Abstract
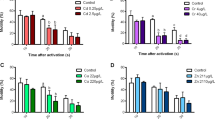
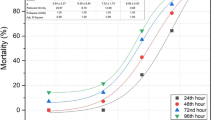
Paracetamol (APAP) is a widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and has been frequently detected in aquatic environment. However, limited information is provided about the toxic effects and detoxification mechanism of APAP in aquatic invertebrates. In the present study, the change of life traits of Daphnia magna (e.g., body length, growth rate and reproduction) was investigated under the chronic APAP exposure (0–5000 μg/L) for 21 day, and the effects of APAP on the expression of the detoxification- and reproduction-related genes including HR96, CYP360A8, CYP314, MRP4, P-gp, EcR and Vtg in the acute exposure (up to 96 h) were also determined. Results showed that the molting frequency, days to the first brood and days to the first egg production of D. magna were affected under the 50 μg/L concentration of APAP in the chronic exposure test. In the acute test, the transcriptional expression of HR96 was up-regulated under APAP exposure for 24 and 48 h. Similar performances were also observed in the expression of CYP360A8, CYP314, MRP4 and P-gp. However, with exposure time extended to 96 h, the induction of HR96 decreased or even reversed in some cases. It may indicate that the defense system in Daphnia is activated for a short time of exposure or becomes adaptive after longer term of exposure. APAP exposure also affected reproduction-related genes expression, which was related to the exposure time and concentration of APAP. In summary, APAP significantly affected the expression of genes associated with detoxification metabolism and altered some physiological parameters in D. magna.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen L, Goto-Kazeto R, Trant JM, Nash JP, Korsgaard B, Bjerregaard P (2006) Short-term exposure to low concentrations of the synthetic androgen methyltestosterone affects vitellogenin and steroid levels in adult male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 76:343–352
Baldwin WS, Marko PB, Nelson DR (2009) The cytochrome P450 (CYP) gene superfamily in Daphnia pulex. BMC Genom 10:169
Bertrand S, Brunet FG, Escriva H, Parmentier G, Laudet V, Robinson-Rechavi M (2004) Evolutionary genomics of nuclear receptors: from twenty-five ancestral genes to derived endocrine systems. Mol Biol Evol 21:1923–1937
Boyd GR, Reemtsma H, Grimm DA, Mitra S (2003) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in surface and treated waters of Louisiana, USA and Ontario, Canada. Sci Total Environ 311:135–149
Campos B, Pina B, Barata CC (2012) Mechanisms of action of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 46:2943–2950
Carlsson C, Johansson AK, Alvan G, Bergman K, Kuhler T (2006) Are pharmaceuticals potent environmental pollutants? Part II: environmental risk assessments of selected pharmaceutical excipients. Sci Total Environ 364:88–95
Choi E, Alsop D, Wilson JY (2018) The effects of chronic acetaminophen exposure on the kidney, gill and liver in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 198:20–29
Cleuvers M (2003) Aquatic ecotoxicity of pharmaceuticals including the assessment of combination effects. Toxicol Lett 142:185–194
Davis DC, Potter WZ, Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR (1974) Species differences in hepatic glutathione depletion, covalent binding and hepatic necrosis after acetaminophen. Life Sci 14:2099–2109
Han GH, Hur HG, Kim SD (2006) Ecotoxicological risk of pharmaceuticals from wastewater treatment plants in Korea: occurrence and toxicity to Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:265–271
Hannas BR, Wang YH, Thomson S, Kwon G, Li H, Leblanc GA (2011) Regulation and dysregulation of vitellogenin mRNA accumulation in daphnids (Daphnia magna). Aquat Toxicol 101:351–357
Hernandez JP, Mota LC, Baldwin WS (2009) Activation of CAR and PXR by dietary, environmental and occupational chemicals alters drug metabolism, intermediary metabolism, and cell proliferation. Curr Pharmacogenom Personal Med 7:81–105
Hirohashi T, Suzuki H, Takikawa H, Sugiyama Y (2000) ATP-dependent transport of bile salts by rat multidrug resistance-associated protein 3 (Mrp3). J Biol Chem 275:2905–2910
Houde M, Carter B, Douville M (2013) Sublethal effects of the flame retardant intermediate hexachlorocyclopentadiene (HCCPD) on the gene transcription and protein activity of Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 140:213–219
Hwang DS, Han J, Won EJ, Kim DH, Jeong CB, Hwang UK, Zhou B, Choe J, Lee JS (2016) BDE-47 causes developmental retardation with down-regulated expression profiles of ecdysteroid signaling pathway-involved nuclear receptor (NR) genes in the copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Aquat Toxicol 177:285–294
Karimullina E, Li Y, Ginjupalli GK, Baldwin WS (2012) Daphnia HR96 is a promiscuous xenobiotic and endobiotic nuclear receptor. Aquat Toxicol 116-117:69–78
Kato Y, Kobayashi K, Oda S, Tatarazako N, Watanabe H, Iguchi T(2007) Cloning and characterization of the ecdysone receptor and ultraspiracle protein from the water flea Daphnia magna. J Endocrinol 193:183–194
Kim Y, Choi K, Jung J, Park S, Kim PG, Park J (2007) Aquatic toxicity of acetaminophen, carbamazepine, cimetidine, diltiazem and six major sulfonamides, and their potential ecological risks in Korea. Environ Int 33:370–375
King-Jones K, Horner MA, Lam G, Thummel CS (2006) The DHR96 nuclear receptor regulates xenobiotic responses in Drosophila. Cell Metab 4:37–48
Kretschmer XC, Baldwin WS (2005) CAR and PXR: xenosensors of endocrine disrupters? Chem Biol Interact 155:111–128
Le TH, Lim ES, Lee SK, Park JS, Kim YH, Min J (2011) Toxicity evaluation of verapamil and tramadol based on toxicity assay and expression patterns of Dhb, Vtg, Arnt, CYP4, and CYP314 in Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol 26:515–523
Li SW, Wang YH, Lin AY (2017) Ecotoxicological effect of ketamine: evidence of acute, chronic and photolysis toxicity to Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:173–179
Liu S, Ding R, Nie X (2019) Assessment of oxidative stress of paracetamol to Daphnia magna via determination of Nrf1 and genes related to antioxidant system. Aquat Toxicol 211:73–80
Liu Y, Wang L, Pan B, Wang C, Bao S, Nie X (2017) Toxic effects of diclofenac on life history parameters and the expression of detoxification-related genes in Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 183:104–113
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Matozzo V, Gagne F, Marin MG, Ricciardi F, Blaise C (2008) Vitellogenin as a biomarker of exposure to estrogenic compounds in aquatic invertebrates: a review. Environ Int 34:531–545
Meinertz JR, Schreier TM, Bernardy JA, Franz JL (2010) Chronic toxicity of diphenhydramine hydrochloride and erythromycin thiocyanate to daphnia, Daphnia magna, in a continuous exposure test system. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:447–451
Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Potter WZ, Gillette JR, Brodie BB (1973) Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. IV. Protective role of glutathione. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 187:211–217
OECD (2004) OECD guideline for testing of chemicals 202-Daphnia sp. acute immobilisation test Organization for the Economic Cooperation and Development. OECD, Paris
Ramos AS, Correia AT, Antunes SC, Goncalves F, Nunes B (2014) Effect of acetaminophen exposure in Oncorhynchus mykiss gills and liver: detoxification mechanisms, oxidative defence system and peroxidative damage. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:1221–1228
Rewitz KF, Gilbert LI (2008) Daphnia Halloween genes that encode cytochrome P450s mediating the synthesis of the arthropod molting hormone: evolutionary implications. BMC Evolut Biol 8:60
Saide K, Sherwood V, Wheeler GN (2019) Paracetamol-induced liver injury modelled in Xenopus laevis embryos. Toxicol Lett 302:83–91
Scheffer GL, Kool M, de Haas M, de Vree JM, Pijnenborg AC, Bosman DK, Elferink RP, van der Valk P, Borst P, Scheper RJ (2002) Tissue distribution and induction of human multidrug resistant protein 3. Lab Investig 82:193–201
Schmidt AM, Sengupta N, Saski CA, Noorai RE, Baldwin WS (2017) RNA sequencing indicates that atrazine induces multiple detoxification genes in Daphnia magna and this is a potential source of its mixture interactions with other chemicals. Chemosphere 189:699–708
Sekimoto T, Iwami M, Sakurai S (2006) Coordinate responses of transcription factors to ecdysone during programmed cell death in the anterior silk gland of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Mol Biol 15:281–292
Sengupta N, Litoff EJ, Baldwin WS (2015) The HR96 activator, atrazine, reduces sensitivity of Daphnia magna to triclosan and DHA. Chemosphere 128:299–306
Shen B, Dong HQ, Tian HS, Ma L, Li XL, Wu GL, Zhu CL (2003) Cytochrome P450 genes expressed in the deltamethrin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Culex pipiens pallens. Pestic Biochem Physiol 75:19–26
Stuer-Lauridsen F, Birkved M, Hansen LP, Lutzhoft HC, Halling-Sorensen B (2000) Environmental risk assessment of human pharmaceuticals in Denmark after normal therapeutic use. Chemosphere 40:783–793
Sturm A, Cunningham P, Dean M (2009) The ABC transporter gene family of Daphnia pulex. BMC Genom 10:170
Subramoniam T (2000) Crustacean ecdysteriods in reproduction and embryogenesis. Comp Biochem Physiol 125:135–156
Ternes TA, Meisenheimer M, McDowell D, Sacher F, Brauch HJ, Haist-Gulde B, Preuss G, Wilme U, Zulei-Seibert N (2002) Removal of pharmaceuticals during drinking water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 36:3855–3863
van Leeuwen CJ, Vermeire TG (2007) Risk Assessment of Chemicals—An Introduction. Part 3. Effects assessment and risk characterization. Springer, Dordrecht. The Netherlands, pp 209–308
Viehoever A (1936) Daphnia—the biological reagent. J Am Pharm Assoc 25:1112–1117
Wang L, Peng Y, Nie X, Pan B, Ku P, Bao S (2016) Gene response of CYP360A, CYP314, and GST and whole-organism changes in Daphnia magna exposed to ibuprofen. Comp Biochem Physiol 179:49–56
Whyte-Allman SK, Hoque MT, Jenabian MA, Routy JP, Bendayan R (2017) Xenobiotic nuclear receptors pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor regulate antiretroviral drug efflux transporters at the blood-testis barrier. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 363:324–335
Wollenberger L, Halling-Sorensen B, Kusk KO (2000) Acute and chronic toxicity of veterinary antibiotics to Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 40:723–730
Xu JJ, Hendriks BS, Zhao J, de Graaf D (2008) Multiple effects of acetaminophen and p38 inhibitors: towards pathway toxicology. FEBS Lett 582:1276–1282
Yamano S, Tatsuno J, Gonzalez FJ (1990) The CYP2A3 gene product catalyzes coumarin 7-hydroxylation in human liver microsomes. Biochemistry 29:1322–1329
Yan Q, Gao X, Peng XY (2012) Research and progress in removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) in wastewater treatment plants. Technol Water Treat 38:13–19
Yang X, Chen F, Meng F, Xie Y, Chen H, Young K, Luo W, Ye T, Fu W (2013) Occurrence and fate of PPCPs and correlations with water quality parameters in urban riverine waters of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:5864–5875
Yin D, Jin H, Yu L, Hu S (2003) Deriving freshwater quality criteria for 2,4-dichlorophenol for protection of aquatic life in China. Environ Pollut 122:217–222
Zhang L (2002) Market analysis of paracetamol. China Pharm 30:11–12.
Zhong Z, Xie QL (2015) Occurence and screening-level risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Liuxi river. Guangdong Chem Ind 42:58–59
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 31770554; 41576110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, R., Liu, S., He, C. et al. Paracetamol affects the expression of detoxification- and reproduction-related genes and alters the life traits of Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 29, 398–406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02199-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02199-z