Abstract
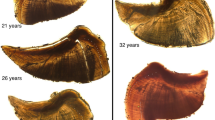
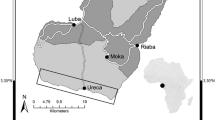
The annual life cycle of Millerichthys robustus is described from an ephemeral pool in Veracruz, Mexico. The state of the pool can be divided into three periods: a flood period lasting from September to March when the pool was filled with water, a drought period from April to June when the pool was dry, and a humid period in July and August when the pool was intermittently filled. Soil substrate was examined in each of these three periods (flood, drought and humid), embryos were found, and the stage of embryonic diapause was determined. During the flood period embryos were in diapause I; during the drought period in diapause II; and during the humid period mainly in diapause III with a small subset in diapause II (an example of a bet-hedging strategy). Two hatching periods (separated by two weeks) were documented during the beginning of the flood period. Fish growth was analyzed in both males and females, with females showing an overall slower growth rate and smaller adult size. In females, ovarian maturity was characterized histologically to understand the reproductive cycle. The onset of sexual maturity began during the third week after hatching (21 days) with the presence of secondary sexual characteristics in females and the beginning of Secondary Growth Stage in some ovarian follicles. All stages of oogenesis, postovulatory follicles and ovulated oocytes were observed from the fourth week post hatching (28 days) until death. M. robustus appears to exhibit similar patterns of embryonic diapause compared to other annual killifish living in seasonal water bodies closer to the equator. This study characterizes (for the first time) the adaptations and life cycle of M. robustus. This information could be useful to evaluate the potential risk of these populations and, if necessary, to develop plans for their conservation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Morales M, Coutiño BB, Rosales SP (1996) Manual general de técnicas histológicas y citoquímicas. México, D.F. Facultad de Ciencias, UNAM, México, D.F
Arenzon A, Caravalho A, Camino M (1999) Reproduction of the annual fish Cynopoecilus melanotaenia (Regan, 1912) in a temporary water body in Rio Grande do Sur, Brazil (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Hydrobiologia 411(0):65–70
Arenzon A, Peret CA, Bohrer MB (2001) Growth of the annual fish Cynopoecilus melanotaenia (Regan, 1912) based in a temporary water body population in Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Bras J Biol 61:117–123
Balaẑek R, Polačik M, Reichard M (2013) Rapid growth, early maturation and short generation time in African anual fishes. EvoDevo 4:24. doi:10.1186/2041-9139-4-24
Berois N, Arezo JM, Papa GN, Clivo AG (2012) Annual fish: developmenal adaptations for an extreme environment. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 1(4):595–602. doi:10.1002/wdev.39
Berois N, Arezo JM, de Sá OR (2014) The neotropical genus Austroplebias: an emerging model of annual killifishes. Cell Dev Biol 3(2):1000136. doi:10.4172/2168-9296.1000136
Brown-Peterson N, Wyanski D, Saborido-Rey F, Macewicz B, Lowerre-Barbier SK (2011) A standardized terminology for describing reproductive development in fishes. Marine and Coastal Fisheries: Dynamics, Management, and Ecosystem Science 3:52–70. doi:10.1080/19425120.2011.555724
Costa WJEM (2011) Phylogenetic position and taxonomic status of Anablepsoides, Atlantirivulus, Cynodonichthys, Laimosemion and Melanorivulus (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae). Ichthyol Explor Fres 22(3):233–249
Costa WJEM (2013) Historical biogeography of aplocheiloid killifishes (Teleostei: Cypronodontiformes). Vertebrate Zoology 63(2):139–154
da Silva GC, Pereira SU, Volcan VM (2011) The opportunistic feeding and reproduction strategies of the annual fish Cynopoecilus melanotaenia (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae) inhabiting ephimeral habitats on southern Brazil. Neotrop Ichthyol 9(1):191–200. doi:10.1590/S1679-62252011000100019
De Vlaming V, Grossman G, Chapman F (1982) On the use the gonadosomatic index. Comp Biochem Physiol 73A(1):31–39
Domínguez-Castanedo O, Mosqueda-Cabrera MA, Valdesalici S (2013) First observations of annualism in Millerichthys robustus (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae). Ichthyol Explor Fres 24(1):15–20
Dorn A, Musilova Z, Platzer M, Reichwald K, Cellerino A (2014) The strange case of East African annual fishes: aridification correlates with diversification for a savannah aquatic group? BMC Evol Biol 14:210–223. doi:10.1186/s12862-014-0210-3
Eschmeyer WN, Fong JD (2016) Species by family/subfamily. Institute for Biodiversity Sciences and Sustainability. California Academy of Sciences. http://researcharchive.Calacademy.Org/research/ichthyology/catalog/SpeciesByFamily.Asp. Accessed 30 Sept 2016
Froese R (2006) Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recomendations. J Appl Ichthyol 22(4):241–253. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00805.x
Furness IA (2015) The evolution of an annual life cycle in killifish: adaptation to ephemeral aquatic environments through embryonic diapause. Biol Rev. doi:10.1111/brv.12194
Furness IA, Lee K, Reznick ND (2015) Adaptation in a variable environment: phenotypic plasticity and bet-hedging during egg diapause and hatching in an annual killifish. Evolution 69(6):1461–1475. doi:10.1111/evo.12669
Grier JH, Mari U, Patiño R (2009) The ovary, Folliculogenesis, and Oogenesis in Teleosts. In: Jamieson BGM (ed) Reproductive Biology and physiology of fishes (Agnsthans and bony fishes). Science Publishers, USA, pp 25–86
Hoaglin D, Mosteller F, Tukey J (1991) Fundamentals of exploratory analysis of variance. Wiley, New York
Inglima K, Perlmutter A, Markofsky J (1981) Reversible stage-specific embryonic inhibition mediated by the presence of adults in the annual fish Nothobranchius guentheri. J Exp Zool 215(1):23–33. doi:10.1002/jez.1402150104
Krause LLE, Wolfgang OF, Maltchik L (2014) Abundance variations and life history traits of two sympatric species of Neotropical annual fish (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae) in temporary ponds of southern Brazil. J Nat Hist 48(31–32):1971–1988. doi:10.1080/00222933.2013.862577
Lorenzen ED, Heller R, Siegismund HR (2012) Comparative phylogeography of African savannah ungulates. Mol Ecol 21(15):3656–3670. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05650.x
Loureiro M, de Sá OR (2016) Diversity of Aplocheiloidei. In: Berois N, García G, de Sá OR (eds) Annual fishes: life history strategy, divesity and evolution. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, USA, pp 3–31
Markofsky J, Matias JR (1977) The effect of temperature and season of collection on the onset and duration of diapause in embryos of the annual fish Nothobranchius guentheri. J Exp Zool 202:49–56. doi:10.1002/jez.1402020107
Markofsky J, Matias JR, Inglima K, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N (1979) The variable effects of ambient and artificial light: dark cycles on embryonic diapause in a laboratory population of the annual fish Nothobranchius guentheri. J Exp Biol 83:203–225
Medina M (1979) El factor de condición múltiple (KM) y su importancia en el manejo de las carpas de Israel (Cyprinus carpio); hembras en estado de madurez V (Nikolsky, 1963). Manuales Técnicos de Acuacultura. Departamento de Pesca, México
Miller RR (2009) Peces dulceacuícolas de México. CONABIO, Sociedad Ictiológica Mexicana, El Colegio de la Frontera Sur y el Consejo de Peces del Desierto, México-Estados Unidos. Ciudad de México, México
Murphy WJ, Collier EG (1997) A molecular phylogeny for aplocheiloid fishes (Atherinomorpha: Cyprinodontiformes): the role of vicariance and the origins of annualism. Mol Biol Evol 14(8):790–799
Passos C, Tassino B, Rosenthal GG, Reichard M (2016) Reproductive behavior and sexual selection in annual fishes. In: Berois N, García G, de Sá OR (eds) Annual fishes: life history strategy, divesity and evolution. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, USA, pp 207–229
Pinceel T, Vanschoenwinkel B, Deckers P, Grégoir A, Ver Eecke T, Brendonck L (2015) Early and late developmental arrest as complementary embryonic bet-hedging strategies in African killifish. Biol J Linn Soc 114(4):941–948. doi:10.1111/bij.12474
Podrabsky J, Hand C (1999) The bioenergetics of embryonic diapause in an annual killifish, Austrofundulus limnaeus. J Exp Biol 202:2567–2580
Podrabsky J, Hand CS (2015) Physiological strategies during animal diapause: lessons from brine shrimp and annual killifish. J Exp Biol 218:1897–1906. doi:10.1242/jeb.116194
Podrabsky J, Carpenter J, Hand S (2001) Survival of water stress in annual fish embryos: dehydration avoidance and egg envelope amyloid fibers. Am J Physiol Integrative Comp Physiol 280:123–131
Podrabsky J, Tingaud-Sequeira A, Cerdá J (2010b) Metabolic dormancy and responses to environmental desiccation in fish embryos. In: Lubzens E (ed) dormancy and resistance in harsh environments. Top Curr Genet 21:203–226
Podrabsky J, Garrett I, Kohl F (2010a) Alternative developmental pathways associated with diapause regulated by temperature and maternal influences in embryos of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus. J Exp Biol 213:3280–3288. doi:10.1242/jeb.045906
Polačik M, Donner TM, Reichard M (2011) Age structure of annual Nothobranchius fishes in Mozambique: is there a hatching synchrony? J Fish Biol 78:796–809. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2010.02893.x
Polačik M, Balaẑek R, Režucha R, Vrtílek M, Terzibasi-Tozzini E, Reichard M (2014) Alterntive intrapopulation life-history strategies and their trade-offs in an African annual fish. J Evol Biol 27:854–865. doi:10.1111/jeb.12359
Reichard M (2016) The evolutionary ecology of african annual fishes. In: Berois N, García G, de Sá OR (eds) Annual fishes: life history strategy, divesity and evolution. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, USA, pp 133–158
Ribeiro AC (2006) Tectonic history and the biogeography of the freshwater fishes from the coastal drainages of estern Brazil: an example of faunal evolution associated with a divergent continental margin. Neotrop Ichthyol 4:225–246. doi:10.1590/1982-0224-20130228
Ricker WE (1975) Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish population. Department of the Environment Fisheries and Marine Services. Ottawa Bulletin 191:203–204
Schalk MC, Montaña GC, Libson EM (2014) Reproductive strategies of two Neotropical killifish, Austrolebias vandenbergi and Neofundulus ornatipinnis (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae) in the Bolivian gran Chaco. Rev Biol Trop 62(1):109–117
Shidlovskiy KM (2010) Collecting Notobranchius in south-western Tanzania. Nothobranchius Archives 1:18–27
Tanizaki K (1988) Ecología de peixes anuaisraros do Estado de Rio de Janeiro – género Cynolebias Stridachner, 1876 (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). In congreso Brasileiro de Zoología, Brazil 15:318
Terzibasi TE, Valenzano M, Benedetti M, Roncaglia P, Cattaneo A, Domenici L, Cellerino A (2008) Large differences in aging phenotype between strains of the short-lived annual fish Nothobranchius furzeri. PLoS One 12(3):e3866. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003866
Terzibasi TE, Dorn A, Ng’oma E, Polačik M, Balaẑek R, Reichwald K, Petzold A, Watters B, Reichard M, Cellerino A (2013) Parallel evolution of senescence in annual fishes in response to extrinsic mortality. BMC Evol Biol 13:77–89. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-77
Valdesalici S (2013, 2013) Pronothobranchius chirioi n. sp. A new annual killifish species from the Niger River drainage, with redescription of P. kiyawensis, P. gambiensis and P. seymouri (Cyprinodontiformes: Nothobranchiidae). Killi-Data Seres:21–41
Valdesalici S, Cellerino A (2003) Extremely short lifespan in the annual fish Nothobranchius furzeri. P Roy Soc Lond B Bio 270:189–191. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2003.0048
Vaz-Ferreira R, Sierra de Soriano, Scagila B (1964) Ecología de la reproducción de los peces del genero Cynolebias Stridachner. Arch Soc Biol Montevideo 161–171
Volcan MV, Fonseca PA, Figueiredo MR, Sampaio AL, Robaldo BR (2012) Effect of temperature on growth of the threatened annual fish Austrolebias nigrofasciatus Costa y Cheffe 2001. Biota Neotrop 12(4):1–6
Volcan MV, Gonҫalves CA, Guadagnin LD (2013) Length-weight relationship of three annual fishes (Rivulidae) from temporary freshwater wetlands of southern Brazil. J Appl Ichthyol 29:1188–1190. doi:10.1111/jai.12214
Wallace AR, Selman K (1981) Cellular and dynamic aspects of oocyte growth in teleosts. Am Zool 21(2):325–343
Watters BR (2009) The ecology and distribution of Nothobranchius fishes. J Am Killifish Assoc 42:37–76
Wildekamp RH, Romand R, Scheel JJ (1986) Cyprinodontidae. In: Daget J, Gosse PJ, Thys van den Audenaerde FD (eds) Check-list of the freshwater fishes of Africa (CLOFFA). Brussels, MRAC; Tervuren; and ORSTOM, Paris, pp 165-276
Wilderkamp RH (2004) A world of killies. Atlas of the oviparous Cyprinodontiform fishes of the world. American Killifish Association, Mishawaka
Williams DD (2006) The biology of temporary waters. Oxford University Press, New York
Winemiller KO (2005) Life history strategies, population regulation, and implications for fisheries management. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62(4):872–885. doi:10.1139/f05-040
Wootton RF (1991) Ecology of teleost fishes. Fish and fisheries. Sereies. Chapman & Hall, 2-6 Bodanz Row, London
Wourms JP (1972a) Developmental biology of annual fishes. I. Stages in the normal development of Austrofundulus myersi. Dahl J Exp Zool 182:143–168
Wourms JP (1972b) Developmental biology of annual fishes. II. Naturally occurring dispersion and reaggregation of blastomers during the development of annual fish eggs. J Exp Zool 182:169–200
Wourms JP (1972c) Developmental biology of annual fishes. III. Pre-embryonic and embryonic diapause of variable duration in eggs of annual fishes. J Exp Zool 182:389–414
Young LJ, Bornik BZ, Marcotte LM, Charlie NK, Wagner NG, Hinch GS, Cooke JS (2006) Integrating physiology and life history to improve fisheries management and conservation. Fish Fish 7:262–283. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2979.2006.00225.x
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the help and support of Victor Rosales Perez and Miguel Mosqueda with the collection of specimens in the field. To Stefano Valdesalici, Bela Nagy, Richard Martino (AKA) and Robert Meyer (AKA) for the valuable information suggested and provided, and to Comisión Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología for scholarship No. 375928. We thank the academic counseling of Bruno A. Marichal Cancino and Liliana García-Calva in this project. (Sampling, management and procedures performed in this research were authorized by SGPA/DGVS/02404/14, /2015 of the Subsecretaría de Gestión para la Protección Ambiental, Dirección General de Vida Silvestre, SEMARNAT). We also sincerely appreciate the thorough and detailed comments by the reviewers that allowed for improvement of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domínguez-Castanedo, O., Uribe, M.C. & Rosales-Torres, A.M. Life history strategies of annual killifish Millerichthys robustus (Cyprinodontiformes:Cynolebiidae) in a seasonally ephemeral water body in Veracruz, México. Environ Biol Fish 100, 995–1006 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-017-0617-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-017-0617-y