Abstract
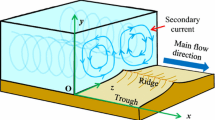
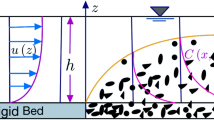
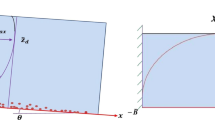
In this work, a mathematical model on concentration distribution is developed for a steady, uniform open channel turbulent flow laden with sediments by incorporating the effect of secondary current through velocity distribution together with the stratification effect due to presence of sediments. The effect of particle-particle interaction at reference level and the effect of incipient motion probability, non-ceasing probability and pick-up probability of the sediment particles at reference concentration are taken into account. The proposed model is compared with the Rouse equation as well as verified with existing experimental data. Good agreement between computed value and experimental data indicates that secondary current influences the suspension of particles significantly. The direction and magnitude (strength) of secondary current lead to different patterns of concentration distribution and theoretical analysis shows that type II profile (where maximum concentration appears at significant height above channel bed surface) always corresponds to upward direction and greater magnitude of secondary current.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karcz I (1981) Reflections on the origin of small scale longitudinal streambed scours. In: Morisawa M (ed) Fluvial geomorphology: a proceedings of the fourth annual geomorphology symposia series. Allen and Unwin, London, pp 149–177
Sambrook Smith GH, Ferguson RI (1996) The gravel-sand transition: flume study of channel response to reduce slope. Geomorphology 16:147–159. doi:10.1016/0169-555X(95)00140-Z
Liao K, Qu J, Tang J, Ding F, Liu H, Zhu S (2010) Activity of wind-blown sand and the formation of feathered sand Ridges in the Kumtagh Desert, China. Boundary Layer Meteorol 135:333–350. doi:10.1007/s10546-010-9469-0
Colombini M (1993) Turbulence driven secondary flows and the formation of sand ridges. J Fluid Mech 254:701–719. doi:10.1017/S0022112093002319
Nezu I, Nakagawa H, Kawashima N (1988) Cellular secondary currents and sand ribbons in fluvial channel flows. In: Proceedings of the 6th Congress APD-IAHR, Madrid, vol 2, pp 51–58
Wang ZQ, Cheng NS (2006) Time-mean structure of secondary flows in open channel with longitudinal bedforms. Adv Water Resour 29(11):1634–1649
Prandtl L (1925) Uber die ausgebildete Turbulenz. Z Angew Math Mech 5:136–139
Blanckaert K, Graf WH (2004) Momentum transport in sharp openchannel bends. J Hydraul Eng 130(3):186–198. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429
Guo J, Julien PY (2001) Turbulent velocity profiles in sediment-laden flows. J Hydraul Res 39(1):11–23
Yang SQ, Tan SK, Lim SY (2004) Velocity distribution and dip-phenomenon in smooth uniform open channel flows. J Hydraul Eng 130(12):1179–1186
Kundu S, Ghoshal K (2012) An analytical model for velocity distribution and dip-phenomenon in uniform open channel flows. Int J Fluid Mech Res 39(5):381–395
Rouse H (1937) Modern concepts of the mechanics of turbulence. Trans ASCE 102:463–543
Umeyama M (1992) Vertical distribution od suspended sediment in uniform open-channel flow. J Hydraul Eng 118(6):936–941
Mazumder BS, Ghoshal K (2006) Velocity and concentration profiles in uniform sediment-laden flow. Appl Math Model 30(1):164–176
Bose SK, Dey S (2009) Suspended load in flows on erodible bed. Int J Sed Res 24:315–324
Cao Z, Wei L, Xie J (1995) Sediment-laden flow in open channels from two-phase flow viewpoint. J Hydraul Eng 121(10):725–735
Chiu CL, McSparran JE (1966) Effect of secondary flow on sediment transport. Proc Am Soc Civ Eng 92:HY5
Yang SQ (2007) Turbulent transfer mechanism in sediment-laden flow. J Geophys Res 112:F01005. doi:10.1029/2005JF000452
Steinour HH (1944) Rate of sedimentation-non flocculated suspensions of uniform spheres. Ind Eng Chem 36(7):618–24. doi:10.1021/ie50415a005
Hawksley PGW (1951) The effect of concentration on the settling of suspensions and flow through porous media. In: Arnold Edward (ed) Some aspects of fluid flow. Edward Arnold, London, pp 114–135
Fu X, Wang G, Shao X (2005) Vertical dispersion of fine and coarse sediment in turbulent open channel flows. J Hydraul Eng 131(10):877–888
Bouvard M, Petkovic S (1985) Vertical dispersion of spherical, heavy particles in turbulent open channel flow. J Hydraul Res 23(1):5–20
Michalik A (1973) Density patterns of the inhomogeneous liquids in the industrial pipeline measured by means of radiometric scanning. La Houille Blanche 1:53–59
Ni JR, Wang GQ, Borthwick AGL (2000) Kinetic theory for particles in dilute and dense solid-liquid flows. J Hydraul Eng 126(12):893–903
Wang GQ, Ni JR (1990) Kinetic theory for particle concentration distribution in two-phase flows. J Eng Mech 116(12):2738–2748
Wang GQ, Fu X (2004) Mechanics of particle vertical diffusion in sediment-laden flows. Chin Sci Bull 49(10):1086–1090
Liu QQ, Shu AP, Singh VP (2007) Analysis of the vertical profile of concentration in sediment-laden flows. J Eng Mech 133(6):601–607
Kaushal DR, Tomita Y (2007) Experimental investigation for near-wall lift of coarse particles in slurry pipeline using \(\gamma \)-ray densitometer. Powder Technol 172:177–187
Ghoshal K (2004) On velocity and suspension concentration in a sediment-laden flow: experimental and theoretical studies. Dissertation, Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata
Glenn SM (1983) A contenental shelf bottom boundary layer model: the effects of waves, currents and a moveable bed. Dissertation, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute/Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Ohmoto T, Cui Z, Hirakawa R (2004) Effects of secondary currents on suspended sediment transport in an open channel flow. In: Jirka GH, Uijttewaal WSJ (eds) International symposium on shallow flows. Taylor and Francis, Delft, pp 511–516
Coleman NL (1986) Effects of suspended sediment on the open-channel velocity distribution. Water Resour Res 22(10):1377–1384
Einstein HA, Chien NS (1955) Effects of heavy sediment concentration near the bed on velocity and sediment distribution. US Army Corps of Engineers, Missouri River Division, report no 8
Wang X, Qian N (1989) Turbulence characteristics of sediment-laden flow. J Hydraul Eng 115(6):781–800
Muste M, Patel VC (1997) Velocity profiles for particles and liquid in open channel flow with suspended sediment. J Hydraul Eng 123(9):742–751
Cellino M, Graf WH (1999) Sediment-laden flow in open-channels under noncapacity and capacity conditions. J Hydraul Eng 125(5):455–462
Muste M, Yu K, Fujita I, Ettema R (2005) Two-phase versus mixed-flow perspective on suspended sediment transport in turbulent channel flows. Water Resour Res 41:W10402. doi:10.1029/2004WR003595
Best J, Bennett S, Bridge J, Leeder M (1997) Turbulence modulation and particle velocities over flat sand beds at low transport rates. J Hydraul Eng 123(12):1118–1129
Graf WH, Cellino M (2002) Suspension flows in open channels: experimental study. J Hydraul Res 40(4):435–447
Righetti M, Romano GP (2004) Particle-fluid interactions in a plane near-wall turbulent flow. J Fluid Mech 505:93–121
Smith JD, McLean S (1977) Spatially averaged flow over a wavy. J Geophys Res 82(12):17351746
Herrmann MJ, Madsen OS (2007) Effect of stratification due to suspended sand on velocity and concentration distribution in unidirectional flows. J Geophys Res 112:C02006. doi:10.1029/2006JC003569
Businger JA, Wyngaard JC, Izumi Y, Bradley EF (1971) Flux-profile relationships in the atmospheric surface layer. J Atmos Sci 28:181–189. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1971)028<0181:FPRITA>2.0.CO;2
Monin AS, Yaglom AM (1971) Stat Fluid Mech. MIT Press, Cambridge
Styles R, Glenn SM (2000) Modeling stratified wave and current bottom boundary layers on the continental shelf. J Geophys Res 105(C10):24119–24139
Carstens MR (1952) Accelerated motion of a spherical particle. Trans AGU 33(5):713–721
Jobson HE, Sayre WW (1979) Predicting concentration in open channels. J Hydraul Div 96(HY10):1983–1996
Yoon JY, Kang SK (2005) A numerical model of sediment-laden turbulent flow in an open channel. Can J Civ Eng 32(1):233–240
Huang S, Sun Z, Xu D, Xia S (2008) Vertical distribution of sediment concentration. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 9(11):1560–1566
Bonakdari H, Larrarte F, Lassabatere L, Joannis C (2008) Turbulent velocity profile in fully-developed open channel flows. Environ Fluid Mech 8:1–17
Bogardi J (1974) Sediment transport in alluvial streams. Akademial Kiodo, Budapest
Soulsby R (1997) Dynamics of marine sands. Thomas Telford, London
Nikuradse J (1950) Laws of flow in rough pipes, translation in National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Technical Memorandum 1292. NACA, Washington, p 62
Jan CD, Wang JS, Chen TH (2006) Discussion of simulation of flow and mass dispersion in meandering channel. J Hydraul Eng 132(3):339–342
Francis JB (1878) On the cause of the maximum velocity of water flowing in open channels being below the surface. Trans ASCE 7(1):109–113
Nezu I, Nakagawa H (1993) Turbulence in open-channel flows. Balkema, IAHR-Monograph
Yang SQ (2005) Interactions of boundary shear stress, secondary current and velocity. Fluid Dyn Res 36:121–136
Yang SQ, Tan SK, Wang XK (2012) Mechanism of secondary currents in open channel flows. J Geophys Res 117:F04014. doi:10.1029/2012JF002510
Coleman JM (1969) Brahmaputra river; channel process and sedimentation. Sed Geol 3:129–239
Ghoshal K, Kundu S (2013) Influence of secondary current on vertical concentration distribution in an open channel flow. J Hydraul Eng 19(2):88–96
Zhiyao S, Tingting W, Fumin X, Ruijie L (2008) A simple formula for predicting settling velocity of sediment particles. Water Sci Eng 1(1):37–43
Sun ZL, Sun ZF, Donahue J (2003) Equilibrium bed-concentration of nonuniform sediment. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 4(2):186–194
Cheng NS (2003) A diffusive model for evaluating thickness of bedload layer. Adv Water Resour 26(8):875–882
Van Rijn LC (1984) Sediment transport, part I: bed load transport. J Hydraul Eng 110(10):1431–1456
Garcia M, Parker G (1991) Entrainment of bed sediment into suspension. J Hydraul Eng 117(4):414–435
Richardson JF, Zaki WN (1954) Sedimantation and fluidization part I. Trans Inst Chem Eng 32:35–53
Absi R (2010) Concentration profiles for fine and coarse sediments suspended by waves over ripples: an analytical study with the 1-DV gradient diffusion model. Adv Water Resour 33:411–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, S., Ghoshal, K. Effects of secondary current and stratification on suspension concentration in an open channel flow. Environ Fluid Mech 14, 1357–1380 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-014-9341-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-014-9341-8