromium levels in vegetables and grains grown on tannery effluent irrigated area of Jajmau, Kanpur (India): influence on dietary intake. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77, 658–664.
Gupta, A. K., & Sinha, S. (2006b). Chemical fractionation and heavy metal accumulation in the plant of Sesamum indicum (L.) var. T55 grown on soil amended with tannery sludge: selection of single extractants. Chemosphere, 64, 161–173.
Gupta, A. K., & Sinha, S. (2007a). Phytoextraction capacity of the plants growing on tannery sludge dumping sites. Bioresource Technology, 98, 1788–1794.
Gupta, A. K., & Sinha, S. (2007b). Phytoextraction capacity of the Chenopodium album L. grown on soil amended with tannery sludge. Bioresource Technology, 98, 442–446.
Hirsch, R. E., & Sussman, M. R. (1999). Improving nutrient capture from soil by the genetic manipulation of crop plants. Trends in Biotechnology, 17, 356–361.
Hsu, Y. T., & Kao, C. H. (2003). Changes in protein and amino acid contents in two cultivars of rice seedlings with different apparent tolerance to cadmium. Plant Growth Regulators, 40, 147–155.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrought, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with folin-phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Mantovia, P., Baldonib, G., & Toderib, G. (2005). Reuse of liquid, dewatered, and composted sewage sludge on agricultural land: effects of long-term application on soil and crop. Water Research, 39, 289–296.
Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral nutrition in higher plants (2nd ed.). London, UK: Academic.
Scheible, W.-R., Morcuende, R., Czechowski, T., Fritz, C., Osuna, D., Palacios-Rojas, N., Schindelasch, D., Thimm, O., Udvardi, M. K., & Stitt, M. (2004). Genome-wide reprogramming of primary and secondary metabolism, protein synthesis, cellular growth processes, and the regulatory infrastructure of Arabidopsis in response to nitrogen. Plant Physiology, 136, 2483–2499.
Shankar, A. K., Djanaguiraman, M., Sudhagar, R., Chandrashekar, C. N., & Pathmanabhan, G. (2004). Differential antioxidative response of ascorbate glutathione pathway enzymes and metabolites to chromium speciation stress in green gram (Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek. Cv. CO4) roots. Plant Science, 166, 1035–1043.
Singh, R. P., Dabas, S., Choudhary, A., & Maheshwari, R. (1998). Effect of lead on nitrate reductase activity and alleviation of lead toxicity by inorganic salts and 6-benzylaminopurine. Biology Plant, 40, 399–404.
Singh, K. P., Mohan, D., Sinha, S., & Dalwani, R. (2004a). Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharged by sewage treatment plants on health agricultural and environmental quality in the wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere, 55, 227–255.
Singh, S., Saxena, R., Pandey, K., Bhatt, K., & Sinha S. (2004b). Response of antioxidants in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) grown on different amendments of tannery sludge: its metal accumulation potential. Chemosphere, 57, 1663–1673.
Singh, S., & Sinha, S. (2004). Morphoanatomical response of two cultivars of Brassica juncea (L.) Czern grown on tannery waste amended soil. Bulletin Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 1017-1024
Singh, R. P., Tripathi, R. D., Dabas, S., Rizvi, S. M. H., Ali, M. B., Sinha, S. K., Gupta, D. K., Mishra, S., & Rai, U. N. (2003). Effect of lead on growth and nitrate assimilation of Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek seedlings in a salt affected environment. Chemosphere, 52, 1245–1250.
Sinha, P., Dube, B. K., & Chatterjee, C. (2006b). Manganese stress alters phytotoxic effects of chromium in green gram physiology (Vigna radiata L.) Cv. Pu 19. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 57, 131–138.
Sinha, S., Gupta, A. K., & Bhatt, K. (2007). Uptake and translocation of metals in fenugreek grown on soil amended with tannery sludge: involvement of antioxidants. Ecotoxicology Environmental Safety, 67, 267–277.
Sinha, S., Gupta, A. K., Bhatt, K., Pandey, K., Rai, U. N., & Singh, K. P. (2006a). Distribution of metals in the edible plants grown at Jajmau, Kanpur (India) receiving treated tannery wastewater: relation with physico-chemical properties of the soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 115, 1–22.
Sinha, S., Mallick, S., Misra, R. K., Singh, S., Basant, A., & Gupta, A. K. (2007). Uptake and translocation of metals in Spinacia oleracea L. grown on tannery sludge-amended and contaminated soils: effect on lipid peroxidation, morpho-anatomical changes and antioxidants. Chemosphere, 67, 176–187.
Sinha, S., Pandey, K., Gupta A. K., & Bhatt, K. (2005). Accumulation of metals in vegetables and crops grown in the area irrigated with river water. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 74, 210–218.
Sinha, S. K., Srivastava, H. S., & Tripathi, R. D. (1994). Inhibition of nitrate reductase activity in presence of divalent cations and growth hormones in maize leaves. Chemosphere, 29, 1775–1782.
Srivastava, H. S. (1974). In vivo activity of the nitrate reductase in maize seedlings. Indian Journal of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 11, 230–232.
Stitt, M., & Krapp, A. (1999). The molecular physiological basis for the interaction between elevated carbon dioxide and nutrients. Plant Cell Environment, 22, 583–622.
Stitt, M., Müller, C., Matt, P., Gibon, Y., Carillo, P., Morcuende, R., Scheible, W.-R., & Krapp, A. (2002). Steps towards an integrated view of nitrogen metabolism. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53, 959–970.
Verma, S., & Dubey, R. S. (2001). Effect of cadmium on soluble sugars and enzymes of their metabolism in rice. Biology Plant, 44, 117–123.
Xiong, Z.-T., Liu, C., & Geng, B. (2006). Phytotoxic effects of copper on nitrogen metabolism and plant growth in Brassica pekinensis Rupr. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64, 273–280.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Director, Dr. Rakesh Tuli, National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow for proving facilities and encouragement. S. Singh is grateful to CSIR (New Delhi) for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, S., Singh, S. & Mallick, S. Comparative growth response of two varieties of Vigna radiata L. (var. PDM 54 and var. NM 1) grown on different tannery sludge applications: effects of treated wastewater and ground water used for irrigation. Environ Geochem Health 30, 407–422 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-007-9125-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-007-9125-x