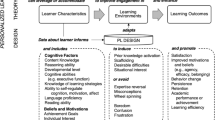
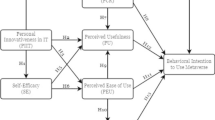
Abstract
The reuse of Learning Designs can bring significant advantages to the educational community such as the diffusion of best teaching practices and the improvement of teaching quality and learning outcomes. Although various tools, including Recommender Systems, have been developed to implement the notion of reusing Learning Designs, their adoption by teachers falls short of expectations. This paper investigates the results of providing explanations for Learning Design recommendations to teachers. To this end, we designed and implemented an explanatory mechanism incorporated into a Recommender System, which propose pre-existing Learning Designs to teachers. We then conducted a user-centric evaluation experiment. Overall, this study provides evidence that explanations should be incorporated into Recommender Systems that propose Learning Designs, as a way of improving the teacher-perceived experience and promoting their wider adoption by teachers. The more teachers accept and adopt Recommender Systems that propose Learning Designs, the more the educational community gains the benefits of reusing Learning Designs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho, S. (2009). Learning Design Representations to Document, Model, and Share Teaching Practice. In L. Lockyer, S. Bennett, S. Agostinho, & B. Harper (Eds.), Handbook of Research on Learning Design and Learning Objects: Issues, Applications, and Technologies (pp. 1–19). Hershey: IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-59904-861-1.ch001.
Agostinho, S., Bennett, S., Lockyer, L., Jones, J., & Harper, B. (2013). Learning designs as a stimulus and support for teachers’ design practices. In H. Beetham & R. Sharpe (Eds.), Rethinking Pedagogy for a Digital Age: Designing for 21st century (pp. 119–132). New York: Routledge.
Beetham, H., & Sharpe, R. (2007). Rethinking pedagogy for a digital age: designing and delivering e-learning. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203961681.
Bennett, S., Agostinho, S., & Lockyer, L. (2005). Reusable learning designs in university education. Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference on Education and Technology, ICET 2005, 2005, 102–106. Retrieved from http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-33751297745&partnerID=40&md5=de22754ab9711f446c2d71bc23695040. Accessed 27 Nov 2018.
Bennett, S., Thomas, L., Agostinho, S., Lockyer, L., Jones, J., & Harper, B. (2011). Understanding the design context for Australian university teachers: implications for the future of learning design. Learning, Media and Technology, 36(2), 151–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439884.2011.553622.
Bennett, S., Agostinho, S., & Lockyer, L. (2017). The process of designing for learning: understanding university teachers’ design work. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65(1), 125–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-016-9469-y.
Cameron, L. (2009). How learning design can illuminate teaching practice. The Future of Learning Design Conference.
Cameron, L., & Campbell, C. (2010). Sharing learning designs that work. In EdMedia: world Conference on Educational Media and Technology (pp. 1914–1919).
Celik, D., & Magoulas, G. D. (2016). A review, timeline, and categorization of learning design tools. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) (Vol. 10013 LNCS, pp. 3–13). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47440-3_1
Chen, L., & Wang, F. (2017). Explaining recommendations based on feature sentiments in product reviews. In Proceedings of the 22Nd International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (pp. 17–28). New York: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3025171.3025173.
Conole, G. (2013). Designing for learning in an open world. New York: Springer New York. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8517-0
Conole, G., & Culver, J. (2010). The design of Cloudworks: applying social networking practice to foster the exchange of learning and teaching ideas and designs. Computers in Education, 54(3), 679–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.09.013.
Conole, G., & Fill, K. (2005). A learning design toolkit to create pedagogically effective learning activities. Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 8, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.5334/2005-8.
Cramer, H., Evers, V., Ramlal, S., van Someren, M., Rutledge, L., Stash, N., Aroyo, L., & Wielinga, B. (2008). The effects of transparency on trust in and acceptance of a content-based art recommender. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction, 18(5), 455–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11257-008-9051-3.
Dalziel, J. (2003). Implementing learning design : the learning activity management system (LAMS). Retrieved from http://hdl.handle.net/1959.14/79594. Accessed 28 Nov 2018.
Dalziel, J., Conole, G., Wills, S., Walker, S., Bennett ǁ, S., Dobozy, E., et al. (2016). The Larnaca declaration on learning design. Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 2016(7), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.5334/jime.407.
Donald, C., Blake, A., Girault, I., Datt, A., & Ramsay, E. (2009). Approaches to learning design: past the head and the hands to the HEART of the matter. Distance Education, 30(2), 179–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/01587910903023181.
Erdt, M., Fernandez, A., & Rensing, C. (2015). Evaluating recommender systems for technology enhanced learning: a quantitative survey. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 1382(c), 1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2015.2438867.
Fazeli, S., Drachsler, H., Bitter-Rijpkema, M., Brouns, F., van der Vegt, W., & Sloep, P. B. (2017). User-centric evaluation of recommender systems in social learning platforms: accuracy is just the tip of the iceberg. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 11, 294–306. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2017.2732349.
Gedikli, F., Jannach, D., & Ge, M. (2014). How should I explain? A comparison of different explanation types for recommender systems. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 72(4), 367–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2013.12.007.
Herlocker, J. L., Konstan, J. A., & Riedl, J. (2000). Explaining collaborative filtering recommendations. In Proceedings of the 2000 ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work (pp. 241–250). New York: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/358916.358995
Hernández-Leo, D., Harrer, A., Dodero, J. M., Asensio-Pérez, J. I., & Burgos, D. (2007). A framework for the conceptualization of approaches to create-by-reuse of learning design solutions. Journal of Universal Computer Science, 13(7), 750–760.
Hernández-Leo, D., Chacón, J., Prieto, L. P., Asensio-Pérez, J. I., & Derntl, M. (2013). Towards an integrated learning design environment. In D. Hernández-Leo, T. Ley, R. Klamma, & A. Harrer (Eds.), Scaling up learning for sustained impact (pp. 448–453). Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Hernández-Leo, D., Asensio-Pérez, J. I., Derntl, M., Prieto, L. P., & Chacón, J. (2014). ILDE: community environment for conceptualizing, authoring and deploying learning activities. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) (Vol. 8719 LNCS, pp. 490–493). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11200-8_48
Hernández-Leo, D., Asensio-Pérez, J. I., Derntl, M., Pozzi, F., Chacón, J., Prieto, L. P., & Persico, D. (2018). An integrated environment for learning design. Frontiers in ICT, 5(May), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fict.2018.00009.
Hinkin, T. R., Tracey, J. B., & Enz, C. A. (1997). Scale construction: developing reliable and valid measurement instruments. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research, 21(1), 100–120. https://doi.org/10.1177/109634809702100108.
Jin, X., Zhou, Y., & Mobasher, B. (2005). A maximum entropy web recommendation system : combining collaborative and content features. Intelligence, 24(6), 612–617. https://doi.org/10.1145/1081870.1081945.
Karga, S., & Satratzemi, M. (2018). A hybrid recommender system integrated into LAMS for learning designers. Education and Information Technologies, 23(3), 1297–1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-017-9668-0.
Koper, R., & Bennett, S. (2008). Learning design: Concepts. In H. Adelsberger, Kinshuk, J. Pawlowski, & D. Sampson (Eds.), (pp. 135–154). Springer Berlin Heidelberg. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74155-8_8.
Kouki, P., Schaffer, J., Pujara, J., O’Donovan, J., & Getoor, L. (2017). User preferences for hybrid explanations. In Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM Conference on Recommender Systems (pp. 84–88). New York: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3109859.3109915.
Laurillard, D. (2012). Teaching as a design science. Building pedagogical patterns for learning and technology. Routledge: Taylor & Francis Group.
Laurillard, D., Charlton, P., Craft, B., Dimakopoulos, D., Ljubojevic, D., Magoulas, G., Masterman, E., Pujadas, R., Whitley, E. A., & Whittlestone, K. (2013). A constructionist learning environment for teachers to model learning designs. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 29(1), 15–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2729.2011.00458.x.
Lee, S. (2014). Rethinking pedagogy for a digital age: designing for twenty-first century learning. Open Learning: The Journal of Open, Distance and E-Learning, 29(2), 174–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/02680513.2014.940498.
Lockyer, L., Bennett, S., Agostinho, S., & Harper, B. (2009). Handbook of Research on Learning Design and Learning Objects. In L. Lockyer, S. Bennett, S. Agostinho, & B. Harper (Eds.). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-59904-861-1.
Maina, M., Craft, B., & Mor, Y. (2015). The Art & Science of Learning Design. Rotterdam: Sense Publishers. Retrieved from https://www.sensepublishers.com/catalogs/bookseries/technology-enhanced-learning-1/the-art-and-science-of-learning-design/. Accessed 27 Nov 2018.
McNee, S., Lam, S., Konstan, J., & Riedl, J. (2003). Interfaces for Eliciting New User Preferences in Recommender Systems. User Modeling 2003, 2702, 148. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44963-9_24.
McNee, S. M., Riedl, J., & Konstan, J. a. (2006). Being accurate is not enough: How accuracy metrics have hurt recommender systems. CHI’06 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 1101. https://doi.org/10.1145/1125451.1125659.
Mor, Y., & Craft, B. (2012). Learning design: reflections on a snapshot of the current landscape. Research in Learning Technology, 20. Retrieved from http://www.researchinlearningtechnology.net/index.php/rlt/article/view/19196/. Accessed 27 Nov 2018.
Muhammad, K. I., Lawlor, A., & Smyth, B. (2016). A live-user study of opinionated explanations for recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (pp. 256–260). New York: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/2856767.2856813.
Muñoz, O. R., Penalba, F. A., & Sánchez, J. F. (2016). The skills, competences, and attitude toward information and communications technology recommender system: an online support program for teachers with personalized recommendations. New Review of Hypermedia and Multimedia, 22(1–2), 83–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/13614568.2015.1036132.
O’Donovan, J., Smyth, B., Gretarsson, B., Bostandjiev, S., & Höllerer, T. (2008). PeerChooser: visual interactive recommendation. In SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1085–1088). Florence: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/1357054.1357222.
Paquette, G., Teja, I. D. la, & K. Lundgren-Cayrol. (2006). Learning design classification definitions. Retrieved from http://helios.licef.ca/residld/4/Classification_Design_P%C3%A9dagogique.doc. Accessed 27 Nov 2018.
Prieto, L., Dimitriadis, Y., Craft, B., Derntl, M., Émin, V., Katsamani, M., … Villasclaras, E. (2013). Learning design Rashomon II: Exploring one lesson through multiple tools. Research in Learning Technology, 21(0). https://doi.org/10.3402/rlt.v21i0.20057.
Pu, P., & Chen, L. (2006). Trust building with explanation interfaces. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (pp. 93–100). New York: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/1111449.1111475.
Pu, P., & Chen, L. (2011). A user - centric evaluation framework for recommender systems. Proceedings of the 5th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems - RecSys ‘11, 157–164. https://doi.org/10.1145/2043932.2043962.
Pu, P., Faltings, B., Chen, L., Zhang, J., & Viappiani, P. (2011). Usability guidelines for product recommenders based on example critiquing research. In Recommender Systems Handbook (pp. 511–545). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-85820-3_16.
Quijano-Sanchez, L., Sauer, C., Recio-Garcia, J. A., & Diaz-Agudo, B. (2017). Make it personal: A social explanation system applied to group recommendations. Expert Systems with Applications, 76, 36–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.01.045.
Resnick, P., & Varian, H. R. (1997). Recommender systems. Communications of the ACM, 40(3), 56–58. https://doi.org/10.1145/245108.245121.
Salter, J., & Antonopoulos, N. (2006). CinemaScreen recommander agent: Combining collaborative and content-based filtering. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 21, 35–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIS.2006.4.
Santos, O. C., & Boticario, J. G. (2011). Requirements for semantic educational recommender systems in formal e-learning scenarios. Algorithms, 4(2), 131–154. https://doi.org/10.3390/a4030131.
Simon, B., Pulkkinen, M., Totschnig, M., & Kozlov, D. (2011). The ICOPER reference model for outcome-based higher education. Retrieved from http://www.icoper.org/results/deliverables/D7-3b. Accessed 27 Nov 2018.
Symeonidis, P., Nanopoulos, A., & Manolopoulos, Y. (2008). Providing justifications in recommender systems. Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Part A: Systems and Humans, 38(6), 1262–1272. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2008.2003969.
Tintarev, N. 2010. Explaining Recommendations. PhD Thesis, University of Aberdeen.
Tintarev, N., & Masthoff, J. (2011). Designing and evaluating explanations for recommender systems. In F. Ricci, L. Rokach, B. Shapira, & P. B. Kantor (Eds.), (pp. 479–510). Springer US. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-85820-3_15.
Tintarev, N., & Masthoff, J. (2012). Evaluating the effectiveness of explanations for recommender systems. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction, 22(4), 399–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11257-011-9117-5.
Tintarev, N., & Masthoff, J. (2015). Explaining recommendations: Design and evaluation. In Recommender Systems Handbook (2nd ed., pp. 353–382). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-7637-6_10.
Verbert, K., Ochoa, X., Derntl, M., Wolpers, M., Pardo, A., & Duval, E. (2012). Semi-automatic assembly of learning resources. Computers & Education, 59(4), 1257–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.06.005.
Weller, M. (2004). Learning objects and the e-learning cost dilemma. Journal of Open, Distance and E-Learning, 19(3), 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/0268051042000280147.
Wills, S., & McDougall, A. (2009). Reusability of online role play: Learning objects or learning designs? In L. Lockyer, S. Bennett, S. Agostinho, & B. Harper (Eds.), Handbook of research on learning design and learning objects: Issues, applications, and technologies (p. ??). Information Science Reference. Retrieved from http://ro.uow.edu.au/asdpapers/96/. Accessed 27 Nov 2018.
Wills, S., & Pegler, C. (2016). A deeper understanding of reuse: learning designs, activities, resources and their contexts. Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 2016(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.5334/jime.405.
Yoo, K. H., & Gretzel, U. (2011). Creating more credible and persuasive recommender systems: the influence of source characteristics on recommender system evaluations. Recommender Systems Handbook, 455–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-85820-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karga, S., Satratzemi, M. Using explanations for recommender systems in learning design settings to enhance teachers’ acceptance and perceived experience. Educ Inf Technol 24, 2953–2974 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09909-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09909-z