Abstract
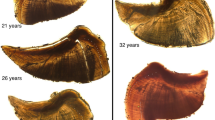
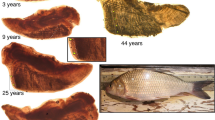
Ultrasonic telemetry is a preferred method for fish-movement studies. Despite surgical tag implantation being the most common method for affixing tags, many studies lack tests addressing the assumption that tagging has no effect on fish performance or survival. The threatened, anadromous green sturgeon, Acipenser medirostris, has little documentation concerning its movements. We evaluated the effects of surgery and tag implantation in juveniles. We compared three groups: tagged fish with dummy transmitters implanted in the peritoneal cavity, sham fish that underwent surgery without tag implantation, and control fish that were handled and anesthetized but did not undergo surgery. We found no differences in growth or critical swimming velocity among groups. Photos of incisions were taken towards the beginning and at the end of the study to assess inflammation and to score each incision for closure and suture retention. Inflammation declined similarly for tagged and sham fish during the study. Ucrit was not related to the extent of inflammation or to post-surgery time. All fish showed healing during the study (ca. 140 day duration) and 10 % of tagged and sham fish showed signs of inflammation by the study end. These results suggest that current ultrasonic surgical tagging methods do not significantly affect the short-term growth or swimming performance of juvenile green sturgeon. Additionally, effects of surgery can be mitigated by minimizing the number of suture entry points and by using rapid-absorbing sutures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams PB, Grimes C, Hightower JE, Lindley ST, Moser ML, Parsley MJ (2007) Population status of North American Green Sturgeon, Acipenser medirostris. Environ Biol Fish 79:339–356. doi:10.1007/s10641-006-9062-z
Adams NS, Rondorf DW, Evans SD, Kelly JE, Perry RW (1998a) Effects of surgically and gastrically implanted radio transmitters on swimming performance and predator avoidance of juvenile chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:781–787. doi:10.1139/f97-285
Adams NS, Rondorf DW, Evans SD, Kelly JE (1998b) Effects of surgically and gastrically implanted radio transmitters on growth and feeding behaviour of juvenile chinook salmon. Trans Am Fish Soc 127:128–136. doi:10.1577/1548-8659
Allen PJ, Hodge B, Werner I, Cech JJ Jr (2006) Effects of ontogeny, season, and temperature on the swimming performance of juvenile green sturgeon (Acipenser medirostris). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 63:1360–1369. doi:10.1139/f06-031
Ammann A, Michel C, MacFarlane R (2011) The effects of surgically implanted acoustic transmitters on laboratory growth, survival and tag retention in hatchery yearling Chinook salmon. Environ Biol Fish. doi:10.1007/s10641-011-9941-9
Baker DW, Peake SJ, Kieffer JD (2008) The effect of capture, handling, and tagging on hematological variables in wild adult lake sturgeon. N Am J Fish Manage 28:296–300. doi:10.1577/M06-255.1
Bartholow J (2005) Recent water temperature trends in the lower Klamath River, California. N Am J Fish Manage 25:152–162. doi:10.1577/M04-007.1
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integ Comp Biol 42:517–525. doi:10.1093/icb/42.3.517
Beamish FWH (1978) Swimming capacity. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol 7. Academic, New York, pp 101–187
Bell WH, Terhune LDB (1970) Water tunnel design for fisheries research. Fish Res Board Can Tech Rep 195:1–69
Brett JR (1964) The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon. J Fish Res Board Can 21:1183–1226
Brown RS, Cooke SJ, Anderson WG, McKinley RS (1999) Evidence to challenge the “2% Rule” for biotelemetry. N Am J Fish Manage 19:867–871. doi:10.1577/1548-8675
Brown RS, Geist DR, Deters KA, Grassell A (2006) Effects of surgically implanted acoustic transmitters >2% of body mass on the swimming performance, survival and growth of juvenile sockeye and Chinook salmon. J Fish Biol 69:1626–1638. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2006.01227.x
Brown RS, Harnish RS, Carter KM, Boyd JW, Deters KA, Eppard MB (2010) An evaluation of the maximum tag burden for implantation of acoustic transmitters in juvenile Chinook salmon. N Am J Fish Manage 30:499–505. doi:10.1577/M09-038.1
Chapman FA, Park C (2005) Comparison of sutures used for wound closure in sturgeon following a gonad biopsy. N Am J Aquacult 67:98–101. doi:10.1577/A04-046.1
Chittenden CM, Butterworth KG, Cubitt KF, Jacobs MC, Ladouceur A, Welch DW, McKinley RS (2009) Maximum tag to body size ratios for an endangered coho salmon (O. kisutch) stock based on physiology and performance. Environ Biol Fish 84:129–140. doi:10.1007/s10641-008-9396-9
Collins MR, Cooke DW, Smith TIJ, Post WC, Russ DC, Walling DC (2002) Evaluation of four methods of transmitter attachment on shortnose sturgeon, Acipenser brevirostrum. J Appl Ichthyol 18:491–494. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0426.2002.00386.x
Cooke SJ (2008) Biotelemetry and biologging in endangered species research and animal conservation: relevance to regional, national, and IUCN Red List threat assessments. Endang Species Res 4:165–185. doi:10.3354/esr00063
Cooke SJ, Bunt CM (2001) Assessment of internal and external antenna configurations of radio transmitters implanted in smallmouth bass. N Am J Fish Manage 21:236–241. doi:10.1577/1548-8675(2001)021<0236:MBOIAE>2.0.CO;2
Cooke SJ, Graeb BDS, Suski CD, Ostrand KG (2003) Effects of suture material on incision healing, growth and survival of juvenile largemouth bass implanted with miniature radio transmitters: case study of a novice and experienced fish surgeon. J Fish Biol 62:1366–1380. doi:10.1046/j.1095-8649.2003.00119.x
Cooke SJ, Woodley CM, Eppard MB, Brown RS, Nielsen JL (2011) Advancing the surgical implantation of electronic tags in fish: a gap analysis and research agenda based on a review of trends in intracoelomic tagging effects studies. Rev Fish Biol Fish 21:127–151. doi:10.1007/s11160-010-9193-3
Croce E, Olmi S (2000) Intracorporeal knot-tying and suturing techniques in laparoscopic surgery: technical details. J Soc Laparoend 4:17–22
Counihan TD, Frost CN (1999) Influence of externally attached transmitters on the swimming performance of juvenile white sturgeon. Trans Am Fish Soc 128:965–970. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(1999)128<0965:IOEATO>2.0.CO;2
Deng X, Van Eenennaam JP, Doroshov SI (2002) Comparison of early life stages and growth of green and white sturgeon. Am Fish Soc Symp 28:237–248
Deters KA, Brown RS, Carter KM, Boyd JW (2009) Performance assessment of suture type in juvenile Chinook salmon surgically implanted with acoustic transmitters. Final Report prepared for the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Portland District, under a Government Order with the U.S. Department of Energy Contract
Deters KA, Brown RS, Carter KM, Bond JW, Eppard MB, Seaburg AG (2010) Performance assessment of suture type, water temperature, and surgeon skill in juvenile chinook salmon surgically implanted with acoustic transmitters. Trans Am Fish Soc 139:888–889. doi:10.1577/T09-043.1
Frost DA, McComas RL, Sandford BP (2010) The effects of a surgically implanted microacoustic tag on growth and survival in subyearling fall chinook salmon. Trans Am Fish Soc 139:1192–1197. doi:10.1577/T09-118.1
Gilliland ER (1994) Comparison of absorbable sutures used in largemouth bass liver biopsy surgery. Prog Fish-Cult 56:60–61. doi:10.1577/1548-8640(1994)056<0060:COASUI>2.3.CO;2
Heublein JC, Kelly JT, Crocker CE, Klimley AP, Lindley ST (2009) Migration of green sturgeon, Acipenser medirostris, in the Sacramento River. Environ Biol Fish 84:248–258. doi:10.1007/s10641-008-9432-9
Huff DD, Lindley ST, Wells BK, Chai F (2012) Green sturgeon distribution in the Pacific ocean estimated from modeled oceanographic features and migration behavior. PLoS ONE 7:e45852. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045852
Israel JA, Cordes JF, Blumberg MA, May B (2004) Geographic patterns of genetic differentiation among collections of green sturgeon. N Am J Fish Manage 24:922–931. doi:10.1577/M03-085.1
Israel JA, May B (2010) Indirect genetic estimates of breeding population size in the polyploid green sturgeon (Acipenser medirostris). Mol Ecol 19:1058–1070. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04533.x
Jepsen N, Mikkelsen JS, Koed A (2008) Effects of tag and suture type on survival and growth of brown trout with surgically implanted telemetry tags in the wild. J Fish Biol 72:594–602. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2007.01724.x
Knights BC, Lasee BA (1996) Effects of implanted transmitters on adult bluegills at two temperatures. Trans Am Fish Soc 125:440–449. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(1996)125<0440:EOITOA>2.3.CO;2
Kynard B, Parker E, Parker T (2005) Behavior of early life intervals of Klamath River green sturgeon, Acipenser medirostris, with a note on body color. Environ Biol Fishes 72:85–97. doi:10.1007/s10641-004-6584-0
Lindley ST, Moser ML, Erickson DL, Belchik M, Welch DW, Rechisky EL, Kelly JT, Heublein J, Klimley AP (2008) Marine migration of North American green sturgeon. Trans Am Fish Soc 137:182–194. doi:10.1577/T07-055.1
Loher T, Rensmeyer R (2011) Physiological responses of Pacific halibut, Hippoglossus stenolepis, to intracoelomic implantation of electronic archival tags, with a review of tag implantation techniques employed in flatfishes. Rev Fish Biol Fish 21:97–115. doi:10.1007/s11160-010-9192-4
Lucas MC (1989) Effects of implanted dummy transmitters on mortality, growth and tissue reaction in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J Fish Biol 35:577–587. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1989.tb03007.x
Lucas MC, Baras E (2000) Methods for studying the spatial behaviour of freshwater fishes in the natural environment. Fish Fish 1:283–316. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2979.2000.00028.x
Mayfield RB, Cech JJ (2004) Temperature effects on green sturgeon bioenergetics. Trans Am Fish Soc 133:961–970. doi:10.1577/T02-144.1
Moore A, Russell I, Potter E (1990) The effects of intraperitoneally implanted dummy acoustic transmitters on the behaviour and physiology of juvenile Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J Fish Biol 37:713–721. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1990.tb02535.x
Moyle PB, Yoshiyama RM, Williams JE, Wikramanayake ED (1995) Fish species of special concern in California, 2nd edn. Final report to CA Department of Fish and Game, contract 2128IF
Mourning TE, Fausch KD, Gowan C (1994) Comparison of visible implant tags and floy anchor tags on hatchery rainbow trout. N Am J Fish Manage 14:636–642. doi:10.1577/1548-8675(1994)014<0636:COVITA>2.3.CO;2
Neely BC, Steffensen KD, Pegg MA (2009) A comparison of gastrically and surgically implanted telemetry transmitters in shovelnose sturgeon. Fish Manag Ecol 16:323–328. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2400.2009.00679.x
Nelson JA, Gotwalt PS, Snodgrass JW (2003) Swimming performance of blacknose dace (Rhinichthys atratulus) mirrors home-stream current velocity. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 60:301–308. doi:10.1139/f03-023
Paukert CP, Chvala PJ, Heikes BL, Brown ML (2001) Effects of implanted transmitter size and surgery on survival, growth, and wound healing of bluegill. Trans Am Fish Soc 130:975–980. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(2001)130<0975:EOITSA>2.0.CO;2
Peake S, McKinley RS, Scruton DA, Moccia R (1997) Influence of transmitter attachment procedures on swimming performance of wild and hatchery-reared Atlantic salmon smolts. Trans Am Fish Soc 126:707–714
Plaut I (2001) Critical swimming speed: its ecological relevance. Comp Biochem Physiol 131:41–50. doi:10.1016/S1095-6433(01)00462-7
R Development Core Team (2012) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org/
Rasband WS (1997–2011). ImageJ, U. S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA, http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/
Robertson MJ, Scruton DA, Brown JA (2003) Effects of surgically implanted transmitters on swimming performance, food consumption and growth of wild Atlantic salmon parr. J Fish Biol 62:673–678. doi:10.1046/j.1095-8649.2003.00055.x
Sandstrom PT, Ammann AJ, Michel C, Singer G, Chapman ED, Lindley S, MacFarlane RB, Klimley AP (2012) Growth, survival, and tag retention of steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and its application to survival estimates. Environ Biol Fish:1–20. doi:10.1007/s10641-012-0051-0
Van Eenennaam JP, Webb MAH, Xin D, Doroshov SI, Mayfield RB, Cech JJ Jr, Hillemeier DC, Willson TE (2001) Artificial spawning and larval rearing of Klamath River green sturgeon. Trans Am Fish Soc 130:159–165. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(2001)130<0159:ASALRO>2.0.CO;2
Van Eenennaam JP, Linares-Casenave J, Doroshov SI (2012) Tank spawning of first generation domestic green sturgeon. J Appl Ichthyol 28:515–511. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0426.2012.02012.x
Wagner GN, Stevens ED (2000) Effects of different surgical techniques: suture material and location of incision site on the behaviour of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 33:103–114. doi:10.1080/10236240009387084
Walsh MG, Bjorgo KA, Isely JJ (2000) Effects of implantation method and temperature on mortality and loss of simulated transmitters in hybrid striped bass. Trans Am Fish Soc 129:539–544. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(2000)129<0539:EOIMAT>2.0.CO;2
Acknowledgments
We thank the Ecological Restoration Program of the California Department of Fish and Game for funding this study. We would also like to give special thanks to Joel Van Eenennaam, Serge Doroshov, Jon Reardon, Natalie Ho, Gabriel Singer, Sarah Cocherell, Scott Weber, Robert Coalter, Oliver Patton, Jennifer Yu, and Paul Lutes and Erik Hallen at UC Davis’ Center for Aquatic Biology and Aquaculture for their contributions to this study. We would also like to thank Jamilynn Poletto for her manuscript comments. We would like to thank Neil Willits for statistical advice and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments in improving this manuscript. All handling, care and experimental procedures used were reviewed and approved by the UC Davis Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC Protocol 15545).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, E.A., Froehlich, H.E., Cocherell, D.E. et al. Effects of acoustic tagging on juvenile green sturgeon incision healing, swimming performance, and growth. Environ Biol Fish 97, 647–658 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-013-0167-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-013-0167-x