Abstract
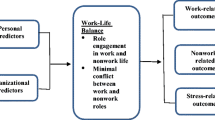
The purpose of this study is to determine the influence of work-life balance and work overload on teacher’s organizational commitment, noting the mediating role of job engagement and the moderating effect of perceived organizational support. A random sample of 278 teachers was collected from the Qassim province of Saudi Arabia to validate the research model. The data analysis using structural equation modeling AMOS 26 indicated that work-life balance has a direct and significant impact on organizational commitment and work overload has a negative impact on organizational commitment. Besides, this study highlighted that job engagement partially mediates the relationship between work-life balance and the organizational commitment of teachers. However, the moderating effect of perceived organizational support was insignificant. The findings of this research have some important implications for policymakers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, B. (2002). Primary school teacher’s workload of Malay language stream in Sibu Division, Sarawak. Master’s thesis, University Putra Malaysia, Serdang
Akar, H., & Ustuner, M. (2019). The relationships between perceptions of teachers’ transformational leadership, organizational justice, organizational support and quality of work life. International Journal of Research in Education and Science, 5(1), 309–322
Akram, M. (2010). Factors affecting the performance of teachers at higher secondary level in Punjab. thesis, University Institute of Education and Research Pir Mehr Ali Shah Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi, Pakistan
Allen, N. J., & Meyer, J. P. (1990). Organizational socialization tactics: A longitudinal analysis of links to newcomers’ commitment and role orientation. Academy of management journal, 33(4), 847–858
Arif, B., & Farooqi, Y. A. (2014). Impact of work life balance on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among university teachers: A case study of University of Gujrat, Pakistan. International journal of multidisciplinary sciences and engineering, 5(9), 24–29
Aryee, S., Srinivas, E. S., & Tan, H. H. (2005). Rhythms of life: Antecedents and outcomes of work-family balance in employed parents. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90, 132–146
Aydin, A., Sarier, Y., & Uysal, S. (2013). The effect of school principals’ leadership styles on teachers’ organizational commitment and job satisfaction. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 13(2), 806–811
Azita, A. R. (2012). Secondary school teachers’ workload in Batu Pahat, Johor Darul Takzim. Master’s thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Skudai Johor
Bahrmos, A. M. A. (2001). Identification of higher education in the Kingdom. Paper presented at a symposium on higher education in the Kingdom of Saudi Ar abia, Girls College, King Saud University, Riyadh
Ballout, H. I. (2009). Career commitment and career success: moderating role of self-efficacy. Career Development International, 14(7), 655–670
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173
Bogler, R., & Nir, A. (2012). The importance of teachers’ perceived organizational support to job satisfaction, what’s empowerment got to do with it? Journal of Educational Admnistration, 50(3), 287–306
Bolino, M. C., & Turnley, W. H. (2005). The personal costs of citizenship behavior: the relationship between individual initiative and role overload, job stress, and work-family conflict. Journal of applied psychology, 90(4), 740
Bollen, K. A., & Lennox, R. (1991). Conventional wisdom on measurement: A structural equation perspective. Psychology Bulletin, 110(2), 305–314
Bove, L. L., Pervan, S. J., Beatty, S. E., & Shiu, E. (2009). Service worker role in encouraging customer organizational citizenship behaviors. Journal of business research, 62(7), 698–705
Bridges, S., & Searle, A. (2011). Changing workloads of primary school teachers:‘I seem to live on the edge of chaos’. School Leadership & Management, 31(5), 413–433
Brislin, R. W. (1980). Translation and content analysis of oral and written materials. in Triandis, H. and Berry, J. (Eds), Handbook of Cross-Cultural Psychology, Allyn and Bacon, Boston, MA, pp. 389–444
Brough, P., Timms, C., O’Driscoll, M. P., Kalliath, T., Siu, O. L., Sit, C., & Lo, D. (2014). Work–life balance: A longitudinal evaluation of a new measure across Australia and New Zealand workers. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 25(19), 2724–2744
Brown, S. P., & Leigh, T. W. (1996). A new look at psychological climate and its relationship to job involvement, effort, and performance. Journal of applied psychology, 81(4), 358
Chafra, J., & Erkutlu, H. (2016). Authentic leadership and organizational job embeddedness in higher education. Hacettepe University Journal of Education, 32(2), 413–426
Choi, D., Oh, I. S., & Colbert, A. E. (2015). Understanding organizational commitment: A meta-analytic examination of the roles of the five-factor model of personality and culture. Journal of applied psychology, 100(5), 1542
Chughtai, A. A., & Zafar, S. (2006). Antecedents and consequences of organizational commitment among Pakistani university teachers. Applied HRM research, 11(1), 39
Churchill, G. (1979). A paradigm for developing better measures of marketing constructs. Journal of Marketing Research, 16(1), 64–73
Conley, S., & You, S. (2017). Key influences on special education teachers’ intentions to leave: The effects of administrative support and teacher team efficacy in a mediational model. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 45(3), 521–540
Craig, W. (2017). How Positive Employee Morale Benefits Your Business. Retrieved on June 2020 from https://www.forbes.com/sites/williamcraig/2017/08/29/how-positive-employee-morale-benefits-your-business/?sh=3cb04e302549
Cropanzano, R., & Mitchell, M. S. (2005). Social exchange theory: An interdisciplinary review. Journal of management, 31(6), 874–900
Curran, P. J., West, S. G., & Finch, J. F. (1996). The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychological methods, 1(1), 16
Dardas, L. A., & Ahmad, M. M. (2015). Coping strategies as mediators and moderators between stress and quality of life among parents of children with autistic disorder. Stress and Health, 31(1), 5–12
De Bruin, G. P. (2006). The dimensionality of the general work stress scale: A hierarchical exploratory factor analysis. SA Journal of Industrial Psychology, 32(4), 68–75
Dwi Putranti, H. R. (2018). Organizational commitment of hospital nurses: an empirical study on work-life balance and burnout management. European Researcher, 9(3), 235–248
Dyer, C. (2006). Research in psychology: A practical guide to methods and statistics’. Blackwell publishing
Eisenberger, R., Armeli, S., Rexwinkel, B., Lynch, P. D., & Rhoades, L. (2001). Reciprocation of perceived organizational support. Journal of applied psychology, 86(1), 42
Eisenberger, R., & Stinglhamber, F. (2011). Perceived organizational support: Fostering enthusiastic and productive employees. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association: American Psychological Association
Eisenberger, R., Cummings, J., Armeli, S., & Lynch, P. (1997). Perceived organizational support, discretionary treatment, and job satisfaction. Journal of applied psychology, 82(5), 812
Eisenberger, R., Huntington, R., Hutchison, S., & Sowa, D. (1986). Perceived organizational support. Journal of Applied psychology, 71(3), 500
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50
Garg, P., & Yajurvedi, N. (2016). Impact of work-life balance practices on employees’ retention and organizational performance – a study on IT industry. Indian Journal of Applied Research, 6(8), 105–108
Giao, H. N. K., Vuong, B. N., Huan, D. D., Tushar, H., & Quan, T. N. (2020). The Effect of Emotional Intelligence on Turnover Intention and the Moderating Role of Perceived Organizational Support: Evidence from the Banking Industry of Vietnam. Sustainability, 12(5), 1857
Gillespie, N. A., Walsh, M., Winefield, A. H., & Stough, C. (2001). Occupational stress in universities: staff perceptions of the causes, consequences and moderators of stress. Work and Stress, 15(1), 53–72
Gino, F., & Staats, B. (2015). It’s the Weekend! Why Are You Working? Harvard business Review. Accessed on December 2020 from https://hbr.org/2015/04/its-the-weekend-why-are-you-working
Goh, J., Pfeffer, J., & Zenios, S. A. (2016). The relationship between workplace stressors and mortality and health costs in the United States. Management Science, 62(2), 608–628
Goyal, M., & Arora, S. (2012). Harnessing work: family life balance among teachers of educational institutions. International Journal of Applied Services Marketing Perspectives, 1(2), 170
Greene, J., Mero, N., & Werner, S. (2018). The negative effects of job embeddedness on performance. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 33(1), 58–73
Growth Potential of Private Education in Saudi Arabia (2018). Retrieved on July 2020 from https://www.strategicgears.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Growth-Potential.pdf
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis – a global perspective (7 ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. (2006). Multivariate data analysis. Uppersaddle River NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall
Hakanen, J. J., Bakker, A. B., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2006). Burnout and work engagement among teachers. Journal of school psychology, 43(6), 495–513
Hallberg, U. E., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2006). “Same same” but different? Can work engagement be discriminated from job involvement and organizational commitment? European psychologist, 11(2), 119–127
Hatam, N., Jalali, M. T., Askarian, M., & Kharazmi, E. (2016). Relationship between family-work and work-family conflict with organizational commitment and desertion intention among nurses and paramedical staff at hospitals. International Journal of Community Based Nursing and Midwifery, 4, pp.107–118
Hayes, A. F., & Scharkow, M. (2013). The relative trustworthiness of inferential tests of the indirect effect in statistical mediation analysis: Does method really matter? Psychological science, 24(10), 1918–1927
Hou, Y., Gao, G., Wang, F., Li, T., & Yu, Z. (2011). Organizational Commitment and Creativity: the Influence of Thinking Styles. Annals of Economics & Finance, 12(2), 411–431
Huynh, J. Y., Metzer, J. C., & Winefield, A. H. (2012). Validation of the four-dimensional connectedness scale in a multi sample volunteer study: A distinct construct from work engagement and organizational commitment. International Society for Third-Sector Research, 23, 1056–1082
Jaharuddin, N. S., & Zainol, L. N. (2019). The Impact of Work-Life Balance on Job Engagement and Turnover Intention. The South East Asian Journal of Management. 13(1), p.7
Jamjoom, Y. (2012). Understanding Private Higher Education in Saudi Arabia Emergence, Development and Perceptions. Institute of Education, University of London, Ph. D. thesis
Johari, J., Tan, F. Y., & Zulkarnain, Z. I. T. (2018). Autonomy, workload, work-life balance and job performance among teachers. International Journal of Educational Management, 32(1), 107–120
Kahn, W. (1990). Psychological conditions of personal engagement and disengagement at work. Academy of Management Journal, 33(4), 692–724
Kelliher, C., Richardson, J., & Boiarintseva, G. (2019). All of work? All of life? Reconceptualising work-life balance for the 21st century. Human Resource Management Journal, 29(2), 97–112
Kumarasamy, M. M., Pangil, F., & Mohd Isa, M. F. (2016). The effect of emotional intelligence on police officers’ work–life balance: The moderating role of organizational support. International Journal of Police Science & Management, 18(3), 184–194
Kuron, L. K., Lyons, S. T., Schweitzer, L., & Ng, E. S. (2015). Millennials’ work values: differences across the school to work transition. Personnel Review, 44(6), 991–1009
Kurtessis, J. N., Eisenberger, R., Ford, M. T., Buffardi, L. C., Stewart, K. A., & Adis, C. S. (2017). Perceived organizational support: A meta-analytic evaluation of organizational support theory. Journal of Management, 43(6), 1854–1884
Laschinger, H. K. S., Purdy, N., Cho, J., & Almost, J. (2006). Antecedents and consequences of nurse managers’ perceptions of organizational support. Nursing Economics, 24(1), 20
Lazar, I., Osoian, C., & Ratiu, P. (2010). The role of work-life balance practices in order to improve organizational performance. European Research Studies, 13, 201–215
Le, H., Newman, A., Menzies, J., Zheng, C., & Fermelis, J. (2020). Work–life balance in Asia: A systematic review. Human Resource Management Review, 30(4), 100766
Li, Y. (2018). Effects of work-life balance on organizational commitment: A study in China’s state-owned enterprise. World Journal of Social Science Research, 5(2), 144–166
Malone, E. K., & Issa, R. R. (2013). Work-life balance and organizational commitment of women in the U.S. construction industry. Journal of Professional Issues in Engineering Education and Practice, 139(2), 87–98
Manju, N. D. (2014). Quality of working life: perception of school teachers. International Journal of Education and Psychological Research, 3(2), 77–80
Mazerolle, S. M., Eason, C. M., Clines, S., & Pitney, W. A. (2015). The professional socialization of the graduate assistant athletic trainer. Journal of Athletic Training, 50(5), 532–541
Menon, M. E. (2012). Do beginning teachers receive adequate support from their headteachers? Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 40(2), 217–231
Meyer, J. P., Allen, N. J., & Gellatly, I. R. (1990). Affective and continuance commitment to the organization: Evaluation of measures and analysis of concurrent and time-lagged relations. Journal of applied psychology, 75(6), 710
Munsamy, M., & Venter, A. B. (2009). Retention factors of management staff in the maintenance phase of their careers in local government. SA Journal of Human Resource Management, 7(1), 1–9
Naqshbandi, M. M., & Jasimuddin, S. M. (2018). Knowledge-oriented leadership and open innovation: Role of knowledge management capability in France-based multinationals. International Business Review, 27(3), 701–713
Nayak, T., Sahoo, C. K., & Mohanty, P. K. (2018). Workplace empowerment, quality of work life and employee commitment: a study on Indian healthcare sector. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 12(2), 117–136
Noor, K. M. (2011). Work-life balance and intention to leave among academics in Malaysian public higher education institutions. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 2(11), 1–9
Pani, D. (2015). A study on quality of working life with special reference to private engineering college teachers in the District of Rayagada. Journal of Management and Science, 5(3), 81–90
Park, B. I., & Ghauri, P. N. (2011). Key factors affecting acquisition of technological capabilities from foreign acquiring firms by small and medium sized local firms. Journal of World Business, 46(1), 116–125
Plewa, C., & Quester, P. (2008). A dyadic study of “champions” in university-industry relationships. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 20(2), 211–226
Podsakoff, P. M., & Organ, D. W. (1986). Self-reports in organizational research: Problems and prospects. Journal of management, 12(4), 531–544.
Pooja, A. A., De Clercq, D., & Belausteguigoitia, I. (2016). Job stressors and organizational citizenship behavior: The roles of organizational commitment and social interaction. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 27(3), 373–405
Poulose, S., & Dhal, M. (2020). Role of perceived work–life balance between work overload and career commitment. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 35(3), 169–183
Pradana, A., & Salehudin, I. (2015). Work overload and turnover intention of junior auditors in greater Jakarta, Indonesia. The South East Asian Journal of Management, 9(2), 108–124
Prather-Jones, B. (2011). How school administrators influence the retention of teachers of students with emotional and behavioral disorders. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 84(1), 1–8
Punia, V., & Kamboj, M. (2013). Quality of work-life balance among teachers in higher education institutions. Learning Community-An International Journal of Educational and Social Development, 4(3), 197–208
Rhoades, L., & Eisenberger, R. (2002). Perceived organizational support: a review of the literature. Journal of applied psychology, 87(4), 698
Roberts, K. (2007). Work-life balance-the sources of the contemporary problem and the probable outcomes: A review and interpretation of the evidence. Employee Relations, 29(4), 334–351
Rothbard, N. P. (2001). Enriching or depleting? The dynamics of engagement in work and family roles. Administrative Science Quarterly, 46(4), 655–684
Saunders, M., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2016). Research methods for business students. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited
Schlichte, J., Yssel, N., & Merbler, J. (2005). Pathways to burnout: Case studies in teacher isolation and alienation. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 50(1), 35–40
Sharifah, S., Suhaida, A. K., & Soaib, A. (2014). Workload of technical secondary school teachers:management and administration perceptions. Malaysian Online Journal of Education Management, 2(4), 21–35
Shimizu, M., Wada, K., Wang, G., Kawashima, M., Yoshino, Y., Sakaguchi, H. … Aizawa, Y. (2011). Factors of working conditions and prolonged fatigue among teachers at public elementary and junior high schools. Ind Health, 49(4), 434–442
Shuck, B., & Wollard, K. (2010). Employee engagement and HRD: A seminal review of the foundations. Human Resource Development Review, 9(1), 89–110
Silva, J. P. D., & Fischer, F. M. (2020). Understudied school teachers’ work/life balance and everyday life typologies. Chronobiology International, 37(9–10), 1513–1515
Tladinyane, R. T. (2012). Psychological career resource, work engagement and organisational commitment foci: A psychological profile for staff retention. doctoral thesis, University of South Africa, South Africa
Top, M., Akdere, M., & Tarcan, M. (2015). Examining transformational leadership, job satisfaction, organizational commitment and organizational trust in Turkish hospitals: public servants versus private sector employees. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 26(9), 1259–1282
Triplett, R., Mullings, J. L., & Scarborough, K. E. (1999). Examining the effect of work-home conflict on work-related stress among correctional officers. Journal of Criminal Justice, 27(4), 371–385
Tubadji, A., & Nijkamp, P. (2015). Cultural impact on regional development application of a PLS-PM model to Greece. Annals of Regional Science, 54(3), 687–720
Vision (2030). Vision 2030: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Acced on July 2020 from http://vision2030.gov.sa/en
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070
Wayne, J. H., Butts, M. M., Casper, W. J., & Allen, T. D. (2017). In search of balance: A conceptual and empirical integration of multiple meanings of work-family balance. Personnel Psychology, 70(1), 167–210
Wieland, H., Hartmann, N. N., & Vargo, S. L. (2017). Business models as service strategy. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45(6), 925–943
Yang, D., & Lu, J. (2014). Rural teachers’ quality of working life (qwl) in china: the case of shanxi province. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 3(4), 39
Yousaf, A., Mishra, A., & Bashir, M. (2020). Brand trust, institutional commitment, and their impact on student loyalty: evidence for higher education in India. Studies in Higher Education, 45(4), 878–891
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdulaziz, A., Bashir, M. & Alfalih, A.A. The impact of work-life balance and work overload on teacher’s organizational commitment: do Job Engagement and Perceived Organizational support matter. Educ Inf Technol 27, 9641–9663 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11013-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11013-8