Summary
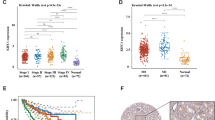
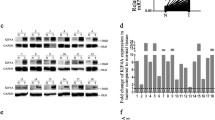
Kinesin family member 4A (KIF4A) is located in the human chromosome band Xq13.1. It has a highly conserved kinesin motor region at its N-terminus, which is followed by a central coiled-coil region and a C-terminus cargo-binding domain that contains a cysteine-rich motif. It is aberrantly expressed in a variety of cancers. Our study aimed to determine the expression of KIF4A in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and to gain new insights into the underlying molecular mechanisms of this disease. Here, we found that KIF4A expression in RCC specimens increased relative to that in normal renal tissues. A significant correlation existed between the expression of KIF4A and the clinicopathologic features of RCC. Elevated KIF4A expression was associated with poor overall survival and disease-free survival. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that KIF4A was an independent prognostic factor for poor survival in human patients with RCC. CCK-8 proliferation assay, cell cycle analysis, and subcutaneous tumor formation analysis in nude mice consistently showed that KIF4A promoted RCC proliferation. Our findings also indicated that KIF4A functions as an accelerator of RCC metastasis as certified through transwell chamber analysis, wound healing assay, and angiogenesis assay. The expression levels of cyclin D1, cyclin E2, matrix metalloproteinase-2, matrix metalloproteinase-9, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, and vascular endothelial growth factor in the KIF4A knockdown group were lower than those in the control group and were consistent with those in classic oncogenic pathways. These findings implied that the expression of KIF4A was significantly related to the tumor incidence, metastasis, and prognosis of patients with RCC. Our work provides new breakthroughs for the diagnosis and treatment of RCC.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 May 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01361-8
References
Srigley JR, Delahunt B, Eble JN, Egevad L, Epstein JI, Grignon D, Hes O, Moch H, Montironi R, Tickoo SK, Zhou M, Argani P (2013) The international society of urological pathology (ISUP) vancouver classification of renal neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol 37(10):1469–1489. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e318299f2d1
Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM (2016) The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part a: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol 70(1):93–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.029
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bensalah K, Dabestani S, Fernandez-Pello S, Giles RH, Hofmann F, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Kuusk T, Lam TB, Marconi L, Merseburger AS, Powles T, Staehler M, Tahbaz R, Volpe A, Bex A (2019) European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2019 update. Eur Urol 75(5):799–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.011
Liu X, Chong Y, Liu H, Han Y, Niu M (2016) CRM1 inhibitor S109 suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest in renal cancer cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 20(2):161–168. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.2.161
Ru-Min W, Yi-Jing Z, Sha M, Ying-Li X, Yan-Su C, Hai-Long L, Jin B, Jun-Nian Z (2015) Preoperative Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Non-metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(9)
Song J, Chen X, Bai J, Liu Q, Li H, Xie J, Jing H, Zheng J (2016) Discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1), a promising biomarker, induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal cancer cells. Tumor Biol 37(8):11509–11521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5021-2
Beksac AT, Paulucci DJ, Blum KA, Yadav SS, Sfakianos JP, Badani KK (2017) Heterogeneity in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol 35(8):507–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.05.006
Miki H, Okada Y, Hirokawa N (2005) Analysis of the kinesin superfamily: insights into structure and function. Trends Cell Biol 15(9):467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2005.07.006
Rath O, Kozielski F (2012) Kinesins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12(8):527–539. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3310
Gul A, Rini BI (2019) Adjuvant therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 125(17):2935–2944. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32144
Haider S, Wang J, Nagano A, Desai A, Arumugam P, Dumartin L, Fitzgibbon J, Hagemann T, Marshall JF, Kocher HM, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T, Scarpa A, Lemoine NR, Chelala C (2014) A multi-gene signature predicts outcome in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genome Med 6(12):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-014-0105-3
Huang Y, Wang H, Lian Y, Wu X, Zhou L, Wang J, Deng M, Huang Y (2018) Upregulation of kinesin family member 4A enhanced cell proliferation via activation of Akt signaling and predicted a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 9(2):141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0114-4
Minakawa Y, Kasamatsu A, Koike H, Higo M, Nakashima D, Kouzu Y, Sakamoto Y, Ogawara K, Shiiba M, Tanzawa H, Uzawa K (2013) Kinesin family member 4A: a potential predictor for progression of human oral cancer. PloS one 8(12):e85951. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085951
Zhou Y, Yang L, Zhang X, Chen R, Chen X, Tang W, Zhang M (2019) Identification of potential biomarkers in glioblastoma through bioinformatic analysis and evaluating their prognostic value. Biomed Res Int 2019:6581576. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6581576
Gao J, Sai N, Wang C, Sheng X, Shao Q, Zhou C, Shi Y, Sun S, Qu X, Zhu C (2011) Overexpression of chromokinesin KIF4 inhibits proliferation of human gastric carcinoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol 32(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0090-0
Zhang H, Zou J, Yin Y, Zhang B, Hu Y, Wang J, Mu H (2019) Bioinformatic analysis identifies potentially key differentially expressed genes in oncogenesis and progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PeerJ 7:e8096. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8096
Liu QH, Wang Y, Yong HM, Hou PF, Pan J, Bai J, Zheng JN (2017) XRCC1 serves as a potential prognostic indicator for clear cell renal cell carcinoma and inhibits its invasion and metastasis through suppressing MMP-2 and MMP-9. Oncotarget 8(65):109382–109392. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22680
Hou PF, Jiang T, Chen F, Shi PC, Li HQ, Bai J, Song J (2018) KIF4A facilitates cell proliferation via induction of p21-mediated cell cycle progression and promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis 9(5):477. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0550-9
Bai J, Yong HM, Chen FF, Mei PJ, Liu H, Li C, Pan ZQ, Wu YP, Zheng JN (2013) Cullin1 is a novel marker of poor prognosis and a potential therapeutic target in human breast cancer. Ann Oncol 24(8):2016–2022. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt147
Xiao-Yi H, Ping-Fu H, Teng-Teng L, Hao-Yu Q, Min-Le L, Tian L, Jin-Jin L, Jin B, Jun-Nian Z (2018) The roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway related lncRNAs in cancer. Int J Biol Sci 14:14
Wu X, Chen H, Gao Q, Bai J, Wang X, Zhou J, Qiu S, Xu Y, Shi Y, Wang X, Zhou J, Fan J (2014) Downregulation of JWA promotes tumor invasion and predicts poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog 53(4):325–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.21981
Bai J, Yong HM, Chen FF, Song WB, Li C, Liu H, Zheng JN (2013) RUNX3 is a prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target in human breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139(11):1813–1823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1498-x
Cao WJ, Mao LL, Zheng JN, Pei DS (2015) p42.3: an abductor of cell cycle. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 15(2):157–162. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520614666140818200202
Mei PJ, Bai J, Miao FA, Li ZL, Chen C, Zheng JN, Fan YC (2019) Relationship between expression of XRCC1 and tumor proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis in glioma. Invest New Drugs 37(4):646–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0667-9
Sati L, Seval-Celik Y, Unek G, Korgun ET, Demir R (2009) The presence of kinesin superfamily motor proteins KIFC1 and KIF17 in normal and pathological human placenta. Placenta 30(10):848–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2009.07.005
Tikhonenko I, Nag DK, Robinson DN, Koonce MP (2009) Microtubule-nucleus interactions in Dictyostelium discoideum mediated by central motor kinesins. Eukaryot Cell 8(5):723–731. https://doi.org/10.1128/ec.00018-09
Taniwaki M, Takano A, Ishikawa N, Yasui W, Inai K, Nishimura H, Tsuchiya E, Kohno N, Nakamura Y, Daigo Y (2007) Activation of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(22 Pt 1):6624–6631. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-07-1328
Gu Y, Lu L, Wu L, Chen H, Zhu W, He Y (2017) Identification of prognostic genes in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma by RNAseq data analysis. Mol Med Rep 15(4):1661–1667. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6194
Wei W, Lv Y, Gan Z, Zhang Y, Han X, Xu Z (2019) Identification of key genes involved in the metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett 17(5):4321–4328. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10130
Menyhart O, Harami-Papp H, Sukumar S, Schafer R, Magnani L, de Barrios O, Gyorffy B (2016) Guidelines for the selection of functional assays to evaluate the hallmarks of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1866(2):300–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.10.002
Wan Q, Shen Y, Zhao H, Wang B, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Bu X, Wan M, Shen C (2019) Impaired DNA double-strand breaks repair by kinesin family member 4A inhibition renders human H1299 non-small-cell lung cancer cells sensitive to cisplatin. J Cell Physiol 234(7):10360–10371. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27703
Hua L, Zhu M, Song X, Wang J, Fang Z, Zhang C, Shi Q, Zhan W, Wang L, Meng Q, Zhou X, Yu R (2014) FRK suppresses the proliferation of human glioma cells by inhibiting cyclin D1 nuclear accumulation. J Neurooncol 119(1):49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1461-y
Malumbres M, Carnero A (2003) Cell cycle deregulation: a common motif in cancer. Prog Cell Cycle Res 5:5–18
Ohtsubo M, Theodoras AM, Schumacher J, Roberts JM, Pagano M (1995) Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 15(5):2612–2624. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.15.5.2612
Han ZX, Wang XX, Zhang SN, Wu JX, Qian HY, Wen YY, Tian H, Pei DS, Zheng JN (2014) Downregulation of PAK5 inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion potentially through the PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling pathway. Brain Tumor Pathol 31(4):234–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-013-0161-1
Zhu X, Ohtsubo M, Bohmer RM, Roberts JM, Assoian RK (1996) Adhesion-dependent cell cycle progression linked to the expression of cyclin D1, activation of cyclin E-cdk2, and phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein. J Cell Biol 133(2):391–403. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.133.2.391
Toyoshima H, Hunter T (1994) p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell 78(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8
Piedagnel R, Murphy G, Ronco PM, Lelongt B (1999) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) and MMP9 are produced by kidney collecting duct principal cells but are differentially regulated by SV40 large-T, arginine vasopressin, and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 274(3):1614–1620. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.3.1614
Yao M, Yoshida M, Kishida T, Nakaigawa N, Baba M, Kobayashi K, Miura T, Moriyama M, Nagashima Y, Nakatani Y, Kubota Y, Kondo K (2002) VHL tumor suppressor gene alterations associated with good prognosis in sporadic clear-cell renal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 94(20):1569–1575. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/94.20.1569
Choueiri TK, Fay AP, Gagnon R, Lin Y, Bahamon B, Brown V, Rosenberg JE, Hutson TE, Baker-Neblett KL, Carpenter C, Liu Y, Pandite L, Signoretti S (2013) The role of aberrant VHL/HIF pathway elements in predicting clinical outcome to pazopanib therapy in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 19(18):5218–5226. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-13-0491
Shi YH, Wang YX, Bingle L, Gong LH, Heng WJ, Li Y, Fang WG (2005) In vitro study of HIF-1 activation and VEGF release by bFGF in the T47D breast cancer cell line under normoxic conditions: involvement of PI-3K/Akt and MEK1/ERK pathways. J Pathol 205(4):530–536. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1734
Wiesener MS, Munchenhagen PM, Berger I, Morgan NV, Roigas J, Schwiertz A, Jurgensen JS, Gruber G, Maxwell PH, Loning SA, Frei U, Maher ER, Grone HJ, Eckardt KU (2001) Constitutive activation of hypoxia-inducible genes related to overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in clear cell renal carcinomas. Cancer Res 61(13):5215–5222
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81672845, 81872304), the Project of Invigorating Health Care through Science, Technology and Education from Jiangsu Province (ZDRCC2016009), the Major Research and Development Program for Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No.2019C03003). The Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent (QNRC2016773), Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (WSN-119), Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX18_2185), the Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Team under Grant (CXTDA2017034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments involved in this study were approved by both the Institutional Review Boards of Xuzhou Medical University and the Ethics Committee of the above hospital.
Informed consent
Each patient provided a written informed consent prior to the study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Incorrect Figure 5 was published.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Lu, Y., Li, L. et al. The kinesin motor protein KIF4A as a potential therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 38, 1730–1742 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-020-00961-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-020-00961-y