Abstract
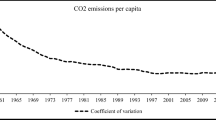
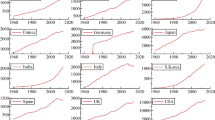
In response to equity concerns surrounding the spatial distribution of CO2 emissions and assumptions of CO2 convergence within some climate models, this paper examines the convergence of CO2 emissions within the OECD over the period 1870–2004. More specifically, using the Local Whittle estimator and its variants we examine whether relative per capita CO2 emissions are fractionally integrated, that is they are long memory processes which, although highly persistant, may revert to the mean/trend in the long run. Our results suggest that CO2 emissions within 13 out of 18 OECD countries are indeed fractionally integrated implying that they converge over time, albeit slowly. Interestingly though, the countries whose emissions are not found to be fractionally integrated are some of the highest polluters within the OECD, at least in per capita terms. Our results have implications both for future studies of CO2 convergence and for climate policy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldy JE (2006) Per capita carbon dioxide emissions: convergence or divergence?. Environ Resour Econ 33(4): 533–555
Bai J, Ng S (2004) A PANIC attack on unit roots and cointegration. Econometrica 72: 1127–1177
Barassi MR, Cole MA, Elliott RJR (2008) Stochastic divergence or convergence of per capita carbon dioxide emissions: re-examining the evidence. Environ Resour Econ 40: 121–137
Bodansky D (2004) International climate efforts beyond 2012: a survey of approaches. Pew Centre on Global Climate Change, Arlington
Boden TA, Marland G, Andres RJ (2009) Global, regional, and national fossil-fuel CO2 emissions. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge
Böhringer C, Welsch H (2004) Contraction and convergence of carbon emissions: an intertemporal multi-region CGE analysis. J Policy Model 26(1): 26–39
Carlino G, Mills L (1993) Are U.S. regional economies converging? A time series analysis. J Monet Econ 32: 335–346
Cole MA, Rayner AJ, Bates JM (1997) The environmental Kuznets curve: an empirical analysis. Environ Dev Econ 2(4): 401–416
Fox R, Taqqu MS (1986) Large sample properties of parameter estimates for strongly dependent stationary Gaussian time series. Ann Stat 14: 517–532
Galeotti M, Lanza A, Pauli F (2006) Reassessing environmental Kuznets curve for COCO2 emissions: a robustness exercise. Ecol Econ 1(15): 152–163
Granger CWJ, Hyung N (2004) Occasional structural breaks and long memory with an application to the S&P 500 absolute stock returns. J Empir Finance 11(3): 399–421
Granger CWJ, Joyeux R (1980) An introduction to long-memory time series models and fractional differencing. J Time Ser Anal 1: 15–30
Holtz-Eakin D, Selden T (1995) Stoking the Fires? CO2 emissions and economic growth. J Public Econ 57(1): 85–101
Hosking J (1981) Fractional differencing. Biometrika 68: 165–176
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (2001) Climate change 2001, synthesis report, IPCC report. http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/un/syreng/spm.pdf
International Energy Agency: (2009) CO2 emissions from fuel combustion 2009 edition. IEA, Paris
Lanne M, Liski M (2004) Trends and breaks in per capita carbon dioxide emissions 1870–2028. Energy J 25(4): 41–66
List JA (1999) Have air pollutant emissions converged amongst U.S. regions? Evidence from unit-root tests. South Econ J 66: 144–155
Mayoral L (2006) Further evidence on the statistical properties of real GNP. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 68: 901–920
Meyer A (2000) Contraction and convergence: the global solution to climate change. Schumacher Briefings
Mishra T (2009) Comment on ‘the uncertain unit root in real GNP: a re-examination’. J Macroecon 31: 167–172
Moon HR, Perron B (2004) Testing for a unit root in panels with dynamic factors. J Econom 122: 81–126
Nieswiadomy ML, Strazicich MC (2004) Are political freedoms converging?. Econ Inq 42(2): 323–340
Panopoulou E, Pantelidis T (2009) Club convergence in carbon dioxide emissions. Environ Resour Econ 44(1): 47–70
Pearce F (2003) Saving the world, plan B. New Sci 180(2425): 6–7
Phillips PCB, Sul D (2003) Dynamic panel estimation and homogeneity testing under cross section dependence. Econom J 6: 217–259
Robinson PM (1995) Gaussian semiparametric estimation of long range dependence. Ann Stat 23: 1630–1661
Romero-Avila D (2008) Convergence in carbon dioxide emissions among industrialised countries revisited. Energy Econ 30: 2265–2282
Shimotsu K, Phillips PCB (2005) Exact local Whittle estimation of fractional integration. Ann Stat 33: 1890–1933
Shimotsu K, Phillips PCB (2006) Local Whittle estimation of fractional integration and some of its variants. J Econom 130: 209–233
Stegman A (2005) Convergence in carbon emissions per capita. Centre for Applied Macroeconomic Analysis, Working Paper 8/2005
Strazicich MC, List JA (2003) Are CO2 emission levels converging among industrial countries?. Environ Resour Econ 24: 263–271
Vogelsang TJ (1998) Trend function hypothesis testing in the presence of serial correlation. Econometrica 66(1): 123–148
Westerlund J, Basher SA (2008) Testing for convergence in carbon dioxide emissions using a century of panel data. Environ Resour Econ 40: 109–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barassi, M.R., Cole, M.A. & Elliott, R.J.R. The Stochastic Convergence of CO2 Emissions: A Long Memory Approach. Environ Resource Econ 49, 367–385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-010-9437-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-010-9437-7