Abstract
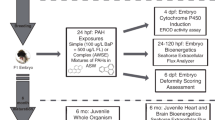
New Bedford Harbor (MA, U.S.A.; NBH) is a Superfund site inhabited by Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) with altered aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr) signaling, leading to resistance to effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). The Ahr is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression of many Phase I and II detoxifying enzymes and interacts with Nrf2, a transcription factor that regulates the response to oxidative stress. This study tested the hypothesis that PCB-resistant killifish exhibit altered sensitivity to oxidative stress. Killifish F1 embryos from NBH and a clean reference site (Scorton Creek, MA, U.S.A.; SC) were exposed to model pro-oxidant and Nrf2-activator, tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ). Embryos were exposed at specific embryonic developmental stages (5, 7, and 9 days post fertilization) and toxicity was assessed, using a deformity score, survival, heart rate, and gene expression to compare sensitivity between PCB -resistant and -sensitive (reference) populations. Acute exposure to tBHQ resulted in transient reduction in heart rate in NBH and SC F1 embryos. However, embryos from NBH were more sensitive to tBHQ, with more frequent and severe deformities, including pericardial edema, tail deformities, small body size, and reduced pigment and erythrocytes. NBH embryos had lower basal expression of antioxidant genes catalase and glutathione-S-transferase alpha (gsta), and upon exposure to tBHQ, exhibited lower levels of expression of catalase, gsta, and superoxide dismutase compared to controls. This result suggests that adaptation to tolerate PCBs has altered the sensitivity of NBH fish to oxidative stress during embryonic development, demonstrating a cost of the PCB resistance adaptation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ahr:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- PCBs:
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls
- TCDD:
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- NBH:
-
New Bedford Harbor
- SC:
-
Scorton creek
- tBHQ:
-
tert-butylhydroquinone
- HAHs:
-
Halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- PCB-126:
-
3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl
- Arnt:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator
- XRE:
-
Xenobiotic response element
- Cyp1a:
-
Cytochrome P4501a
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid-related factor-2
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant response element
- tBOOH:
-
tert-butylhydroperoxide
- IVF:
-
In vitro fertilization
- ER:
-
Elizabeth River
References
Aluru N, Karchner SI, Hahn ME (2011) Role of DNA methylation of AHR1 and AHR2 promoters in differential sensitivity to PCBs in Atlantic Killifish Fundulus heteroclitus. Aquat Toxicol 101(1):288–294. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.010
Armstrong PB, Child JS (1965) Stages in the normal development of Fundulus heteroclitus. Biol Bull 128(2):143–168
Arzuaga X, Elskus A (2010) Polluted-site killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) embryos are resistant to organic pollutant-mediated induction of CYP1A activity, reactive oxygen species, and heart deformities. Environ Toxicol Chem 29(3):676–682. doi:10.1002/etc.68
Bacanskas LR, Whitaker J, Di Giulio RT (2004) Oxidative stress in two populations of killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) with differing contaminant exposure histories. Mar Environ Res 58(2–5):597–601. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.03.048
Bello SM (1999) Characterization of resistance to halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons in a population of Fundulus heteroclitus from a marine superfund site. Ph.D. Thesis. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution/Massachusetts Institute of Technology Joint Program in Oceanography
Bello SM, Franks DG, Stegeman JJ, Hahn ME (2001) Acquired resistance to Ah receptor agonists in a population of Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) inhabiting a marine superfund site: in vivo and in vitro studies on the inducibility of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes. Toxicol Sci 60(1):77–91
Nelson W, Bergen B, SJ B, Morrison G, Voyer R, Strobel C, Rego S, Thursby G, Pesch C (1996) New Bedford Harbor long-term monitoring assessment report: baseline sampling. US Environmental Protection Agency. National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory, Atlantic Ecology Division, Narragansett, RI
Billiard SM, Timme-Laragy AR, Wassenberg DM, Cockman C, Di Giulio RT (2006) The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway in mediating synergistic developmental toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to zebrafish. Toxicol Sci 92(2):526–536. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfl011
Billiard SM, Meyer JN, Wassenberg DM, Hodson PV, Di Giulio RT (2008) Nonadditive effects of PAHs on Early Vertebrate Development: mechanisms and implications for risk assessment. Toxicol Sci 105(1):5–23. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm303
Bozinovic G, Sit TL, Hinton DE, Oleksiak MF (2011) Gene expression throughout a vertebrate’s embryogenesis. BMC Genomics 12:132. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-132
Clark BW, Di Giulio RT (2012) Fundulus heteroclitus adapted to PAHs are cross-resistant to multiple insecticides. Ecotoxicology 21(2):465–474. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0807-x
Clark BW, Matson CW, Jung D, Di Giulio RT (2010) AHR2 mediates cardiac teratogenesis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and PCB-126 in Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). Aquat Toxicol 99(2):232–240. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.05.004
Crews ST (1998) Control of cell lineage-specific development and transcription by bHLH-PAS proteins. Genes Dev 12(5):607–620
Denison MS, Nagy SR (2003) Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:309–334. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.135828
Denison MS, Soshilov AA, He G, DeGroot DE, Zhao B (2011) Exactly the same but different: promiscuity and diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor. Toxicol Sci 124(1):1–22. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr218
Dimichele L, Taylor MH (1980) The environmental control of hatching in Fundulus heteroclitus. J of Exp Zool 214(2):181–187. doi:10.1002/jez.1402140209
Fernandez-Salguero PM, Hilbert DM, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ (1996) Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are resistant to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 140(1):173–179. doi:10.1006/taap.1996.0210
Gharavi N, Haggarty S, El-Kadi AO (2007) Chemoprotective and carcinogenic effects of tert-butylhydroquinone and its metabolites. Curr Drug Metab 8(1):1–7
Gu Y-Z, Hogenesch JB, Bradfield CA (2000) The PAS Superfamily: sensors of Environmental and Developmental Signals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40(1):519–561. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.40.1.519
Hirabayashi Y, Inoue T (2010) Benzene-induced bone-marrow toxicity: a hematopoietic stem-cell-specific, aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated adverse effect. Chem Biol Interact 184(1–2):252–258. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.12.022
Hou JL, Zhuang P, Zhang LZ, Feng L, Zhang T, Liu JY, Feng GP (2011) Morphological deformities and recovery, accumulation and elimination of lead in body tissues of Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis, early life stages: a laboratory study. J Appl Ichthyol 27(2):514–519. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0426.2011.01703.x
Jones DP (2006) Redefining oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(9–10):1865–1879. doi:10.1089/ars.2006.8.1865
Jonsson ME, Jenny MJ, Woodin BR, Hahn ME, Stegeman JJ (2007) Role of AHR2 in the expression of novel cytochrome P450 1 family genes, cell cycle genes, and morphological defects in developing zebra fish exposed to 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl or 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Sci 100(1):180–193. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm207
Kahl R, Weinke S, Kappus H (1989) Production of reactive oxygen species due to metabolic activation of butylated hydroxyanisole. Toxicology 59(2):179–194
Kahler CP (2000) Evaluation of the use of the solvent dimethyl sulfoxide in chemiluminescent studies. Blood Cells Mol Dis 26(6):626–633. doi:10.1006/bcmd.2000.0340
Kalthoff S, Ehmer U, Freiberg N, Manns MP, Strassburg CP (2010) Interaction between oxidative stress sensor Nrf2 and xenobiotic-activated aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the regulation of the human phase II detoxifying UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A10. J Biol Chem 285(9):5993–6002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.075770
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S (2007) Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:89–116. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.46.120604.141046
Kinnison MT, Hairston NG (2007) Eco-evolutionary conservation biology: contemporary evolution and the dynamics of persistence. Functional Ecol 21(3):444–454. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2435.2007.01278.x
Kobayashi M, Itoh K, Suzuki T, Osanai H, Nishikawa K, Katoh Y, Takagi Y, Yamamoto M (2002) Identification of the interactive interface and phylogenic conservation of the Nrf2-Keap1 system. Genes Cells 7(8):807–820
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Watai Y, Tong KI, Shibata T, Uchida K, Yamamoto M (2006) Oxidative and electrophilic stresses activate Nrf2 through inhibition of ubiquitination activity of Keap1. Mol Cell Biol 26(1):221–229. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.1.221-229.2006
Kohle C, Bock KW (2007) Coordinate regulation of Phase I and II xenobiotic metabolisms by the Ah receptor and Nrf2. Biochem Pharmacol 73(12):1853–1862. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.009
Lee JM, Johnson JA (2004) An important role of Nrf2-ARE pathway in the cellular defense mechanism. J Biochem Mol Biol 37(2):139–143
Lesser MP (2006) Oxidative stress in marine environments: biochemistry and physiological ecology. Annu Rev Physiol 68:253–278. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.68.040104.110001
Loro VL, Jorge MB, Silva KR, Wood CM (2012) Oxidative stress parameters and antioxidant response to sublethal waterborne zinc in a euryhaline teleost Fundulus heteroclitus: protective effects of salinity. Aquat Toxicol 110–111:187–193. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.01.012
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101(1):13–30. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.006
Ma Q, Kinneer K, Yongyi B, Chan J, Kan Y (2004) Induction of murine NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin requires the CNC (cap ‘n’ collar) basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2): cross-interaction between AhR (aryl hydrocarbon receptor) and Nrf2 signal transduction. Biochem J 377(1):205–213
Matson CW, Clark BW, Jenny MJ, Fleming CR, Hahn ME, Di Giulio RT (2008) Development of the morpholino gene knockdown technique in Fundulus heteroclitus: a tool for studying molecular mechanisms in an established environmental model. Aquat Toxicol 87(4):289–295. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.02.010
Meyer JN, Di Giulio RT (2003) Heritable Adaptation and Fitness Costs in Killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) Inhabiting a Polluted Estuary. Ecol Appl 13(2):490–503
Meyer JN, Nacci DE, Di Giulio RT (2002) Cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) in Killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus): heritability of Altered Expression and Relationship to Survival in Contaminated Sediments. Toxicol Sci 68(1):69–81. doi:10.1093/toxsci/68.1.69
Meyer JN, Smith JD, Winston GW, Di Giulio RT (2003) Antioxidant defenses in killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) exposed to contaminated sediments and model prooxidants: short-term and heritable responses. Aquat Toxicol 65(4):377–395
Miao W, Hu L, Scrivens PJ, Batist G (2005) Transcriptional regulation of NF-E2 p45-related factor (NRF2) expression by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-xenobiotic response element signaling pathway: direct cross-talk between phase I and II drug-metabolizing enzymes. J Biol Chem 280(21):20340–20348. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412081200
Mimura J, Yamashita K, Nakamura K, Morita M, Takagi T, Nakao K, Ema M, Sogawa K, Yasuda M, Katsuki M, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1997) Loss of teratogenic response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in mice lacking the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Genes Cells 2(10):645–654
Mukaigasa K, Nguyen LT, Li L, Nakajima H, Yamamoto M, Kobayashi M (2012) Genetic Evidence of an Evolutionarily Conserved Role for Nrf2 in the Protection against Oxidative Stress. Mol Cell Biol 32(21):4455–4461. doi:10.1128/MCB.00481-12
Nacci D, Coiro L, Champlin D, Jayaraman S, McKinney R, Gleason TR, Munns WR Jr, Specker JL, Cooper KR (1999) Adaptations of wild populations of the estuarine fish Fundulus heteroclitus to persistent environmental contaminants. Mar Biol 134(1):9–17. doi:10.1007/s002270050520
Nacci DE, Champlin D, Coiro L, McKinney R, Jayaraman S (2002) Predicting the occurrence of genetic adaptation to dioxinlike compounds in populations of the estuarine fish Fundulus heteroclitus. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(7):1525–1532
Nacci D, Champlin D, Jayaraman S (2010) Adaptation of the Estuarine Fish Fundulus heteroclitus (Atlantic Killifish) to Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs). Estuar Coast 33(4):853–864. doi:10.1007/s12237-009-9257-6
Nakamura Y, Kumagai T, Yoshida C, Naito Y, Miyamoto M, Ohigashi H, Osawa T, Uchida K (2003) Pivotal role of electrophilicity in glutathione S-transferase induction by tert-butylhydroquinone. Biochemistry 42(14):4300–4309. doi:10.1021/bi0340090
Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Pickett CB (2003) Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:233–260. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.140229
Nguyen T, Yang CS, Pickett CB (2004) The pathways and molecular mechanisms regulating Nrf2 activation in response to chemical stress. Free Radic Biol Med 37(4):433–441. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.04.033
Okey AB (2007) An aryl hydrocarbon receptor odyssey to the shores of toxicology: the Deichmann Lecture. International Congress of Toxicology-XI. Toxicol Sci 98(1):5–38
Oleksiak MF, Karchner SI, Jenny MJ, Franks DG, Welch DB, Hahn ME (2011) Transcriptomic assessment of resistance to effects of an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) agonist in embryos of Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) from a marine Superfund site. BMC Genomics 12:263. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-263
Ownby DR, Newman MC, Mulvey M, Vogelbein WK, Unger MA, Arzayus LF (2002) Fish (Fundulus heteroclitus) populations with different exposure histories differ in tolerance of creosote-contaminated sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(9):1897–1902
Peters JM, Narotsky MG, Elizondo G, Fernandez-Salguero PM, Gonzalez FJ, Abbott BD (1999) Amelioration of TCDD-induced teratogenesis in aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-null mice. Toxicol Sci 47(1):86–92
Pierron F, Baudrimont M, Gonzalez P, Bourdineaud JP, Elie P, Massabuau JC (2007) Common pattern of gene expression in response to hypoxia or cadmium in the gills of the European glass eel (Anguilla anguilla). Environ Sci Technol 41(8):3005–3011
Powell WH, Bright R, Bello SM, Hahn ME (2000) Developmental and tissue-specific expression of AHR1, AHR2, and ARNT2 in dioxin-sensitive and -resistant populations of the marine fish Fundulus heteroclitus. Toxicol Sci 57(2):229–239
Prasch AL, Teraoka H, Carney SA, Dong W, Hiraga T, Stegeman JJ, Heideman W, Peterson RE (2003) Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor 2 Mediates 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Developmental Toxicity in Zebrafish. Toxicol Sci 76:138–150
Prince R, Cooper KR (1995) Comparisons of the effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on chemically impacted and nonimpacted subpopulations of Fundulus heteroclitus: i. TCDD toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 14(4):579–587
Samson SL, Paramchuk WJ, Gedamu L (2001) The rainbow trout metallothionein-B gene promoter: contributions of distal promoter elements to metal and oxidant regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1517(2):202–211
Schlezinger JJ, Struntz WD, Goldstone JV, Stegeman JJ (2006) Uncoupling of cytochrome P450 1A and stimulation of reactive oxygen species production by co-planar polychlorinated biphenyl congeners. Aquat Toxicol 77(4):422–432. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.01.012
Schmidt JV, Bradfield CA (1996) Ah receptor signaling pathways. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:55–89. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.12.1.55
Sharma R, Yang Y, Sharma A, Awasthi S, Awasthi YC (2004) Antioxidant role of glutathione S-transferases: protection against oxidant toxicity and regulation of stress-mediated apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 6(2):289–300. doi:10.1089/152308604322899350
Shin S, Wakabayashi N, Misra V, Biswal S, Lee GH, Agoston ES, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW (2007) NRF2 modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling: influence on adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 27(20):7188–7197. doi:10.1128/MCB.00915-07
Timme-Laragy AR, Levin ED, Di Giulio RT (2006) Developmental and behavioral effects of embryonic exposure to the polybrominated diphenylether mixture DE-71 in the killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). Chemosphere 62(7):1097–1104. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.037
Timme-Laragy AR, Van Tiem LA, Linney EA, Di Giulio RT (2009) Antioxidant responses and NRF2 in synergistic developmental toxicity of PAHs in zebrafish. Toxicol Sci 109(2):217–227. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp038
Timme-Laragy AR, Goldstone JV, Hansen JM, Stegeman JJ, Hahn ME (2012a) Glutathione dynamics and differential sensitivity to pro-oxidants during zebrafish devlopment. Abstract 1183. Toxicologist 126 (1)
Timme-Laragy AR, Karchner SI, Franks DG, Jenny MJ, Harbeitner RC, Goldstone JV, McArthur AG, Hahn ME (2012b) Nrf2b, novel zebrafish paralog of oxidant-responsive transcription factor NF-E2-related factor 2 (NRF2). J Biol Chem 287(7):4609–4627. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.260125
Tingaud-Sequeira A, Zapater C, Chauvigne F, Otero D, Cerda J (2009) Adaptive plasticity of killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) embryos: dehydration-stimulated development and differential aquaporin-3 expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296(4):R1041–R1052. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.91002.2008
Trinkaus J (1967) Fundulus. In: FW Hilt NW (ed) Methods in Developmental Biology. Thomas Y. Crowell Company, New York, pp 113-122
Turner C, Sawle A, Fenske M, Cossins A (2012) Implications of the solvent vehicles dimethylformamide and dimethylsulfoxide for establishing transcriptomic endpoints in the zebrafish embryo toxicity test. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(3):593–604. doi:10.1002/etc.1718
van Ommen B, Koster A, Verhagen H, van Bladeren PJ (1992) The glutathione conjugates of tert-butyl hydroquinone as potent redox cycling agents and possible reactive agents underlying the toxicity of butylated hydroxyanisole. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 189(1):309–314
Wakabayashi N, Slocum SL, Skoko JJ, Shin S, Kensler TW (2010) When NRF2 talks, who’s listening? Antioxid Redox Signal 13(11):1649–1663. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3216
Wassenberg DM, Di Giulio RT (2004) Synergistic embryotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists with cytochrome P4501A inhibitors in Fundulus heteroclitus. Environ Health Perspect 112(17):1658–1664
Weis JS, Weis P, Heber M, Vaidya S (1981) Methylmercury tolerance of killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) embryos from a polluted vs non-polluted environment. Mar Biol 65(3):283–287. doi:10.1007/BF00397123
Wells PG, Bhuller Y, Chen CS, Jeng W, Kasapinovic S, Kennedy JC, Kim PM, Laposa RR, McCallum GP, Nicol CJ, Parman T, Wiley MJ, Wong AW (2005) Molecular and biochemical mechanisms in teratogenesis involving reactive oxygen species. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207(2 Suppl):354–366. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2005.01.061
White RD, Shea D, Stegeman JJ (1997) Metabolism of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl by the marine fish scup (Stenotomus chrysops) in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos 25(5):564–572
Whitehead A, Triant DA, Champlin D, Nacci D (2010) Comparative transcriptomics implicates mechanisms of evolved pollution tolerance in a killifish population. Mol Ecol 19(23):5186–5203. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04829.x
Whitehead A, Pilcher W, Champlin D, Nacci D (2012) Common mechanism underlies repeated evolution of extreme pollution tolerance. Proc Biol Sci 279(1728):427–433. doi:10.1098/rspb.2011.0847
Wirgin I, Waldman JR (2004) Resistance to contaminants in North American fish populations. Mutat Res 552(1–2):73–100. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.06.005
Wu M, Shariat-Madar B, Haron MH, Wu M, Khan IA, Dasmahapatra AK (2011) Ethanol-induced attenuation of oxidative stress is unable to alter mRNA expression pattern of catalase, glutathione reductase, glutathione-S-transferase (GST1A), and superoxide dismutase (SOD3) enzymes in Japanese rice fish (Oryzias latipes) embryogenesis. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 153(1):159–167. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.10.002
Yang L, Kemadjou JR, Zinsmeister C, Bauer M, Legradi J, Muller F, Pankratz M, Jakel J, Strahle U (2007) Transcriptional profiling reveals barcode-like toxicogenomic responses in the zebrafish embryo. Genome Biol 8(10):R227. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-10-r227
Yeager RL, Reisman SA, Aleksunes LM, Klaassen CD (2009) Introducing the “TCDD-inducible AhR-Nrf2 gene battery”. Toxicol Sci 111(2):238–246. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp115
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Diana Franks, Drs. Sibel Karchner, Larissa Williams, Neel Aluru, and Jared Goldstone for assistance and helpful discussions. This research was funded by a WHOI Summer Student Fellowship to R. Harbeitner supported by the Arthur Vining Davis Foundation and WHOI Academic Programs Office funds and National Science Foundation grant OCE 0649139, by National Institutes of Health grants P42ES007381 (Superfund Basic Research Program at Boston University; Hahn), F32ES017585 (Timme-Laragy), and R01ES016366 (Hahn), and by Walter A. and Hope Noyes Smith.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harbeitner, R.C., Hahn, M.E. & Timme-Laragy, A.R. Differential sensitivity to pro-oxidant exposure in two populations of killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). Ecotoxicology 22, 387–401 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-1033-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-1033-x